Abstract
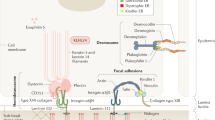
Epidermolysis bullosa is a family of inherited blistering skin disorders characterized by blister formation in response to mechanical trauma. Major types of epidermolysis bullosa include epidermolysis bullosa simplex, hemidesmosomal epidermolysis bullosa, junctional epidermolysis bullosa, and dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa.
Current treatment for epidermolysis bullosa consists of supportive care for skin and other organ systems and entails a combination of wound management, infection support for chronic wounds, surgical management as needed, nutritional support, and preventative screening for squamous cell carcinoma in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. The regimen must be tailored specifically to the severity and extent of skin and systemic involvement in each case.
Recent studies have identified specific protein and genetic abnormalities for most epidermolysis bullosa subtypes. These new advancements in the understanding of molecular pathophysiology have provided much of the basis for current efforts to develop effective gene and protein therapy for epidermolysis bullosa.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Use of tradenames is for product identification only and does not imply endorsement.
References
Burgeson R.E., Christiano A.M. The dermal-epidermal junction. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1997; 9 (5): 651–658
Marinkovich M.P. The molecular genetics of basement membrane diseases. Arch Dermatol 1993; 129: 1557–1565
Fuchs E., Green H. The expression of keratin genes in epidermis and cultured epidermal cells. Cell 1978; 15 (3): 887–897
Heida Y., Nishizawa Y., Uematsu J., et al. Identification of a new major hemidesmosomal protein, HD1: a major high molecular mass component of isolated hemidesmosomes. J Cell Biol 1992; 116: 1497–1506
Liu J.G., Mayne R. The complete cDNA coding sequence and tissue-specific expression of the mouse laminin alpha4 chain. Matrix Biol 1996; 15 (6): 433–437
Sawamura D.K., Li K., Chu M.L., et al. Human bullous pemphigoid antigen (BPAG1): amino acid sequence deduced from cloned cDNAs predicts biologically important peptide segments and protein domains. J Biol Chem 1991; 266: 17784–17790
Rezniczek G.A., de Pereda J.M., Reipert S., et al. Linking integrin alpha6beta4-based cell adhesion to the intermediate filament cytoskeleton: direct interaction between the beta4 subunit and plectin at multiple molecular sites. J Cell Biol 1998; 141 (1): 209–225
Borradori L., Chavanas S., Schaapveld R.Q., et al. Role of the bullous pemphigoid antigen 180 (BP180) in the assembly of hemidesmosomes and cell adhesion: reexpression of BP180 in generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa keratinocytes. Exp Cell Res 1998; 239 (2): 463–476
Rousselle P., Lunstrum G.P., Keene D.R., et al. Kalinin: an epithelium-specific basement membrane adhesion molecule that is a component of anchoring filaments. J Cell Biol 1991; 114: 567–576
Marinkovich M.P., Lunstrum G.P., Burgeson R.E. The anchoring filament protein kalinin is synthesized and secreted as a high molecular weight precursor. J Biol Chem 1992; 267: 17900–17906
Marinkovich M.P., Lunstrum G.P., Keene D.R., et al. The dermal-epidermal junction of human skin contains a novel laminin variant. J Cell Biol 1992; 119: 695–703
Giudice G.J., Emery D.J., Diaz L.A. Cloning and primary structural analysis of the bullous pemphigoid autoantigen BP180. J Invest Dermatol 1992; 99 (3): 243–250
Sonnenberg A., Calafat J., Janssen H., et al. Integrin a6b4 complex is located in hemidesomosomes, suggesting a major role in epidermal cell-basement membrane adhesion. J Cell Biol 1991; 113: 907–917
Champliaud M.F., Lunstrum G.P., Rousselle P., et al. Human amnion contains a novel laminin variant, laminin 7, which like laminin 6, covalently associates with laminin 5 to promote stable epithelial-stromal attachment. J Cell Biol 1996; 132 (6): 1189–1198
Niessen C.M., Hogervorst F., Jaspars L.H., et al. The a6 b4 integrin is a receptor for both laminin and kalinin. Exp Cell Res 1994; 211: 360–367
Burgeson R.E., Lundstrum G.P., Rokosova B. The structure and function of type VII collagen. Ann NY Acad Sci 1990; (580): 32–43
Rousselle P., Keene D.R., Ruggiero F., et al. Laminin 5 binds the NC-1 domain of type VII collagen. J Cell Biol 1997; 138 (3): 719–728
