ISSN: 0973-7510
E-ISSN: 2581-690X
The current study is trying to identify some effects of scabies on some vital indicators such as (ECP, IgE, MCP-1 and IL-17). The results showed that levels of ECP has significant increase (P<0.05 (9569.3 ±256.10 pg /ml), (9872.9± 260.50) respectively in comparison with the control group (7665.2 ± 385.72 pg /ml), (7834.1± 251.43 pg /ml) respectively, The result proved that there was the significant increase (P (9721.1 ±181.15 pg /ml), (7749.7± 226.75) respectively in concentration of (ECP) in patients with S. scabiei and total healthy individuals. The levels of IgE had significant increase (P (284.8 ±34.05 IU /ml), (249.85± 13.682 IU /ml) respectively in comparison with the control group (119.5 ± 11.24 IU /ml), (108.77± 8.3 IU /ml) respectively. The result indicate that there was significant increase (P (267.134 ±18. 334 IU /ml), (114.13± 6.94 IU /ml) respectively in concentration of (IgE) in total patients infected with S. scabiei and total control group. The levels of MCP-1 has significant increase (P (271.76 ±29. 88 pg /ml), (246.983± 27.57 pg /ml) respectively in comparison with the control group (153. 27 ± 21.071pg/ml), (154.67± 22.973 pg /ml) respectively, Also it revealed the significant increase (P (259.29±20. 22 pg /ml), (153. 97± 15.21 pg /ml) respectively in concentration of (MCP-1) in S. scabiei patients and total healthy individuals. IL-17 had significant increase (P (16.318 ±0. 71 pg /ml), (16.847± 0.58 pg /ml) respectively in comparison with the control group (5. 6009 ±0. 45 pg/ml), (5.2023± 0. 35 pg /ml) respectively. The current study shows that there was significant increase (P (16.583±0. 45pg /ml), (16.4016± 0.28 pg /ml) respectively in concentration of (IL-17) in total patients infected with S. scabiei and total healthy individuals. The levels of IL-2 had significant increase (P (21.14 ±0. 8081 pg /ml), (21.800± 1.0644 pg /ml) respectively in comparison with total healthy individuals (7. 447 ±0. 2422 pg/ml), (7.7235± 0. 1716 pg /ml) respectively, Also it revealed the significant increase (P (20.972±0. 6626pg /ml), (7.5853± 0.1480 pg /ml) respectively in concentration of (IL-2) in total patients infected with S. scabiei and total control group. Conclusions: the results indicate that infection of scabies influences on the human immunity represented by the ECP, IgE MCP-1 and IL-17 in patients infected with scabies and may be used as good biomarkers in detection of scabies.
scabies, Eosinophilia, Cationic protein, IgE, IL-17, MCP-1.
Scabies is an important skin disease infested human, domestic and wild animals caused by microscopic obligate ectoparasites called Sarcoptes scabiei that lives and reproduces in the epidermis of skin for human and many mammalian hosts and lead to significant human and animal morbidity and mortality (Beugnet et al.,2016). It is one of the three most common skin diseases in children, along with ringworm and bacterial skin infections (Vos, 2012) .As of 2010 it affects nearly 100 million people (1.5% of the world population) and is common in both sexes (Georgis, 2014). The symptoms may be worsens during the night and the skin is scratched, due to itching, and the skin layer breakdown and injury to other types of bacterial infection. The mites intersect into the skin to live and shed their eggs there (Al-Hadraawy and Hessen, 2017). Symptoms of scabies occur due to the sensitivity of the mites, Infection is usually caused by ten to fifteen mites and the scabies infection is caused by direct contact with the skin of the injured person as in intercourse, the disease may spread before the onset of symptoms, and overcrowded living conditions may increase the likelihood of spread of the disease such as child care centers, adjacent homes and prisons (Al-Hadraawy and Hessen, 2017). Immune response of the host displays delayed inflammatory and adaptive immune responses to this parasite for reason the ability of mites to modulate multiple features of the human’s inflammatory and immune responses, In some cases small holes can be seen on the skin, symptoms usually appear after 4-6 weeks, they appear in most parts of the body or in certain areas only, such as the wrists and between the fingers or along the waist circumference, the head may be affected (Al-Hadraawy et al., 2016;Walton, 2010).
This study was done on 58 patients consist of (29 male and 29 female) and 30 healthy control separate to (15 male and 15 female). All these cases were collected from Hospitals in University of Kufa and diagnosis by light microscopic method for examining on the Sarcoptes scabiei mite or its eggs, at zoological laboratory of faculty of science in An-Najaf province from March 2017 to February 2018.
