Summary
Synopsis
Nifedipine antagonises influx of calcium through cell membrane slow channels, and sustained release formulations of the calcium channel blocker have been shown to be effective in the treatment of mild to moderate hypertension and both stable and variant angina pectoris. Preliminary findings also indicate that these formulations are effective in the treatment of Ray naud’s phenomenon and hypertension in pregnancy, and that they reduce the frequency of ischaemic episodes in some patients with silent myocardial ischaemia. The exact mechanism of action of nifedipine in all of these disorders has not been defined. However, its potent peripheral and coronary arterial dilator properties, together with improvements in oxygen supply/demand, are of particular importance.
A major goal of sustained release therapy is to permit reductions in the frequency of nifedipine administration, preferably to once daily, and thus improve patient compliance. Two new once-daily formulations — the nifedipine gastrointestinal therapeutic system (GITS) and a fixed combination capsule comprising sustained release nifedipine 20mg and atenolol 50mg — have exhibited marked antihypertensive efficacy. The GITS preparation has also been used effectively in the treatment of stable angina pectoris, and both formulations appear to be well tolerated.
Sustained release nifedipine formulations are generally better tolerated than their conventionally formulated counterparts, particularly with regard to reflex tachycardia. Adverse effects seem to be dose related, are mainly associated with the drug’s potent vasodilatory action, and include headache, flushing and dizziness. Generally, these effects are mild to moderate in severity and transient, usually diminishing with continued treatment.
Thus, sustained release nifedipine formulations are useful and established cardiovascular therapeutic agents which have demonstrable efficacy in various forms of angina, mild to moderate hypertension and Raynaud’s phenomenon. Further, promising results shown by the nifedipine GITS formulation, with its advantage of once daily administration suggest that it is likely to become one of the preferred nifedipine formulations for the treatment of hypertension and the various forms of angina.
Pharmacodynamic Properties
Nifedipine inhibits influx of calcium through cardiac muscle and vascular smooth muscle cell membranes. It differs from diltiazem and verapamil, particularly with regard to sinoatrial and atrioventricular node function, where it may enhance conduction.
Repeated administration of sustained release nifedipine reduces systolic and diastolic blood pressure by about 10 to 20%, whereas a fixed combination sustained release nifedipine/atenolol capsule and nifedipine gastrointestinal therapeutic system (GITS) reduce blood pressure by approximately 20%. Administered once daily, the latter formulation effectively controls blood pressure in a dose-dependent manner throughout a 24-hour dosing interval.
Single doses of conventional nifedipine formulations increase heart rate by 12 to 17%, but these increases range from only 6 to 9% during longer term (1 to 6 weeks) administration. In contrast to conventional nifedipine formulations, sustained release preparations are generally not associated with postdose tachycardia.
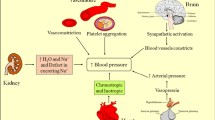
The main haemodynamic actions of nifedipine are peripheral arterial vasodilation with subsequent reductions in systemic vascular resistance and afterload, and an increase in cardiac index. Nifedipine has a small, direct negative inotropic effect in vitro and after intracoronary administration to humans. This is usually not observed after oral administration. Sustained release nifedipine may increase cardiac output, and it increased cardiac efficiency and reduced cardiac power in patients with hypertension. Further, the fixed combination sustained release nifedipine/ atenolol formulation caused a marked regression of left ventricular hypertrophy after 1 year’s treatment.
Nifedipine has antianginal effects which parallel those of diltiazem, verapamil,β-blockers and nitrates. It improves clinical status and reduces ECG signs of myocardial ischaemia on exercise or atrial pacing. In addition, it increases coronary blood flow, particularly to myocardial areas supplied by stenotic arteries, without significantly altering myocardial oxygen consumption. Nifedipine also relieves coronary vasospasm in variant (Prinzmetal) angina, and improves exercise performance by reducing myocardial oxygen demand in patients with effort angina.
Generally, the vasocdlating action of nifedipine is greater in hypertensive patients than in normotensive volunteers. Nifedipine significantly increases forearm blood flow and brachial artery compliance, while significantly reducing forearm vascular resistance and characteristic impedance.
Nifedipine reduces plasma levels of β-thromboglobulin, a protein released during platelet activation, in patients with Raynaud’s phenomenon, and reverses thrombocytopenia in women with pre-eclampsia. Data regarding the effect of nifedipine on serum lipids are conflicting with reports of no significant effects, increases in high density lipoprotein (HDL), HDL2 and apolipoprotein A-I and A-II, and significant decreases in apolipoprotein E, and low density lipoprotein (LDL): HDL and apolipoprotein B: A-I ratios. However, animal experiments have indicated that nifedipine may slow the progression of new atherosclerotic lesions. This was confirmed in the International Nifedipine Trial on Antiatherosclerotic Therapy (INTACT) in which nifedipine (formulation not stated) significantly reduced the progression of new atherosclerotic lesions in patients with mild to moderate coronary artery disease.
Administration of sustained release nifedipine for 6 to 52 weeks had no effect on glucose tolerance in hypertensive patients with or without concomitant diabetes. In a large number of single-dose studies involving healthy volunteers and subjects with impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes, nifedipine also had no significant effect on glucose tolerance. Thus, the weight of evidence indicates that nifedipine has no real diabetogenic potential.
Nifedipine rarely has marked renal effects. However, renal blood flow increases significantly and renovascular resistance decreases significantly after 4 weeks’ nifedipine administration to patients with essential hypertension. Nifedipine increases glomerular filtration rate (+11 to +46%) in hypertensive patients with or without concomitant glomerulonephritis, but usually does not alter this parameter in healthy volunteers. Increases in plasma renin activity are noted after the acute administration of nifedipine, whereas during longer term administration both increases and decreases in plasma renin activity have been recorded. Plasma aldosterone levels do not change in parallel with alterations in plasma renin activity. However, angiotensin II levels increase, particularly in younger normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Nifedipine has significant diuretic and natriuretic actions, may also significantly increase urinary potassium excretion, and has a significant uricosuric action.