Fine J.D., Eady R.A., Bauer E.A., et al. Revised classification system for inherited epidermolysis bullosa: report of the Second International Consensus Meeting on diagnosis and classification of epidermolysis bullosa. J Am Acad Dermatol 2000; 42 (6): 1051–1066
Uitto J., Pulkkinen L., McLean W.H. Epidermolysis bullosa: a spectrum of clinical phenotypes explained by molecular heterogeneity. Mol Med Today 1997; 3 (10): 457–465
Bruckner-Tuderman L., Höpfner B., Hammami-Hauasli N. Biology of anchoring fibrils: lessons from dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Matrix Biol 1999; 18 (1): 43–54
Marinkovich M.P., Herron G.S., Khavari P.A., et al. Inherited epidermolysis bullosa. In: Freedberg I.M., editor. Dermatology in general medicine. New York: MacGraw-Hill, 1999: 690–702
Bonidas J.M., Rothman A.L., Spstein E.H. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex: evidence in two families for keratin gene abnormalities. Science 1991; 254: 1202–1205
Coulombe P.A., Hutton M.E., Letai A., et al. Point mutations in human keratin 14 genes of epidermolysis bullosa simplex patients: genetic and functional analyzes. Cell 1991; 66: 1301–1311
Hovnanian A., Duquesnoy P., Amselem S. Genetic linkage of recessive epidermolysis bullosa to the type VII collagen gene. J Clin Invest 1992; (90): 1033–1037
Jonkman M.F., Herres K., Pas H.H., et al. Effects of keratin 14 ablation on the clinical and cellular phenotype in a kindred with recessive epidermolysis bullosa simplex. J Invest Dermatol 1996; 107 (5): 764–769
Koebner H. Hereditare Anlage zur Blasenbildung. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 1886; 12: 21
Weber F.P. Recurrent bullous eruption on the feet in a child. Proc R Soc Med 1926; 19: 72
Meneguzzi G., Marinkovich M.P., Aberdan D., et al. Kalinin is abnormally expressed in epithelial basement membranes of Herlitz’s junctional epidermolysis bullosa patients. Exp Dermatol 1992; 1 (5): 221–229
Jonkman M.F., de Jong M.C.J.M., Heeres K., et al. 180-kD bullous pemphigoid antigen (BP180) is deficient in generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa. J Clin Invest 1995; 95 (3): 1345–1352
Aberdam D., Galliano M.F., Vailly J., et al. Herlitz’s junctional epidermolysis bullosa is linked to mutations in the gene (LAMC2) for the g2 subunit of nicein/kalinin (LAMININ-5). Nat Genet 1994; 6 (3): 299–304
Pulkkinen L., Christiano A.M., Gerecke D., et al. A homozygous nonsense mutation in the ß 3 chain gene of laminin 5 (LAMB3) in Herlitz junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Genomics 1994; 24 (2): 357–360
Pulkkinen L., Christiano A.M., Airenne T., et al. Mutations in the g2 chain gene (LAMC2) of kalinin/laminin 5 in the junctional forms of epidermolysis bullosa. Nat Genet 1994; 6: 293–298
Kivirikko S., McGrath J.A., Pulkkinen L., et al. Mutational hotspots in the LAMB3 gene in the lethal (Herlitz) type of junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Hum Mol Genet 1996; 5 (2): 231–237
Marinkovich M.P., Verrando P., Keene D.R., et al. The basement membrane proteins kalinin and nicein are structurally and immunologically identical. Lab Invest 1993; 69: 295–299
Hashimoto I., Schnyder U.W., Anton-Lamprecht I. Epidermolysis bullosa hereditaria with junctional blistering in an adult. Dermatologica 1976; 152 (2): 72–86
Hintner H., Wolff K. Generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa. Arch Dermatol 1982; 118 (6): 375–384
Uitto J., Pulkkinen L., Christiano A.M. Molecular basis of the dystrophic and junctional form of epidermolysis bullosa: mutations in the type VII collagen and kalinin (laminin-5) genes. J Invest Dermatol 1994; 103 (5 Suppl.): S39–S46
Parente M.G., Chung L.C., Fyynanen J., et al. Human type VII collagen: cDNA cloning and chromosomal mapping of the gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1991; 88 (16): 6931–6935
McGrath J.A., Schofield D.M., Mayou B.J., et al. Epidermolysis bullosa complicated by squamous cell carcinoma: report of 10 cases. J Cutan Pathol 1992; 19 (2): 116–123
Smith L.T. Ultrastructural findings in epidermolysis bullosa. Arch Dermatol 1993; 129 (12): 1578–1584
Marinkovich M.P. Update on inherited bullous dermatoses. Dermatol Clin 1999; 17 (3): 473–485
McLean W.H., Pulkkinen L., Smith P.J., et al. Loss of plectin causes epidermolysis bullosa with muscular dystrophy: cDNA cloning and genomic organization. Genes Dev 1996; 10 (14): 1724–1735