Isolation of serum
Six milliliters of blood were collected from two groups; healthy and patients, then drawn in sterile tubes and left at room temperature for 25 minutes. Then centrifugation was done at 3500 rpm for 6 minutes. Serum was collected and kept in sterile tubes at deep freeze at -20 until use.
Detection of immune markers
ECP, IgE MCP-1 and IL-17 human biomarkers were used in the current study provided from Elabscience Company, Bulgaria and determined by using ELISA device (Human reader, Germany) according to Manufacturer Company.
Statistical analysis
Graph pad prism version 10 computer software was used in the current study. T-test was used to comparison between mean of all samples. When P-value less than 0.05 considered as statistically significant (Al-Hadraawy, 2016; Aljanaby AAJ and Alhasnawi, 2017).
Eosinophilic cationic protein (ECP)
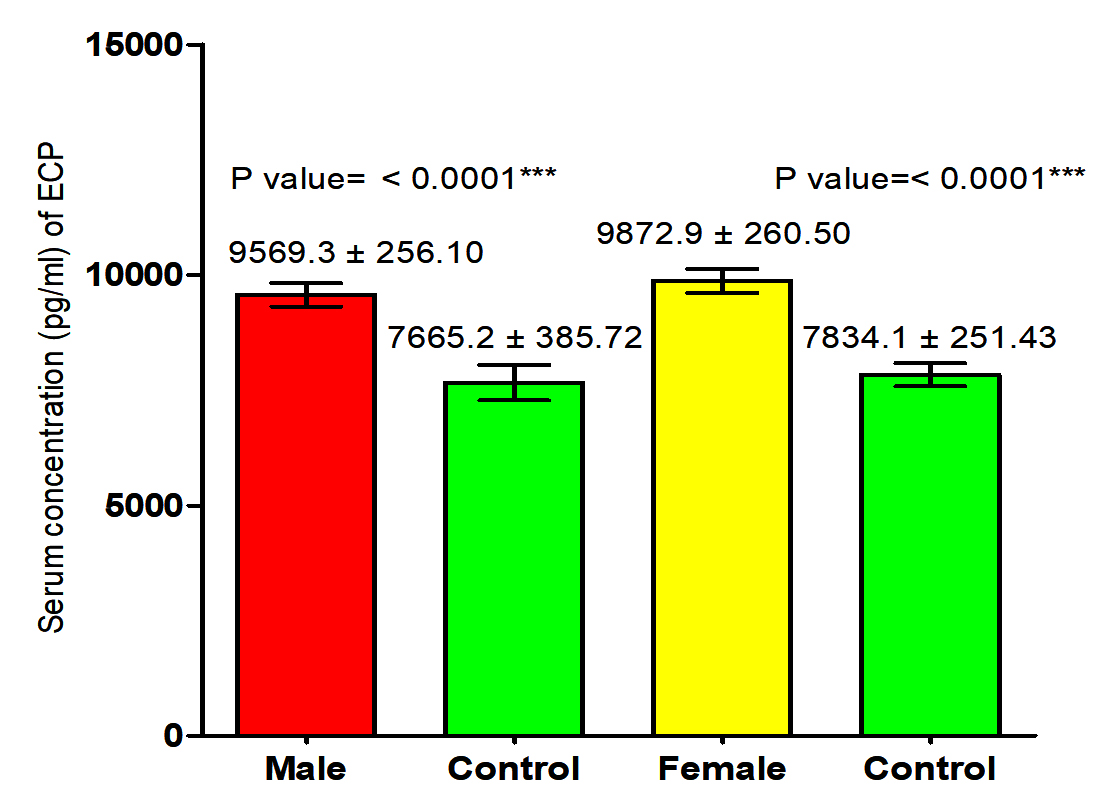
The results of the current study proved that there was significant increase in ECP level in male and female patients with S. scabiei were significant increase (P<0.05 (9569.3 ±256.10 pg /ml), (9872.9± 260.50) respectively in compared to the control group (7665.2 ± 385.72 pg /ml), (7834.1± 251.43 pg /ml) respectively. The results indicate that there was significant increase (P (9721.1 ±181.15 pg /ml), (7749.7± 226.75) respectively in concentration of ECP in total scabies patients and total healthy individuals (Fig. 1,2).
 Fig. 2. Comparison between serum level of ECP in total patients infection with Sarcoptes scabiei and total control group.