Pharmacokinetic Properties
Nifedipine is almost completely absorbed from the jejunum after the administration of an oral dose. However, as a result of extensive and variable first-pass hepatic extraction, it has a relatively low bioavailability ranging from 43 to 77%. Absorption of nifedipine from sustained release oral tablets is prolonged (tmax=1.2 to 4.0 hours) in comparison with immediate release capsules (tmax=0.5 to 1.9 hours). Food increases the bioavailability of a sustained release nifedipine tablet and may also delay gastric emptying, thereby increasing the dissolution of a ‘biphasic’ nifedipine formulation in the stomach.
Nifedipine’s absorption from the gastrointestinal therapeutic system (GITS) is unaffected by gastrointestinal pH or motility. This formulation has an oral bioavailability of 55 to 65% after a single dose, and 75 to 85% at steady-state. As with other nifedipine formulations, the GITS tablet exhibits a linear pharmacokinetic profile and plasma nifedipine concentrations begin to rise 2 hours after, and plateau approximately 6 hours after, GITS administration. ‘Dose-dumping’ does not occur with this sustained release formulation, and although food increases the rate of absorption of nifedipine from the GITS this is not associated with alterations in bioavailability.
The mean steady-state apparent volume of distribution of nifedipine is 1.32 L/kg after oral administration. Nifedipine is highly bound to plasma proteins (92 to 98%), in particular albumin.
Assuming complete absorption of an orally administered nifedipine dose, about 30 to 40% of the drug is eliminated by first-pass metabolism. Nifedipine undergoes oxidation to 3 pharmacologically inactive metabolites which are subsequently excreted in the urine together with traces of unchanged nifedipine. Two types of nifedipine metaboliser — fast and slow — have been postulated. These may arise because of oxidation polymorphism with a genetic basis. Mexican populations may have a prevalence of slow metabolisers, whereas fast metabolisers may be found more frequently in European populations.
After oral administration of radiolabelled nifedipine approximately 70 to 80% of the total administered radioactivity appears in the urine in the form of metabolites, along with trace amounts of unchanged nifedipine. The remaining radioactivity is recovered in the faeces, also in the form of metabolites. The intrinsic clearance of nifedipine from the plasma ranges from 21 to 37 L/h and the rate of nifedipine elimination is probably dependent on drug metabolising activity and hepatic blood flow. Elimination half-life values of sustained release nifedipine (3.8 to 16.9 hours) are about 2 to 6 times greater than those of immediate release nifedipine capsules.
In elderly volunteers, administration of sustained release nifedipine results in greater values for Cmax, AUC, mean residence time and elimination half-life than in younger volunteers. Although Cmax values may be significantly reduced in patients with severe renal impairment, the pharmacokinetic profile of nifedipine is usually not altered in such patients.
Therapeutic Efficacy
Sustained release nifedipine (20 to 80 mg/day) has produced statistically significant blood pressure reductions of about 20% in patients with essential hypertension in noncomparative as well as in placebo-controlled trials. Generally, response rates (usually the percentage of patients attaining a goal diastolic blood pressure of ≤ 95mm Hg) have ranged from about 80 to 85%. Sustained release nifedipine is also an effective antihypertensive agent when used in combination with β-blockers, ACE inhibitors and/or diuretics, and Black patients have responded well to the drug. Unlike conventionally formulated nifedipine, reflex tachycardia is usually not a feature of sustained release nifedipine therapy.
The majority of comparative trials suggest that sustained release nifedipine has an antihypertensive efficacy which is generally similar to that of β-blockers, ACE inhibitors and other calcium antagonists, although marked tolerability differences exist between these agents. Combined sustained release nifedipine and atenolol regimens have been extensively studied and such combinations cause significantly greater blood pressure reductions than either agent alone.
The nifedipine GITS (30 to 180mg administered once daily) produces mean blood pressure reductions ranging from 8 to 22% and associated response rates of about 60 to 80% in patients with hypertension. Preliminary studies suggest that nifedipine GITS is at least as effective as hydrochlorothiazide in elderly and Caucasian patients, more effective than hydrochlorothiazide in Blacks, and more effective than propranolol in Caucasians. Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring has confirmed the antihypertensive efficacy of nifedipine GITS throughout a 24-hour dosage interval.
The efficacy of sustained release nifedipine in elderly patients (> 60 years of age) with hypertension is similar to that of ACE inhibitors, although the latter agents appear to have slightly better tolerability profiles in this population. The fixed sustained release nifedipine/atenolol combination appears to be effective and well tolerated in elderly patients. In addition, preliminary results suggest that sustained release nifedipine is effective when used alone and in combination with atenolol or methyldopa in hypertension during pregnancy although its effects, if any, on the fetus remain undefined. Sustained release nifedipine also appears to be effective and suitable for use in patients with malignant hypertension and in hypertensive patients with severe concomitant diseases (e.g. renal, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease, diabetes, asthma and systemic lupus erythematosus).
In patients with stable angina pectoris, sustained release nifedipine has significantly improved both subjective and objective symptoms of angina. Its antianginal efficacy parallels that of nisoldipine, and sustained release and conventional formulations of isosorbide mononitrate. However, in contrast to nitrate regimens, tolerance usually does not occur during long term therapy with sustained release nifedipine. Nifedipine GITS and other sustained release nifedipine formulations have shown superior antianginal efficacy to conventional nifedipine formulations. In the treatment of patients with variant angina pectoris, sustained release formulations of nifedipine and isosorbide dinitrate are similarly effective, although headache has occurred in significantly more nitrate recipients.