Chavanas S., Pulkkinen L., Gache Y., et al. A homozygous nonsense mutation in the PLEC1 gene in patients with epidermolysis bullosa simplex with muscular dystrophy. J Clin Invest 1996; 98 (10): 2196–2200
Elliott C.E., Becker B., Oehler S., et al. Plectin transcript diversity: identification and tissue distribution of variants with distinct first coding exons and rodless isoforms. Genomics 1997; 42 (1): 115–125
Ruzzi L., Gagnoux-Palacios L., Pinola M., et al. A homozygous mutation in the integrin alpha6 gene in junctional epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia. J Clin Invest 1997; 99 (12): 2826–2831
Vidal F., Aberdam D., Miquel C., et al. Integrin ß 4 mutations associated with junctional epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia. Nat Genet 1995; 10 (2): 229–234
Zimmer K.P., Schumann H., Mecklenbeck S., et al. Esophageal stenosis in childhood: dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa without skin blistering due to collagen VII mutations. Gastroenterology 2002; 122 (1): 220–225
Pulkkinen L., Rouan F., Bruckner-Tuderman L., et al. Novel ITGB4 mutations in lethal and nonlethal variants of epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia: missense versus nonsense. Am J Hum Genet 1998; 63 (5): 1376–1387
Nakano A., Pulkkinen L., Murrell D., et al. Epidermolysis bullosa with congenital pyloric atresia: novel mutations in the ß 4 integrin gene (ITGB4) and genotype/ phenotype correlations. Pediatr Res 2001; 49 (5): 618–626
Tidman M.J., Eady R.A.J. Hemidesmosome heterogeneity in junctional epidermolysis bullosa revealed by morphometric analysis. J Invest Dermatol 1986; (86): 51–56
Tidman M.J., Eady R.A.J. Evaluation of anchoring fibrils and other components of the dermal-epidermal junction in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa by a quantitative ultrastructural technique. J Invest Dermatol 1985; (84): 374–377
Pearson R.W. Histopathologic and ultrastructional findings in certain genodermatoses. Clin Dermatol 1985; (3): 143–174
Lin AN, Carter DM, editors. Epidermolysis bullosa: basic and clinical aspects. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1992: 302
Carter D.M., Lin A.N., Varghese M.C., et al. Treatment of junctional epidermolysis bullosa with epidermal autografts. J Am Acad Dermatol 1987; 17 (2 Pt 1): 246–250
Hill J.C., Grimwood R.E., Parsons D.S. Treatment of chronic erosions of junctional epidermolysis bullosa with human epidermal allografts. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 1992; 18 (5): 396–400
Bastin K.T., Steeves R.A., Richards M.J. Radiation therapy for squamous cell carcinoma in dystrophic epidermolysis: case reports and literature review. Am J Clin Oncol 1997; 20 (1): 55–58
Ladd A.L., Kibele A., Gibbons S. Surgical treatment and postoperative splinting of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J Hand Surg [Br] 1996; 21 (5): 888–897
Terrill P.J., Mayou B.J., Pemberton J. Experience in the surgical management of the hand in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Br J Plast Surg 1992; 45 (6): 435–442
Vozdvizhensky S.I., Albanova V.I. Surgical treatment of contracture and syndactyly of children with epidermolysis bullosa. Br J Plast Surg 1993; 46 (4): 314–316
Terrill P.J., Mayou B.J., McKee P.H., et al. The surgical management of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (excluding the hand). Br J Plast Surg 1992; 45 (6): 426–434
Travis S.P., McGrath J.A., Turnbull A.J., et al. Oral and gastrointestinal manifestations of epidermolysis bullosa. Lancet 1992; 340: 1505–1506
Griffin R.P., Mayou B.J. The anesthetic management of patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: a review of 44 patients over a 10 year period. Anesthesia 1993; 48 (9): 810–815
Shah M.D., Berman W.F. Endoscopic balloon dilation of esophageal strictures in children. Gastrointest Endosc 1993; 39 (2): 153–156
Haynes L., Atherton D.J., Ade-Ajayi N., et al. Gastrostomy and growth in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Br J Dermatol 1996; 134 (5): 872–879
Haynes L., Atherton D., Clayden G. Constipation in epidermolysis bullosa: successful treatment with a liquid fiber-containing formula. Pediatr Dermatol 1997; 14 (5): 393–396