Fig. 2. Comparison between serum level of ECP in total patients infection with Sarcoptes scabiei and total control group. Serum concentration of IgE (IU/ml)
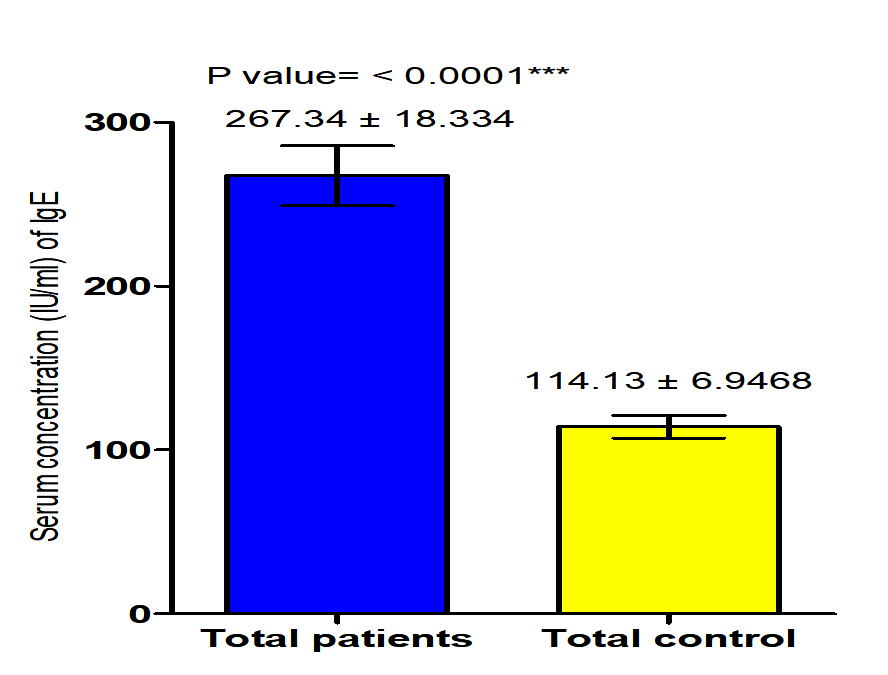
The current study revealed that concentration of IgE in both male and female patients with S. scabiei were significant increase (P<0.05 (284.8 ±34.05 IU /ml), (249.85± 13.682) respectively in compared to the control group (119.5 ± 11.24 pg /ml), (108.77± 8.3 IU /ml) respectively, on the other hand, it revealed the significant increase (P (267.134 ±18. 334 IU /ml), (114.13± 6.94 IU /ml) respectively in concentration of IgE in patients with S. scabiei and total healthy individuals (Fig. 3,4).
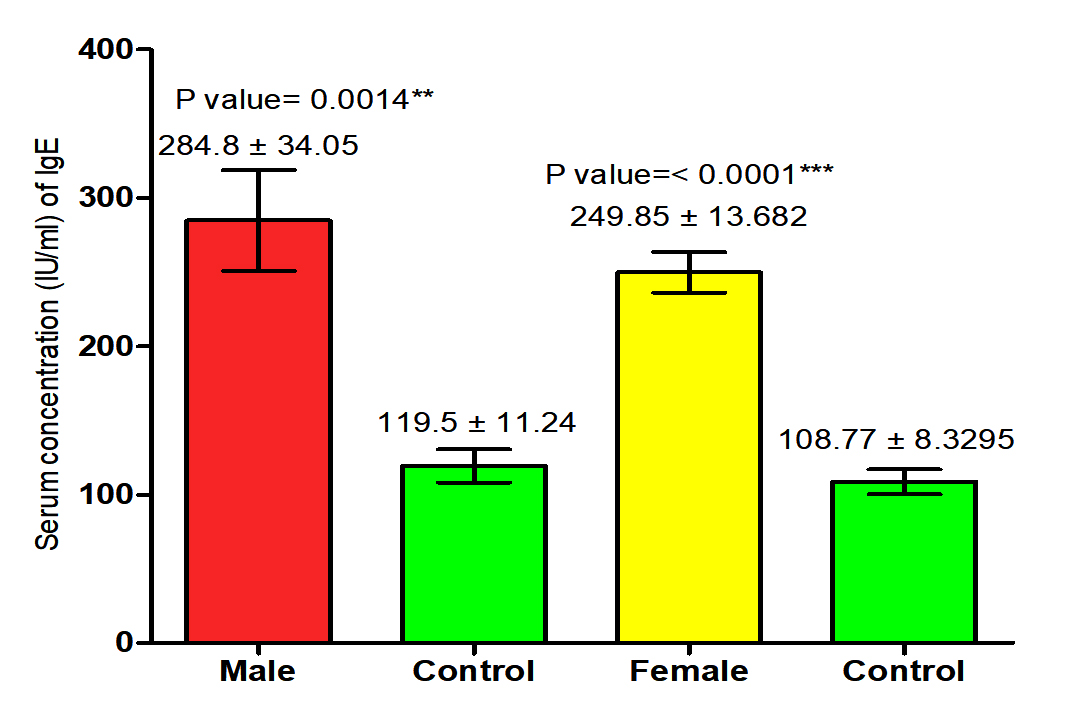 Fig. 3. Comparison between serum level of IgE in male and female with Sarcoptes scabiei and control group.