The Nifedipine-Total Ischemia Awareness Program has assessed the efficacy of nifedipine (formulation not stated) in the management of silent myocardial ischaemia. In this study, 83% (113/136) of patients had silent and/or symptomatic episodes of myocardial ischaemia. Addition of nifedipine to previous antianginal regimens significantly reduced the mean frequency of ST segment depression. Preliminary findings with sustained release nifedipine in the treatment of silent myocardial ischaemia have been promising and the results of INTACT have shown that nifedipine significantly reduces the progression of new atherosclerotic lesions in patients with mild to moderate coronary artery disease. However, the effect of nifedipine on cardiac mortality in these patients remains unclear.
Initial findings suggest that sustained release nifedipine is effective in the treatment of Raynaud’s phenomenon. Indeed, both ‘biphasic’ (5mg immediate release and 15mg sustained release) and sustained release nifedipine have improved subjective and objective symptoms of the disorder. Other studies indicate that sustained release nifedipine may be a useful agent in the treatment of perniosis (chilblains).
Sustained release nifedipine has also been used successfully, both pre- and postoperatively, in the management of labile high blood pressure due to phaeochromocytoma.
Tolerability
In worldwide use, nifedipine is associated with an overall incidence of adverse effects of about 20%. These effects are usually related to its vasodilatory action, are mild to moderate in severity and transient; they include headache (about 7%), flushing (5.3 to 7.4%), dizziness (3.1 to 12.1%) and lower leg oedema (0.6 to 7.7%) and usually necessitate treatment cessation in 2 to 6% of patients. Other adverse effects associated with nifedipine therapy include gastrointestinal symptoms (occurring with an incidence of 5.2 to 7.5%) and transient hypotension (about 5%). Nifedipine has also been reported to cause nocturia and joint pain, and there are several reports of gingival hyperplasia, but the latter reaction is relatively uncommon and readily resolves after treatment withdrawal. Some cases of increasing angina frequency, and paradoxical worsening of cardiac ischaemia, have occurred during nifedipine treatment. In addition, the abrupt cessation of nifedipine therapy has led to isolated instances of coronary artery spasm, hypertensive crisis, and a worsening of asthma symptoms.
Sustained release nifedipine and nifedipine GITS tablets are generally better tolerated than conventional nifedipine formulations because of a slower absorption, a more gradual onset of action and lower peak plasma concentrations. Atenolol reduces the vasodilator adverse effects of nifedipine, and conversely, nifedipine may decrease the incidence of adverse effects resulting from β-blockade. In comparative trials, the use of a fixed sustained release nifedipine/atenolol combination has been associated with a better tolerability profile than either agent alone.
Dosage and Administration
For the treatment of hypertension and Raynaud’s phenomenon and for the prophylaxis of the various forms of angina pectoris, sustained release nifedipine tablets are administered at an initial oral dosage of 20mg twice daily, increasing to 40mg twice daily if necessary. For these indications, the nifedipine GITS starting dosage is 30mg once daily, titrated at weekly intervals to a maximum of 150mg once daily if necessary. A sustained release nifedipine/atenolol fixed combination capsule (20/50mg) may be administered once daily for the treatment of essential hypertension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abadie E, Passa P. Diabetogenic effects of nifedipine. British Medical Journal 289: 438, 1984
Abramson M, Littlejohn GO. Hepatic reactions to nifedipine. Medical Journal of Australia 142: 47–48, 1985
Adebayo GI, Coker HAB, Fagbure F. Renal effects of nifedipine in healthy normotensive volunteers: effects of dose, formulation, duration of treatment, and chlorothiazide coadministration. Fundamental Clinical Pharmacology 2: 541–549, 1988
Adebayo GI, Mabadeje AFB. Effect of nifedipine on antipyrine and theophylline disposition. Biopharmaceutics and Drug Disposition 11: 157–164, 1990
Ahmad S. Nifedipine-induced acute psychosis. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 32: 408, 1984
Akhras F, Chambers J, Jefferies S, Jackson G. A randomised double-blind crossover study of isosorbide mononitrate and nifedipine retard in chronic stable angina. International Journal of Cardiology 24: 191–196, 1989
Andersen L, Kolendorf K, Thorsteinsson B. Nifedipine does not decrease insulin secretion. Acta Endocrinologica 100 (Suppl. 247): 7, 1982
Anderton JL, Vallance BD, Stanley NN, Crowe PF, Mittra B, et al. Atenolol and sustained release nifedipine alone and in combination in hypertension. Drugs 35 (Suppl. 4): 22–26, 1988
Angelino PF, Tortore P, Algrananti R. Hemodynamic studies on the new coronary therapeutic drug nifedipine (BAY a 1040); 2nd International Adalat Symposium, pp. 128–139, 1975
Aoki K, Kondo S, Mochizuki A, Yoshida T, Kato S, et al. Antihypertensive effects of cardiovascular Ca2+ -antagonist in hypertension patients in the absence and presence of beta-adrenergic-blockade. American Heart Journal 96: 218–226, 1978
Aoki K, Sato K, Kawaguchi Y, Yamamoto M. Acute and long-term hypotensive effects and plasma concentrations of nifedipine in patients with essential hypertension. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 23: 197–201, 1982