Lin A.N., Murphy F., Brodie S.E., et al. Review of ophthalmic findings in 204 patients with epidermolysis bullosa. Am J Ophthalmol 1994; 118 (3): 384–390
Tong L., Hodgkins P.R., Denyer J., et al. The eye in epidermolysis bullosa. Br J Ophthalmol 1999; 83 (3): 323–326
Wright J.T., Fine F.D., Johnson L. Dental carries risk of hereditary epidermolysis bullosa. Pediatr Dent 1994; 16 (6): 427–432
Lechner-Gruskay D., Honig P.J., Pereira G., et al. Nutritional and metabolic profile of children with epidermolysis bullosa. Pediatr Dermatol 1988; 5 (1): 22–27
Birge K. Nutrition management of patients with epidermolysis bullosa. J Am Diet Assoc 1995; 95 (5): 575–579
Darling T.N., Bauer J.W., Hintner H., et al. Generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa. Adv Dermatol 1997; 13: 87–119
Fridge J.L., Vichinsky E.P. Correction of the anemia of epidermolysis bullosa with intravenous iron and erythropoietin. J Pediatr 1998; 132 (5): 871–873
Atherton D.J., Cox I., Hann I. Intravenous iron (III) hydroxide-sucrose complex for anemia in epidermolysis bullosa [letter]. Br J Dermatol 1999; 140 (4): 773
Caldwell-Brown D., Stern R.S., Lin A.N., et al. Lack of efficacy of phenytoin in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: Epidermolysis Bullosa Study Group. N Engl J Med 1992; 327 (3): 163–167
Unger W.P., Nethercott J.R. Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica treated with vitamin E and oral corticosteroids. Can Med Assoc J 1973; 108 (9): 1136–1138
Smith E.B., Michener W.M. Vitamin E treatment of dermolytic bullous dermatosis: a controlled study. Arch Dermatol 1973; 108 (2): 254–256
Shirakata Y., Shiraishi S., Sayama K., et al. High-dose tocopherol acetate therapy in epidermolysis bullosa siblings of the Cockayne-Touraine type. J Dermatol 1993; 20 (11): 723–725
Fritsch P., Klein G., Aubock J., et al. Retinoid therapy of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J Am Acad Dermatol 1983; 9 (5): 766–767
Andreano J.M., Tomecki J.K. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex responding to isotretinoin. Arch Dermatol 1988; 124 (9): 1445–1446
Husz S., Olah J., Korom I., et al. Cyclosporin for dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Lancet 1989; II (8676): 1393–1394
Coberly S.B.M., Tran H.T., Keene D.R., et al. Exogenous laminin 5 protein therapy corrects JEB keratinocyte adhesive defects in vitro and basement membrane defects in a JEB skin equivalent system [abstract]. J Invest Dermatol 1997; 108: 549A
Khavari P.A. Genetic correction of inherited epidermal disorders. Hum Gene Ther 2000; 11 (16): 2277–2282
Dellambra E., Vailly J., Pellegrini G., et al. Corrective transduction of human epidermal stem cells in laminin-5-dependent junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Hum Gene Ther 1998; 9 (9): 1359–1370
Robbins P.B., Lin Q., Goodnough J., et al. In vivo restoration of laminin 5 ß 3 expression and function in junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001; 98 (9): 5193–5198
Dellambra E., Prislei S., Salvati A.L., et al. Gene correction of integrin ß 4-dependent pyloric atresia-junctional epidermolysis bullosa keratinocytes establishes a role for ß 4 tyrosines 1422 and 1440 in hemidesmosome assembly. J Biol Chem 2001; 276 (44): 41336–41342
Blau H., Khavari P. Gene therapy: progress, problems, prospects. Nat Med 1997; 3 (6): 612–613
Santana E., Peritz A.E., Iyer S., et al. Different frequency of gene targeting events by the RNA-DNA oligonucleotide among epithelial cells. J Invest Dermatol 1998; 111 (6): 1172–1177
Lin M.T., Pulkkinen L., Uitto J., et al. The gene gun: current applications in cutaneous gene therapy. Int J Dermatol 2000; 39 (3): 161–170
Lin M.T., Wang F., Uitto J., et al. Differential expression of tissue-specific promoters by gene gun. Br J Dermatol 2001; 144 (1): 34–39
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to gratefully acknowledge the assistance of Eric Lin and Nancy Griffiths in the preparation of this manuscript, the funding assistance of the Palo Alto VA Health Care System and NIH grants P01-44102 and R01-AR47223, and the support and encouragement of the Epidermolysis Bullosa Medical Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pai, S., Marinkovich, M.P. Epidermolysis Bullosa. Am J Clin Dermatol 3, 371–380 (2002). https://doi.org/10.2165/00128071-200203060-00001
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00128071-200203060-00001