Fig. 3. Comparison between serum level of IgE in male and female with Sarcoptes scabiei and control group. Serum concentration of MCP-1 (pg/ml)
The current study revealed that concentration of (MCP-1) in both male and female patients with S. scabiei were significant increase (P<0.05 (271.76 ±29. 88 pg /ml), (246.983± 27.57) respectively in compared to the control group (153. 27 ± 21.07 1IU/ml), (154.67± 22.973 pg /ml) respectively, on the other hand, revealed the significant increase (P (259.29±20. 22 pg /ml), (153. 97± 15.21 pg /ml) respectively in concentration of (MCP-1) in total patients with S. scabiei and total healthy individuals (Fig. 5, 6).
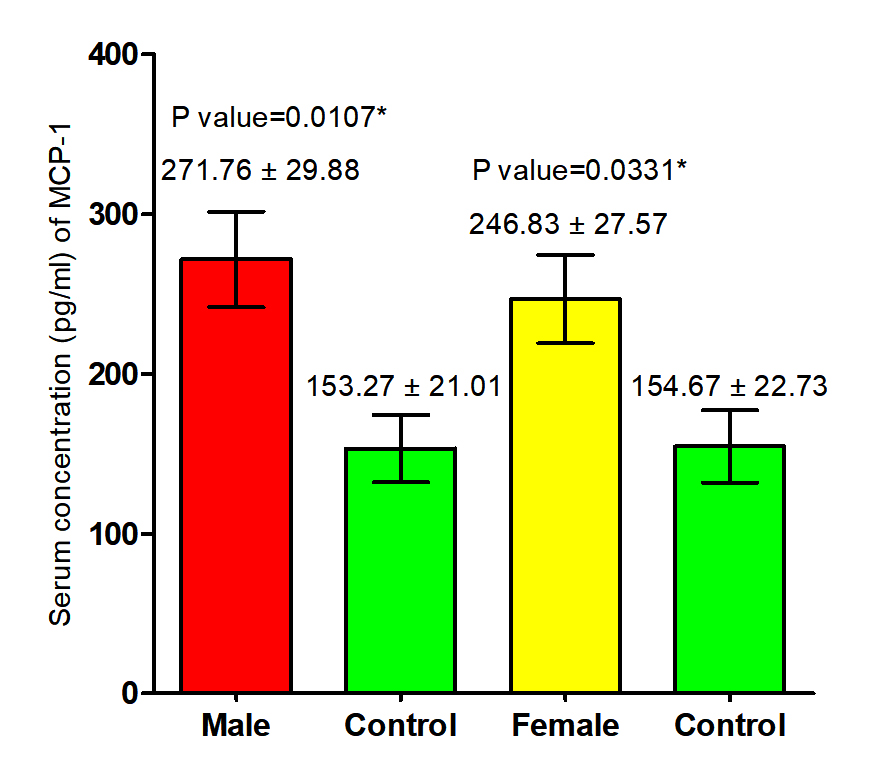 Fig. 5. Comparison between serum level of MCP-1 in male and female with Sarcoptes scabiei and control group.
Fig. 5. Comparison between serum level of MCP-1 in male and female with Sarcoptes scabiei and control group.  Fig. 6. Comparison between serum level of MCP-1 in total patients and total control with Sarcoptes scabiei.