Aoki K, Yoshida T, Kato S, Tazume K, Soto I, et al. Hypotensive action and increased plasma renin activity by calcium antagonist (nifedipine) in hypertensive patients. Japanese Heart Journal 17: 479–484, 1976
Artigou JY, Benichou M, Berland J, Fressinaud P, Grollier G, et al. A randomised, double-blind therapeutic trial of enalapril versus slow-release nifedipine in mild to moderate essential hypertension. Presse Médicale 19: 13–16, 1990
Aschermann M, Bultas J, Karetová D, Kölbel F, Kozáková M, et al. Randomized double-blind comparison of isosorbide dinitrate and nifedipine in variant angina pectoris. American Journal of Cardiology 65: 46J-49J, 1990
Austin MB, Robson RA, Bailey RR. Effect of nifedipine on renal function of normal subjects and hypertensive patients with renal functional impairment. New Zealand Medical Journal 96: 829–831, 1983
Australian Adverse Drug Reactions Bulletin. Joint pain with nifedipine. August 1989
Azizi M, Chatellier G. Nifedipine and coronary artery disease. Lancet 336: 173–174, 1990
Babany G, Uzzan F, Larrey D, Degott C, Bourgeois P, et al. Alcoholic-like liver lesions induced by nifedipine. Journal of Hepatology 9: 252–255, 1989
Baksi A, Fraser D, Jeffcoate W, Ferriss B, Smart W on behalf of Multicentre Study Group. Enalapril in hypertensive diabetics: a comparison with nifedipine retard. Diabetes 39 (Suppl. 1): 107, 1990
Banzet O, Colin JN, Thibonnier M, Singlas E, Alexandre JM, et al. Acute antihypertensive effect and pharmacokinetics of a tablet preparation of nifedipine. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 24: 145–150, 1983
Barak S, Kaplan I. The CO2 laser in the excision of gingival hyperplasia caused by nifedipine. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 15: 633–635, 1988
Baunack AR, Weihrauch TR. Comprehensive analysis of the efficacy of nifedipine in esophageal motor disturbances causing angina-like chest pain and/or dysphagia (1977–1988). Hepatogastroenterology 36: 296, 1989
Bellini G, Battilana G, Puppis E, Rigoni A, Cosenzi A, et al. Renal response to acute nifedipine administration in normotensive and hypertensive patients during normal and low sodium intake. Current Therapeutic Research 35: 974–981, 1984
Bhatnager SK, Amin MMA, Al-Yusuf AR. Diabetogenic effects of nifedipine. British Medical Journal 289: 19, 1984
Birkebaek NH, Gerdes LU, Nielsen A, Faergeman o, Vejby-Christensen H. Effect of nifedipine and captopril on plasma lipoproteins in hypertensive patients. Current Therapeutic Research 46: 619–624, 1989
Bittar N. Usefulness of nifedipine for myocardial ischemia and the nifedipine gastrointestinal therapeutic system. American Journal of Cardiology 64: 31F-34F, 1989
Bogaert MG, Rosseel MT, Joos R, Boelaert J. Plasma concentrations of nifedipine in patients with renal failure. Arzneimittel-Forschung 34: 307–308, 1984
Bolli R, Triana F, Jeroudi MO. Postischemic mechanical and vascular dysfunction (myocardial ’stunning’ and microvascular ’stunning’) and the effects of calcium-channel blockers on ischemia/reperfusion injury. Clinical Cardiology 12: III16–III25, 1989
Bonaduce D, Canonico V, Mazza F, Nicolino A, Ferrara N, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of slow-release nifedipine in systemic hypertension by ambulatory intraarterial blood pressure monitoring. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 7: 145–151, 1985
Bondi A, Ciofalo G. Effectiveness, tolerance, and long-term compliance with nifedipine slow-release in hypertensive patients with concomitant and severe pathologies. Current Therapeutic Research 43: 815–823, 1988
Bonus B, Saddler MC, Black HR. A randomized double-blind parallel study assessing the efficacy of nifedipine gits vs. hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) in the management of mild to moderate hypertension in the elderly patient. American Journal of Hematology 3: 113A, 1990
Bortel LV, Böhm R, Mooij J, Schiffers P, Rahn KH. Total and free steady-state plasma levels and pharmacokinetics of nifedipine in patients with terminal renal failure. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 37: 185–189, 1989
Brauman A, Golik A, Gilboa Y, Hertzianu I. Effect of nifedipine on metabolism of glucose and secretion of insulin in diabetic patients. Diabetologia 27: 260A, 1984
Bravo EL, Krakoff LR, Tuck ML, Friedman CP, the MATH Study Group. Antihypertensive effectiveness of nifedipine gastrointestinal therapeutic system in the elderly. American Journal of Hypertension 3: 326S–332S, 1990
Breimer DD, Schellens JHM, Soons PA. Nifedipine: variability in its kinetics and metabolism in man. Pharmacology and Therapeutics 44: 445–454, 1989
Bursztyn M, Grossman E, Rosenthal T. Long-acting nifedipine in moderate and severe hypertensive patients with serious concomitant diseases. American Heart Journal 110: 96–101, 1985
Bursztyn M, Many A, Rosenthal T. Nifedipine in the treatment of hypertension in systemic lupus erythematosus. Angiology 38: 359–362, 1987
Bursztyn M, Tordjman K, Grossman E, Rosenthal T. Hypertensive crisis associated with nifedipine withdrawal. Archives of Internal Medicine 146: 397, 1986
Bühler F. Kalzium-Antagonisten: Kennt man ein Absetz-Syndrom? Münchener Medizinische Wochenschrift 125: 13, 1983
Challenor V, Waller DG, Gruchy BS, Renwick AG, George CF, et al. The effects of food and posture on the pharmacokinetics of a biphasic release preparation of nifedipine. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 22: 565–570, 1986
