Summary
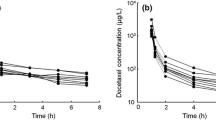
The effects of the primary tumour in situ or of gastrectomy on the bioavailability and other pharmacokinetic parameters of etoposide, after oral administration of commercially available etoposide (Vepesid®, Bristol-Myers Squibb) capsules, were studied in 8 patients with histologically proven gastric carcinoma. The dose of etoposide was 50mg. The oral bioavailability was found to be 56 ± 14%, which was similar to values reported in other studies in patients without malignancies of the gastrointestinal tract. After intravenous and oral administration, the apparent volumes of distribution were 21.5 ± 10.4 and 27.7 ± 11.1 L/m2, respectively, the mean residence times were 9.0 ± 2.6 and 10.2 ± 2.7 hours, respectively, and the elimination half-lives were 11.8 ± 5.9 and 7.8 ± 1.7 hours, respectively. These pharmacokinetic parameters were not significantly different after intravenous and oral administration. The plasma clearance of etoposide was 21.6 ± 3.2 ml/min/m2. The bioavailability of etoposide was not significantly altered (p > 0.05) by reversing the sequence of administration, nor were the apparent volume of distribution, the mean residence time or the terminal half-life of etoposide in plasma. Although the number of patients was small, it can be concluded that the pharmacokinetic parameters of etoposide are not altered in the presence of gastric cancer or gastrectomy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Slevin ML. Low-dose oral etoposide: A new role for an old drug? [editorial]. J Clin Oncol 1990; 8: 1607–9
Slevin ML, Clark PI, Joel SP, et al. A randomized trial to evaluate the effect of schedule on the activity of etoposide in small cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 1989; 7: 1333–40
Clark PI, Slevin ML. The clinical pharmacology of etoposide and teniposide. Clin Pharmacokinet 1987; 12: 223–52
Thompson DS, Hainsworth JD, Hande KR, et al. Prolonged administration of low-dose, infusional etoposide in patients with etoposide-sensitive neoplasms: a phase I/II study. J Clin Oncol 1993; 11: 1322–8
Clark PI, Joel SP, Slevin ML. A pharmacokinetic hypothesis for the clinical efficacy of etoposide in small cell lung cancer. Proc Am Assoc Clin Oncol 1989; 8: 66
Slevin ML, Joel SP. Prolonged oral etoposide in small cell lung cancer [editorial]. Ann Oncol 1993; 4: 529–32
Desoize B, Woirin V, Legros M, et al. Reduced oral etoposide bioavailability in patients with advanced cancer of the head and neck. J Natl Cancer Inst 1992; 84: 348–50
D’Incalci M, Farina P, Sessa C, et al. Pharmacokinetics of VP 16-213 given by different administration methods. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1982; 7: 141–5
Joel SP, Dolega-Ossowksi E, Jones K, et al. The bioavailability of oral etoposide during prolonged administration and development of a limited sampling strategy for the estimation of AUC after an oral dose. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 1991; 32: 178
Taal BG, Teller FGM, Ten Bokkel-Huinink WW, et al. Etoposide, leucovorin, 5-fluorouracil, (ELF) combination chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer: Experience with two treatment schedules incorporating intravenous or oral etoposide. Ann Oncol 1994; 5: 90–2
Proost JH, Meijer DKF. MWPHARM, an integrated software package for drug dosage regimen calculation and therapeutic drug monitoring. Computers Biol Med 1992; 22: 155–63
Gibaldi M, Perrier D. Pharmacokinetics (revised and expanded). 2nd ed. New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc., 1982: 45–199
Powers JD. Statistical considerations in pharmacokinetic study design. Clin Pharmacokinet 1993; 24: 380–7
Sinkule JA, Evans WE. High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of the semisynthetic epipodophyllotoxins teniposide and etoposide using electrochemical detection. J Pharm Sci 1984; 73: 164–86
Armbrecht U, Lundell L, Lindstedt G, et al. Causes of malabsorption after total gastrectomy with Roux-en-Y reconstruction. Acta Chir Scand 1988; 154: 37–41
Walther B, Clementsson C, Vallgren S, et al. Fat malabsorption in patients before and after total gastrectomy, studies by the triolein breath test. Scand J Gastroenterol 1989; 24: 309–14
Rieu PNMA, Jansen JBMJ, Joosten HJM, et al. Effect of gastrectomy with either Roux-en-Y or Billroth II anastomosis on small-intestinal function. Scand J Gastroenterol 1990; 25: 185–92
Yamamoto Y, Amano T, Fujimoto Y, et al. The effect of gastrectomy on serum 5-FU concentrations of patients administered UFT per os [in Japanese with English abstract]. Jpn J Cancer Clin 1987; 33: 377–81
Maehara Y, Takeuchi H, Oshiro T, et al. Effect of gastrectomy on the pharmacokinetics of tegafur, uracil, and 5-fluorouracil after oral administration of a 1:4 tegafur and uracil combination. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1994; 33: 445–9
Cavalli F, Zucchetti M, Gentili D, et al. Phase I and clinical pharmacological evaluation of daily oral etoposide (VP16). Proc ASCO 1992; 11: 109
Hande KR, Krozely MG, Greco FA, et al. Bioavailability of low-dose oral etoposide. J Clin Oncol 1993; 11: 374–7
Marzola M, Zucchetti M, Colombo N, et al. Low-dose oral etoposide in epithelial cancer of the ovary. Ann Oncol 1993; 4: 517–9
Cunningham D, McTaggert L, Soukop M, et al. Etoposide: a pharmacokinetic profile including an assessment of bioavailability. Med Oncol Tumor Pharmacother 1986; 3: 95–9
Slevin ML, Joel SP, Whomsley R. The effect of dose on the bioavailability of oral etoposide: confirmation of a clinically relevant observation. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1989; 24: 329–31
Harvey VJ, Slevin ML, Joel SP, et al. The effect of dose on the bioavailability of oral etoposide. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1986; 16: 178–81
Beijnen JH, Holthuis JJM, Kerkdijk HG, et al. Degradation kinetics of etoposide in aqueous solution. Int J Pharm 1988; 41: 169–78
Shah JC, Chen JR, Chow D. Preformulation study of etoposide: identification of physicochemical characteristics responsible for the low and erratic oral bioavailability of etoposide. Pharm Res 1989; 6: 408–12
Minami H, Shimokata K, Saka H, et al. Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of a 14-day infusion of etoposide in patients with lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 1993; 11: 1602–8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jonkman-de Vries, J.D., Rosing, H., van Tellingen, O. et al. Pharmacokinetics of Etoposide after Oral and Intravenous Administration in Patients with Gastric Carcinoma. Clin. Drug Invest. 10, 86–95 (1995). https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-199510020-00003
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-199510020-00003