Fig. 6. Comparison between serum level of MCP-1 in total patients and total control with Sarcoptes scabiei. Serum concentration of IL-17 (pg/ml)
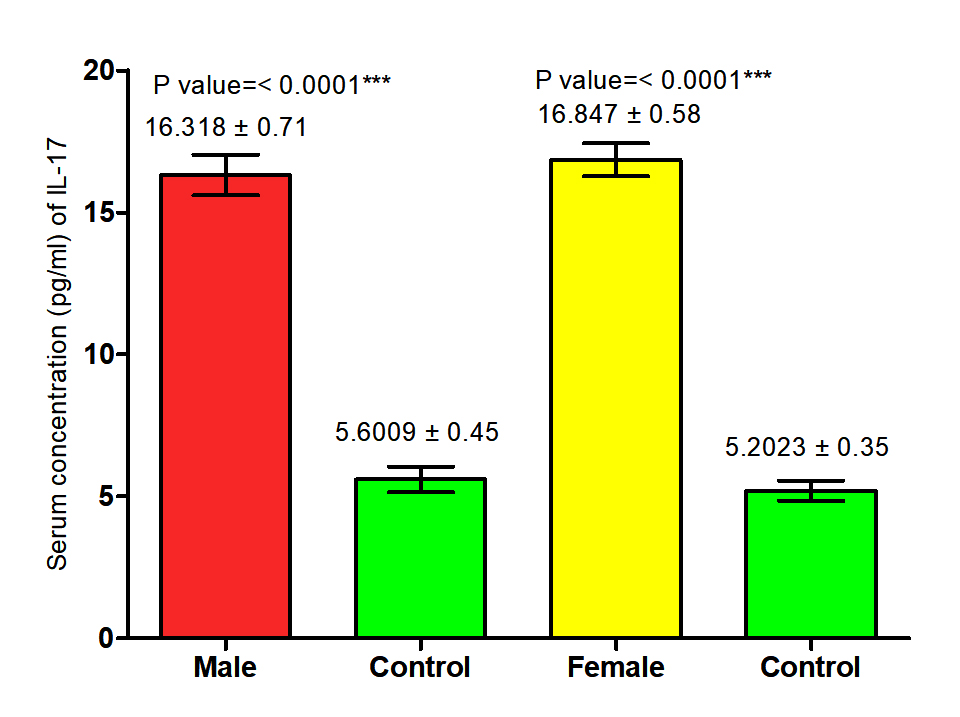
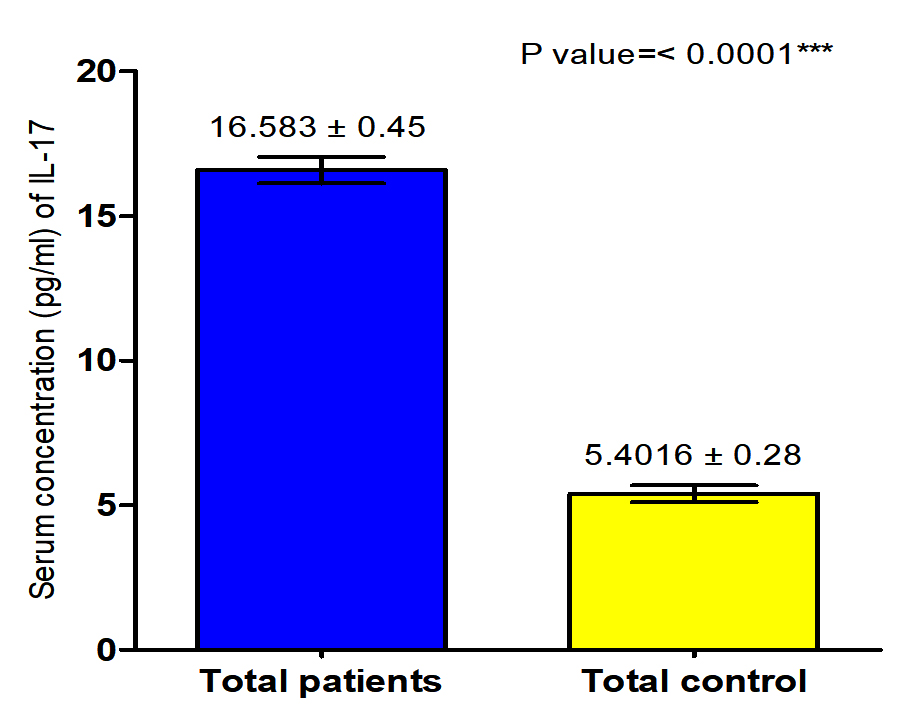
The current study revealed that concentration of (IL-17) in both male and female patients with S. scabiei were significant increase (P<0.05 (16.318 ±0. 71 pg /ml), (16.847± 0.58) respectively in compared to the control group (5. 6009 ±0. 45 pg/ml), (5.2023± 0. 35 pg /ml) respectively, and proved that there was significant increase (P (16.583±0. 45pg /ml), (16.4016± 0.28 pg /ml) respectively in concentration of (IL-17) in total patients with S. scabiei and total healthy individuals (Fig. 7,8).