Challenor VF, Waller DG, Renwick AG, George CF. Slow release nifedipine plus atenolol in chronic stable angina pectoris. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 28(5): 509–516, 1989
Charles S, Ketelslegers J-M, Buysschaert M, Lambert AE. Hyperglycaemic effect of nifedipine. British Medical Journal 283: 19–20, 1981
Chellingsworth MC, Kendall MJ. Effects of nifedipine, verapamil and diltiazem on renal function. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 25: 599–602, 1988
Chellingsworth MC, Kendall MJ, Wright AD, Singh BM, Pasi J. The effects of verapamil, diltiazem, nifedipine and propranolol on metabolic control in hypertensives with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Journal of Human Hypertension 3: 35–39, 1989
Chimori K, Miyazaki S, Nakajima T, Miura K. Preoperative management of pheochromocytoma with the calcium-antagonist nifedipine. Clinical Therapeutics 7: 372–379, 1985
Christensen CK, Lederballe Pedersen O, Mikkelsen E. Renal effects of acute calcium blockade with nifedipine in hypertensive patients receiving beta-adrenoceptor-blocking drugs. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 32: 572–576, 1982
Chung M, Reitberg DP, Gaffney M, Singleton W. Clinical pharmacokinetics of nifedipine gastrointestinal therapeutic system. A controlled-release formulation of nifedipine. American Journal of Medicine 83 (Suppl. 6B): 10–14, 1987
Clas D, Hould FS, Rosenthall L, Arzoumanian A, Fried GM. Nifedipine inhibits cholecystokinin-induced gallbladder contraction. Journal of Surgical Research 46; 479–483, 1989
Clémenty J, Guivarc’h H, Schwebig A, Bricaud H. Captopril versus nifedipine — a double blind study in aged hypertensive patient. Abstract. European Heart Journal 10 (Suppl): 306, 1989
Coccia G, Bortolotti M, Michetti P, Dodero M. Sublingual nifedipine in the treatment of hypertensive lower esophageal sphincter: clinical and manometric results. Gastroenterology 98 (Suppl. 5): A337, 1990
Cohn PF, Vetrovec GW, Nesto R, Gerber FR, the Total Ischemia Awareness Program Investigators. The Nifedipine-Total Ischemia Awareness Program: a national survey of painful and painless myocardial ischemia including results of antiischemic therapy. American Journal of Cardiology 63: 534–539, 1989
Constantine G, Beevers DG, Reynolds AL, Luesley DM. Nifedipine as a second line antihypertensive drug in pregnancy. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 94: 1136–1142, 1987
Conway J, Johnston J, Bird R. Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in the comparison of atenolol, nifedipine and their combination. Journal of Hypertension 5 (Suppl. 5): 629, 1987
Corea L, Alunni G, Bentivoglio M, Boschetti E, Cosmi F, et al. Acute and long-term effects of nifedipine on plasma renin activity and plasma catecholamines in controls and hypertensive patients before and after metoprolol. Acta Therapeutica 6: 177–187, 1980
Corriveau ML, Rosen BJ, Keller CA, Chun DS, Dolan GF. Effect of posture, hydralazine, and nifedipine on hemodynamics, ventilation, and gas exchange in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. American Review of Respiratory Disease 138: 1494–1498, 1988
Covinsky JO, Hamburger SC. Slow channel blockers. Southern Medical Journal 76: 55–64, 1983
Creager MA, Pariser KM, Winston EM, Rasmussen HM, Miller KB, et al. Nifedipine-induced vasodilation in patients with Raynaud’s phenomenon. American Heart Journal 108: 370–373, 1984
Czuczwar SJ, Chodkowska A, Kleinrok Z, Malek U, Jagiello-Wójtowicz E. Effects of calcium channel inhibitors upon the efficacy of common antiepileptic drugs. European Journal of Pharmacology 176: 75–83, 1990
Daniels AR, Opie LH. Atenolol plus nifedipine for mild to moderate systemic hypertension after fixed doses of either agent alone. American Journal of Cardiology 57: 965–970, 1986
Davidson AR. Lymphocyte sensitisation in nifedipine-induced hepatitis. British Medical Journal 281: 1354, 1980
Deanfield JE, Selwyn AP, Chierchia S, Maseri A, Ribeiro P, et al. Myocardial ischaemia during daily life in patients with stable angina: its relation to symptoms and heart rate changes. Lancet 1: 753–758, 1983
Deedwania P, Shah J, Robison C, Watson P, Hurks C. Effects of nifedipine on glucose tolerance and insulin release in man. Clinical Research 32: 46A, 1984
Diamond JR, Cheung JY, Fang LST. Nifedipine-induced renal dysfunction. Alterations in renal hemodynamics. American Journal of Medicine 77: 905–909, 1984
Droste C, Roskamm H. Silent myocardial ischemia. American Heart Journal 118: 1807, 1989
Duckett GK, Cheadle B. Hypertension in the elderly: a study of a combination of atenolol and nifedipine. British Journal of Clinical Practice 44: 52–54, 1990
Duffy J, Macdonald G. The antihypertensive efficacy of nifedipine alone and in combination in general practice. Current Medical Research and Opinion 10: 566–572, 1987
Dustan HP. Calcium channel blockers. Potential medical benefits and side effects. Hypertension 13 (Suppl. I): 1137–1140, 1989
D’Arcy PF. Nifedipine: interaction with cimetidine not ranitidine. International Pharmacy Journal 2: 45, 1988
D’Arcy PF. Drug reactions and interactions. International Pharmacy Journal 3: 136, 1989
D’Arcy PF. Cyclosporin-nifedipine interaction. International Pharmacy Journal 4: 48, 1990
de Simone G, Ferrara LA, Fasano ML, di Lorenzo L, Lauria R. Slow-release nifedipine versus placebo in the treatment of arterial hypertension. A double-blind ergometric evaluation of cardiac workload. Japanese Heart Journal 26: 219–225, 1985
Ebner F, Donath M. Mode of action and efficacy of nifedipine. 4th International Adalat Symposium, pp. 25–37, 1980