The present study indicate that there was significant increase in the serum level of eosinophilic cationic protein in both male and female patients with S. scabiei parasite compared to control group, also in total patients with S. scabiei compared to the total control group, this increase may be due to interaction between the human immune response and S. scabiei antigens or influences of products from scabies mites that caused activated eosinophils, neutrophils, basophils and others immune cells which produced in high numbers in allergic inflammation and helminthes infections to produce cytokines, the granulocytes of eosinophil appear in large numbers at inflammatory sites and in response to infections caused by parasites, These granular cells have positively charged proteins, the eosinophil cationic protein is one of four essential proteins that enter the surrounding tissue and stimulate the secretion of the amino acid granules, although ECP varies widely from one patient to another, some studies show that the measurement of this protein by serum monitors many inflammatory diseases, ECP is one of the important natural defense against invading parasites , allergic inflammatory disease and gastrointestinal diseases (Wardlaw 1994; Sajad et al., 2017; Majeed and Aljanaby , 2019). The present study similar to study of Czech et al.) 1992) who revealed that serum concentrations of ECP have been related with atopic dermatitis activity and correlated with erythema, papules, pruritus and skin score. The results of study corresponding to study of Charlotte et al.) 2009) who recorded that concentration of serum ECP was elevated in patients with allergic disease as compared with the healthy controls groups due to elevated blood eosinophil counts, basophils, neutrophils and others immune cells. The results of study showed a significant increase in the serum level of IgE in male and female patients infected with S. scabiei parasite compared to control group, also in total patients with S. scabiei compared to the total control group, this increase may be due to allergenic protein which secretion from S. scabiei in host skin lead to type1 hypersensitivity reaction in patients infested with scabies which is responsible for expelling the parasite and products from the borrows by the intense itching and scratching, which in turn leads to sudden reduction in parasite density at time when itching started (Al-Rawi, 2000; Adam et al., 2019). The sensitization of the host to the mites and its products may be has an important role in pathogenesis of scabies (Van Nest, 1986). The current study agreed with study of (Elmaraghy and Elmeghawry, 2011; Al-Hadraawy and Hessen, 2017) were showed a significant increase in the serum level of IgE in male and female patients infected with S. scabiei parasite compared to control group. But not agreed with study of Ibrahim et al. (2012) who revealed that concentration of IgE was lower than its cut off concentration in 50% of patients with scabies, whereas the rest patients with scabies had elevated concentration of IgE. Also agreed with study of Jayaraj et al. (2011) who revealed that levels of IgE immunoglobulin was elevated in patients with scabies in compared to control group. The current study agreed with study of Maizels et al. (2005) that showed a significant increase in the serum level of total IgE in patients infected with helminthes parasite infections and allergic diseases in compared to control group. The results of study showed a significant increase in the serum level of MCP-1 in male and female patients infected with Sarcoptes scabiei parasite compared to control group, also in total patients with S. scabiei compared to the total control group, this increase may be due to interaction between the human immune response and S. scabiei antigens (Sajad et al., 2017; Hayder and Aljanaby, 2019), or may be due to essential role of S. scabiei in demonstrate chemotaxis of neutrophils, eosinophils, macrophages, and Th2- lymphocytes into the skin have shown increased expression levels of keratinocyte-derived chemokines including IL-8, MCP-1, Eotaxin, and Eotaxin-2 (Shiraki et al., 2006; Aljanaby 2013). The results of study agreed with study of Cheng et al. (2010) who reported that the concentration of MCP-1 elevated in patients with scabies as compared to the total control group due to action of macrophage migration inhibitory factor which can induce secretion of TNFa Tumor Necrosis Factor-ב (TNF-ב), INFc Interferon gamma (IFNד), IL-1b, IL-12, IL-6, IL-8 (CXCLD ), MCP-1 and others from mammalian cells and expression of the cell adhesion molecules ICAM-1 and VCAM-1.
The results of study showed a significant increase in the serum level of IL-17 in male and female patients infected with Sarcoptes scabiei parasite compared to control group, also in total patients with S. scabiei compared to the total control group, this increase may be due to hypersensitivity reactions in patients infested with scabies caused by the secretion of different materials by S. scabiei in the host skin (McCarthy et al., 2004; Hengge et al., 2006; Liu et al., 2016; Aljanaby and Medhat 2017). During 4 weeks from infestation of scabies the immunity developed and appears of first symptom (Walton et al., 2008). The human body is facing numerous pathogens every day, but only few of them causing diseases that because we have natural defense system that called innate immune system. It is the first line of host defense (Judith et al., 2013; Mohy et al., 2018 ).Also may by digging the adult female mite in the host skins and stimulated the immune response of host through the life cycle of Sarcoptes scabiei (Currie et al., 2010; Al-Hadraawy and Hessen, 2017). The current results may be due to stimulating many cells of the innate immune system; in particular, they recruit to and activate neutrophils, eosinophils and other immune cells at sites of inflammation, and stimulate endothelial and epithelial cells to synthesize the different inflammatory cytokines particularly the interleukin-17 which is associated with hyper-IgE syndrome, also associated with the skin inflammation and producing CD4+ (T-helper) (Weaver et al., 2007; Kai et al., 2013; Hahn et al., 2016; Aljanaby et al., 2018). The results of current study agreed with study of Luo (2016) who recorded that higher concentration of interleukin-17 and interleukin -23 in crusted scabies are the first to indicate a contribution of Th17 associated cytokines to a dysregulated immune response in crusted scabies pathology (Arlian and Morgan, 2006; Gonzalez-Lombana et al,. 2013; Martin et al., 2014).
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the Central Hospital of Al-Najaf for providing all samples in this study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethics Statement
The ethics of statement in this study according to College of Medicine, University of Kufa, Iraq.
Data Availability
All datasets generated or analyzed during this study are included in the manuscript and are also available in the University of Kufa, Faculty of Science, Iraq and authors.
Funding
None.
Author’s Contribution
AAM collected samples and did the measurement of immune biomarkers. AAJ and SKA wrote the manuscript. AAJ did the statistical analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
- Beugnet F, Vos C, Liebenberg J, Lיnaןg H, Diane L, and Josephus F. Efficacy of afoxolaner in a clinical field study in dogs naturally infested with Sarcoptes scabiei, Parasite. 2016; 23(26)1-10.
Crossref - Vos T. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study2010. Lancet. 2012; 380(9859): 216366.
- Georgi P. arasitology for Veterinarians . Elsevier Health Sciences. 2014; PP 68. ISBN 9781455739882.
- Al-Hadraawy SK and Hessen HB. Hematological and Epidemiological Study for Patients Infected with Scabies. J. Pharm. Sci. & Res. 2017; 9(6): 897-900.
- Al-Hadraawy SK, Al-Hadraawy MK, Ali HA, Hydar MK. Evaluation levels of immunoglobin g and lipid profile in patients infected with hydatid cyst in al-najaf governate, Iraq. Asian Jr. of Microbiol. Biotech. Env. Sc. 2016; 18(1): 101-104
- Walton SF. The immunology of susceptibility and resistance to scabies. Parasite Immunology, 2010; 32(8): 532–540.
Crossref - Aljanaby AAJ and Alhasnawi HMRJ. Phenotypic and Molecular Characterization of Multidrug Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Different Clinical Sources in Al-NajafProvince-Iraq. Pak J Biol Sci. 2017; 20(5): 217-232.
Crossref - Wardlaw AJ. Eosinophils in the 1990s: new perspectives on their role in health and disease”. Postgrad Med J. 1994; 70:(826): 536–52.
Crossref - Sajad AB, Kate EM, Xiaosong L and Shelley FW. Host immune responses to the itch mite, Sarcoptes scabiei, in humans, Parasites & Vectors. 2017; 10:385.
Crossref - Majeed HT, Aljanaby AAJ. Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns and Prevalence of Some Extended Spectrum Beta-Lactamases Genes in Gram-Negative Bacteria Isolated from Patients Infected with Urinary Tract Infections in Al-Najaf City, Iraq. Avicenna journal of medical biotechnology. 2019; 11(2):192.
- Czech W, Krutmann J, Schצpf E. and Kapp A. Serum eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) is a sensitive measure for disease activity in atopic dermatitis”. Br. J. Dermatol. 1992; 126(4): 351–5.
Crossref - Charlotte W, Jenny R and Per V. Eosinophil Cationic Protein (ECP) Is Processed during Secretion, J Immunol; 2009; 183: 3949-3954.
Crossref - Al-Rawi JR. Immunology of scabies. Iraqi J. Comm. Med. 2000; 13(1): 88-90.
- Adam RW, Al-Labban HMY, Aljanaby AAJ, Abbas NA. Synthesis, Characterization and Antibacterial Activity of Some New of Novel 1,2,3-Triazole-Chalcone Derivatives from N-Acetyl-5H-Dibenzo [b,f] Azepine- 5-Carboxamide. Nano Biomed. Eng. 2019; 11(2): 99-110.
Crossref - Van Nest D. Immunology of scabies. Parasitology Today, 1986; 247: 159-167.
Crossref - Walton SF, Beroukas D, Roberts-Thomson P and Currie BJ. New insights into disease pathogenesis in crusted (Norwegian) scabies: the skin immune response in crusted scabies. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008; 158: 1247–55.
Crossref - Elmaraghy MA and El Meghawry AM. Inflammatory Allergic Immune Response in Scabies Pyoderma. Journal of American Science. 2011; 7(8): 577-582.
- Ibrahim L, Nancy DG, Libby J, Nancy B, David A, Luckenbaugh W, Joseph H, William ZP, Carlos A and Zarate JR. A Rando-mized, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Pilot Trial of the Oral Selective NR2B Antagonist MK-0657 in Patients With Treatment-Resis-tant Major Depressive Disorder. J Clin Psycho-pharmacol. 2012; 32(4): 551–557.