Eicher JC, Morelon P, Chalopin JM, Tanter Y, Louis P, et al. Acute renal failure during nifedipine therapy in a patient with congestive heart failure. Critical Care Medicine 16: 1163–1164, 1988
Ekelund L-G, Ekelund C, Rössner S. Antihypertensive effects at rest and during exercise of a calcium blocker, nifedipine, alone and in combination with metoprolol. Acta Medica Scandinavica 212: 71–75, 1982
Eliraz A, Wishnitzer R, Fink A. Exacerbation of asthmatic symptoms after cessation of nifedipine therapy. Annals of Allergy 52: 125–127, 1984
Elkayam U, Weber L, Campese VM, Massry SG, Rahimtoola SH. Renal hemodynamic effects of vasodilation with nifedipine and hydralazine in patients with heart failure. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 4: 1261–1267, 1984
Ene MD, Williamson PJ, Roberts CJC, Waddell G. The natriuresis following oral administration of the calcium antagonists - nifedipine and nitrendipine. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 19: 423–427, 1985
Engelman RM, Hadji-Rousou I, Breyer RH, Whittredge P, Harbison W, et al. Rebound vasospasm after coronary revascularization in association with calcium antagonist withdrawal. Annals of Thoracic Surgery 37: 469–472, 1984
Erlemeier H-H, Küpper W, Hempel NB, Bleifield W. Anti-ischemic effects of slow-release formulations of nifedipine, isosorbide-5-mononitrate and their combination in patients with coronary heart disease. Cardiology 75: 409–418, 1988
Eränkö PO, Palva ES, Konno K, Venho VMK. Regulatory control of synonym drug bioavailability; bioinequivalency of nifedipine preparations. Pharmaceutical Medicine 4: 197–205, 1990
Farringer JA, Green JA, O’Rourke RA, Linn WA, Clementi WA. Nifedipine-induced alterations in serum quinidine concentrations. American Heart Journal 108: 1570–1572, 1984
Fedeli L, Colozza M, Boschetti E, Sabalich I, Aristei C, et al. Pharmacokinetics of vincristine in cancer patients treated with nifedipine. Cancer 64: 1805–1811, 1989
Fell PJ. Long-term treatment of hypertension in the elderly with a combination of atenolol and nifedipine. Current Medical Research and Opinion 12: 66–70, 1990
Ferlito S, Fichera C, Carra G, Puleo F, Calafato M, et al. Effect of nifedipine on blood sugar, insulin and glucagon levels after an oral glucose load. Panminerva Medica 23: 75–80, 1981
Ferrara LA, de Simone G, Mancini M, Fasano ML, Pasanisi F, et al. Changes in left ventricular mass during a double-blind study with chlorthalidone and slow-release nifedipine. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 27: 525–528, 1984
Ferrari M, Olivieri M, De Gasperi M, Lechi A. Differential effects of nifedipine and diltiazem on methacholine-induced bronchospasm in allergic asthma. Annals of Allergy 63: 196–200, 1989
Ferrés E, López Colomés JL, Moreno A, Villena J. Gingival hyperplasia associated with nifedipine. Revista Clinica Espanola 184: 341–342, 1989
Finch MB, Copeland S, Passmore AP, Johnston GD. A double-blind cross-over study of nifedipine retard in patients with Raynaud’s phenomenon. Clinical Rheumatology 7: 359–365, 1988
Fiorentini C, Galli C, Tamborini G. Tosi E, Riva S. Hemodynamic and renin responses to nifedipine in renovascular hypertension. American Heart Journal 119: 353, 1990
Fitzsimons TJ, Hart W, von Frankenberg H, Sanderson JE, Joy MD, et al. Low-dose atenolol and nifedipine for the treatment of hypertension. Journal of Drug Development 3: 13–19, 1990
Foster TS, Hamann SR, Richards VR, Bryant PJ, Graves DA, et al. Nifedipine kinetics and bioavailability after single intravenous and oral doses in normal subjects. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 23: 161–170, 1983
Franz I-W. Tönnesmann U, Behr U, Ketelhut R. Regression of left ventricular hypertrophy during combined atenolol and nifedipine treatment. Drugs 35 (Suppl. 4): 39–43, 1988
Frishman WH, Garofalo JL, Rothschild A, Rothschild M, Greenberg SM, et al. Multicenter comparison of the nifedipine gastrointestinal therapeutic system and long-acting propranolol in patients with mild to moderate systemic hypertension receiving diuretics. A preliminary experience. American Journal of Medicine 83 (Suppl. 6B): 15–19, 1987
Frishman WH, Garofalo JL, Rothschild A, Rothschild M, Greenberg SM, et al. The nifedipine gastrointestinal therapeutic system in the treatment of hypertension. American Journal of Cardiology 64: 65F-69F, 1989
Fujii S, Matsumura S, Nakayama H, Andou S, Yoshizaki Y, et al. Effect of long-term treatment with slow-release nifedipine on glucose homeostasis in hypertensive-diabetic patients. Japanese Pharmacology and Therapeutics 18: 2127–2133, 1990
Gavras I, Mulinari R, Gavras H, Higgins Jr JT, Reeves RL, et al. Antihypertensive effectiveness of the nifedipine gastrointestinal therapeutic system. American Journal of Medicine 83 (Suppl. 6B): 20–23, 1987
Gerstenblith G, Ouyang P, Achuff SC, Bulkley BH, Becker LC, et al. Nifedipine in unstable angina. A double-blind, randomized trial. New England Journal of Medicine 306: 885–889, 1982
Gibaldi M. Food increases the absorption of another retinoid and of prolonged-release nifedipine. Perspectives in Clinical Pharmacy 8: 22, 1990
Gilchrist NL, Nicholls MG, Ewer TC, Livesey JH, Sainsbury R. A comparison of long acting nifedipine and enalapril in elderly hypertensives: a randomised, single-blind, cross-over study. Journal of Human Hypertension 2: 33–39, 1988
Gill JS, Al-Hussary N, Zezulka AV, Pasi KJ, Atkins TW, et al. Effect of nifedipine on glucose tolerance, serum insulin, and serum fructosamine in diabetic and nondiabetic patients. Clinical Therapeutics 9: 304–310, 1987