Crossref - Jayaraj R, Hales B, Viberg L, Pizzuto S and Holt D. A diagnostic test for scabies: IgE specificity for a recombinant allergen of Sarcoptes scabiei. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2001; 71: 403–407.
Crossref - Maizels RM. Infections and allergy – helminths, hygiene and host immune regulation. Curr Opin Immunol . 2005; 17(6):656-661.
Crossref - Hayder T and Aljanaby AAJ. Antibiotics susceptibility patterns of Citrobacter freundii isolated from pa-tients with urinary tract infection in Al-Najaf governorate – Iraq. Int.J.Pharm.Sci. 2019; 10(2): 1481-1488.
Crossref - Shiraki Y, Ishibashi M, hiruma A, nishikawa Y and ikeda I. Cytokine secretion profiles of human keratinocytes during Trichophyton tonsurans and Arthroderma benhamiae infections. J. Med. Micro. 2006; 55: 1175-1185.
Crossref - Aljanaby AJJ. Antibacterial activity of an aqueous extract of Petroselinum crispum leaves against pathogenic bacteria isolated from patients with burns infections in Al-najaf Governorate, Iraq. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2013; 39: 3709.
Crossref - Cheng Q, McKeown, SJ, Santos L, Santiago FS, Khachigian, LM, Morand EF and Hickey MJ. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor increases leukocyte–endothelial inter-actions in human endothelial cells via promo-tion of expression of adhesion molecules. J. Immunol. 2010; 185: 1238–1247.
Crossref - McCarthy JS, Kemp DJ, Walton SF and Currie BJ. Scabies: more than just an irritation. Postgrad Med. J. 2004; 80: 382-387.
Crossref - Hengge UR, Currie BJ, Jager G, Lupi O and Schwartz RA. Scabies: a ubiquitous neglected skin disease. Lancet Infectious Diseases. 2006; 6(12) 769-779.
Crossref - Liu JM, Wang HW, Chang FW, Liu, YP, Chiu FH, Lin, YC, Cheng KC and Hsu RJ. The effects of climate factors on scabies. A 14-year population-based study in Taiwan. Parasite. 2016; 23:54.
Crossref - Aljanaby AAJ and Medhat AR. Prevalence of Some Antimicrobials Resistance Associated-genes in Salmonella typhi Isolated from Patients Infected with Typhoid Fever. J. Biol. Sci. 2017; 17(4): 171-184.
Crossref - Judith A, Owen JP, Sharon A, Stranford A and Patricia P. J. Kubby Immunology book. 2013; 7th edition.
- Mohy AA, Aljanaby AAJ and Al-Hadraawy SK. Serum concentrations of CD4+ and CD8+ in patients infected with scabies caused by Sarcoptes scabiei. JAPER. 2018; 1(8):121-126.
- Currie BJ and McCarthy JS. Permethrin and ivermectin for scabies. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362(8): 717-725.
Crossref - Weaver CT, Hatton RD and Mangan PR. IL-17 family cytokines and the expanding diversity of effector T cell lineages. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007; 25: 821–852.
Crossref - Kai HH, Christian C, Bernhard L, Jens-Malte B. Cytokines and the Skin Barrier, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013; 14: 6720-6745.
Crossref - Hahn J, Knopf J, Maueroder C, Kienhofer D, Leppkes M. and Herrmann M. (2016) Neutrophils and neutrophil extracellular traps orchestrate initiation and resolution of inflammation. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016; 34:(4 Suppl 98):6–8.
- Aljanaby AAJ, Tuwaij N S S and Al-khilkhali H J B. Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from older smokers and non-smokers of inpatients in intensive care unit infected with chronic pneumonia in AL-Najaf hospital, Iraq. J Pharm Sci & Res. 2018; 10(5): 1093-1097.
- Luo DQ, Huang MX, Liu JH, Tang W, Zhao YK and Sarkar R. Bullous scabies. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2016; 95(3):689–93.
Crossref - Arlian L, Morgan M, Paul C. Evidence that scabies mites (Acari: Sarcoptidae) influence production of interleukin-10 and the function of T-regulatory cells (Tr1) in humans. J Med Entomol. 2006; 43: 283–287.
Crossref - Gonzalez-Lombana C, Gimblet C, Bacellar O, Oliveira WW and Passos S. IL-17 mediates immunopathology in the absence of IL-10 following Leishmania major infection. PLoS Pathog. 2013; 9: e1003243.
Crossref - Martin JC, Baeten DL and Josien R. Emerging role of IL-17 and Th17 cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol. 2014; 154: 1–12.
Crossref
© The Author(s) 2019. Open Access. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License which permits unrestricted use, sharing, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.