Ginsburg R, Lamb IH, Schroeder JS, Hu M, Harrison DC. Randomized double-blind comparison of nifedipine and isosorbide dinitrate therapy in variant angina pectoris due to coronary artery spasm. American Heart Journal 103: 44–48, 1982
Giugliano D, Torella R, Cacciapuoti F, Gentile S, Verza M, et al. Impairment of insulin secretion in man by nifedipine. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 18: 395–398, 1980
Giuntoli F, Rossi A, Scalabrino A, Natali A, Saba P, et al. Antihypertensive and metabolic effects of long-term treatment with nifedipine (Adalat®). Clinical Trials Journal 22: 231–238, 1985
Goldstein MR. Nifedipine and coronary artery disease. Lancet 336: 172, 1990
Gottlieb SO, Brinker JA, Mellits ED, Achuff SC, Baughman KL, et al. Effect of nifedipine on the development of coronary bypass graft stenoses in high-risk patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Circulation 80 (Suppl. II): 228, No. 4, 1989
Gotto Jr AM. Calcium channel blockers and the prevention of atherosclerosis. American Journal of Hypertension 3: 342S–346S, 1990
Greaves MW, Dowd PM, Hawk JLM. Dermatopharmacology: drugs around the corner. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 19: 323–329, 1988
Grunwald Z. Painful edema, erythematous rash, and burning sensation due to nifedipine. Drug Intelligence and Clinical Pharmacy 16: 492, 1982
Grupo de Trabajo de Nifedipina Retardada. An open study to evaluate the efficacy and tolerability of sustained-release nifedipine in the treatment of mild to moderate essential hypertension. Medicina Clinica 91: 493–495, 1988
Guazzi MD, De Cesare N, Galli C, Tamborini G, et al. Nitrendipine vs. long-acting nifedipine in mild, moderate and severe hypertension. Angiology 37: 508–518, 1986
Guazzi MD, Fiorentini C, Olivari MT, Bartorelli A, Necchi G, et al. Short and long-term efficacy of a calcium-antagonistic agent (nifedipine) combined with methyldopa in the treatment of severe hypertension. Circulation 61: 913–919, 1980
Hall-Craggs M, Light PD, Peters RW. Development of immune complex nephritis during treatment with the calcium channel-blocking agent nifedipine. Human Pathology 15: 691–694, 1984
Hamann SR, Kaltenborn KE, McAllister Jr RG. Nifedipine-pro-pranolol interaction: dependence of cardiovascular effects on plasma drug concentrations. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 10: 182–189, 1987
Hamann SR, McAllister Jr RG. Measurement of nifedipine in plasma by gas-liquid chromatography and electron-capture detection. Clinical Chemistry 29: 158–160, 1983
Harding JJ, van Heyningen R. Drugs, including alcohol, that act as risk factors for cataract, and possible protection against cataract by aspirin-like analgesics and cyclopenthiazide. British Journal of Ophthalmology 72: 809–814, 1988
Hasebe N, Fujikane T, Watanabe M, Matsuhashi H, Kawamura Y, et al. A case of acute respiratory failure precipitated by long-acting nifedipine. Kokyu to Junkan 36: 1255–1259, 1988
Hayashi H, Takumi K, Ishikawa T, Yabe S, Ohsugi S, et al. Limitation of myocardial ischemic injury by nifedipine in patients with acute myocardial infarction evaluated by body surface mapping. Abstract. European Heart Journal 5 (Suppl. 1): 221, 1984
Heagerty AM, Swales JD. A double-blind randomized cross-over study of the efficacy and tolerability of nifedipine and nitrendipine in the treatment of mild to moderate hypertension. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 27: 411–416, 1989
Heagerty AM, Swales J, Baksi A, Maclean D, Saltissi S, et al. Nifedipine and atenolol singly and combined for treatment of essential hypertension: comparative multicentre study in general practice in the United Kingdom. British Medical Journal 296: 468–472, 1988
Henderson AF, Costello JF. The effect of nifedipine on bronchial reactivity to inhaled histamine and methacholine: a comparative study in normal and asthmatic subjects. British Journal of Diseases of the Chest 82: 374–381, 1988
Henry M, Wehrlen M, Pelletier B, Capron M-H. Spironolactone versus nifedipine in essential hypertension. American Journal of Cardiology 65: 36K–38K, 1990
Heyman SN, Heyman A, Halperin I. Diabetogenic effect of nifedipine. DICP, Annals of Pharmacotherapy 23: 236–237, 1989
Hiramatsu K, Yamagishi F, Kubota T, Yamada T. Acute effects of the calcium antagonist, nifedipine, on blood pressure, pulse rate, and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in patients with essential hypertension. American Heart Journal 104: 1346–1350, 1982
Hirasawa K, Shen WF, Kelley DT, Roubin G, Tateda K, et al. Effect of food ingestion on nifedipine absorption and haemo-dynamic response. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 28: 105–107, 1985
Hofmann F, Nastainczyk W, Rohrkasten A, Schneider T, Sieber M. Regulation of the L-type calcium channel. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 8: 393–398, 1987
Horster FA. Pharmacokinetics of nifedipine-14 C in man. 2nd International Adalat Symposium, pp. 124–127, 1975
Houston MC, Olafsson L, Burger MC, Lichtenstein MJ. Effects of nifedipine gits and atenolol monotherapy on serum lipids in mild to moderate hypertension. Clinical Research 38: 542A, 1990
Hoyo-Vadillo C, Castaneda-Hernández G, Herrera JE, Vidal-Gárate J, Moreno-Ramos A, et al. Pharmacokinetics of nifedipine slow release tablet in Mexican subjects: further evidence for an oxidation polymorphism. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 29: 816–820, 1989
Ihenacho HNC, Ikeh VO, Ugwu EC, Offiah EC. Nifedipine in the treatment of hypertension in blacks: a double-blind placebo-controlled trial in Nigerian hypertensives. Current Therapeutic Research 40: 196–202, 1986
Ishiguro M, Hirano T, Watanabe S, Arakawa M. Hemodynamic effects of nifedipine slow-release tablets in patients with essential hypertension. Current Therapeutic Research 46: 529–539, 1989
Isles CG, Johnson AOC, Milne FJ. Slow release nifedipine and atenolol as initial treatment in blacks with malignant hypertension. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 21: 377–383, 1986
Jackson SHD, Shah K, Debbas NMG, Johnston A, Peverel-Cooper CA, et al. The interaction between i.v. theophylline and chronic oral dosing with slow release nifedipine in volunteers. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 21: 389–392, 1986
Jee LD, Opie LH. Acute hypotensive response to nifedipine added to prazosin in treatment of hypertension. British Medical Journal 287: 1514, 1983
Jelen-Esselborn S, Blobner M. Potentiation of nondepolarizing muscle relaxants by nifedipine during isoflurane anesthesia. Anaesthesist 39: 173–178, 1990
Kallenberg CGM, Wouda AA, Kuitert JJ, Tijssen J, Wesseling H. Nifedipine in Raynaud’s phenomenon: relationship between immediate, short term and longterm effects. Journal of Rheumatology 14: 284–290, 1987
Kato K, Iinuma H, Motomiya T, Hosoda S, Kurita A, et al. Evaluation of antianginal effect of nisoldipine (BAY k 5552) in patients with angina of effort using a treadmill exercise test. Rinsho Iyaku 4: 1989–2016, 1988
Kay R, Blake J, Rubin D. Possible coronary spasm rebound to abrupt nifedipine withdrawal. Correspondence. American Heart Journal 103: 308, 1982
Kazumi T, Yoshino G, Masuda T, Ishida Y, Yoshida M, et al. Long-term effects of nifedipine treatment on blood pressure, lipoproteins, apolipoproteins, and glycemic control in diabetic patients with hypertension. Current Therapeutic Research 48: 246–252, 1990
Kazumi T, Yoshino G, Okutani T, Kato J-I, Kasama T, et al. Plasma lipoprotein and apolipoprotein concentrations and glycemic control during short-term treatment with nifedipine in hypertensive patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Current Therapeutic Research 46: 951–958, 1989
Keidar S, Binenboim C, Palant A. Muscle cramps during treatment with nifedipine. British Medical Journal 285: 1241–1242, 1982
Kiowski W, Bertel O, Erne P, Bolli P, Hulthén L, et al. Hemodynamic and reflex responses to acute and chronic antihypertensive therapy with the calcium entry blocker nifedipine. Hypertension 5 (Suppl. I): 70–74, 1983
Kirch W, Hoensch H, Ohnhaus EE, Janisch HD. Ranitidin-Nifedipin Interaktion. Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift 109: 1223, 1984
Kirch W, Janisch HD, Heidemann H, Ramsch K, Ohnhaus EE. Einfluss von Cimetidin und Ranitidin auf pharmakokinetik und antihypertensiven Effekt von Nifedipin. Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift 108: 1757–1761, 1983
Kirch W, Ohnhaus EE, Hoensch H, Janisch HD. Ranitidine increases bioavailability of nifedipine. Abstract. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 37: 204, 1985
Kivity S, Ganem R, Greif J, Topilsky M. The combined effect of nifedipine and sodium cromoglycate on the airway response to inhaled hypertonic saline in patients with bronchial asthma. European Respiratory Journal 2: 513–516, 1989
Kivity S, Yarchovsky J. Relapsing anaphylaxis to bee sting in a patient treated with a beta-blocker and Ca blocker. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 85: 669–670, 1990
Kleinbloesem CH, van Brummelen P, Danhof M, Faber H, Urquhart J, et al. Rate of increase in the plasma concentration of nifedipine as a major determinant of its haemodynamic effects in humans. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 41: 26–30, 1987
Kleinbloesem CH, van Brummelen P, Faber H, Danhof M, Vermeulen NPE, et al. Variability in nifedipine pharmacokinetics and dynamics: a new oxidation polymorphism in man. Biochemical Pharmacology 33: 3721–3724, 1984c
Kleinbloesem CH, van Brummelen P, van de Linde JA, Voogd PJ, Breimer DD. Nifedipine: kinetics and dynamics in healthy subjects. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 35: 742–749, 1984a
Kleinbloesem CH, van Harten J, van Brummelen P, Breimer DD. Liquid Chromatographic determination of nifedipine in plasma and of its main metabolite in urine. Journal of Chromatography 308: 209–216, 1984b
Kondo S, Kuchiki A, Yamamoto K, Akimoto K, Takahashi K, et al. Identification of nifedipine metabolites and their determination by gas chromatography. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 28: 1–7, 1980
Kozjek F, Primozic S, Mrhar A, Karba R, Raemsch KD, et al. The bioavailability of oral nifedipine formulations: a statistical and simulation approach. Biopharmaceutics and Drug Disposition 8: 23–35, 1987
Krakoff LR, Bravo EL, Tuck ML, Friedman CP, the Modern Approach to the Treatment of Hypertension (MATH) Study Group. Nifedipine gastrointestinal therapeutic system in the treatment of hypertension: results of a multicenter trial, American Journal of Hypertension 3: 318S–325S, 1990
Kroneberg G. Pharmacology of nifedipine (Adalat). 1st International Nifedipine Adalat Symposium, pp. 3–10, 1975
Kroneberg G, Krebs R. Pharmacology of nifedipine. 4th International Adalat Symposium, pp. 14–24, 1980
Kurnik PB, Tiefenbrunn AJ, Ludbrook PA. The dependence of the cardiac effects of nifedipine on the responses of the peripheral vascular system. Circulation 69: 963–972, 1984
Lamaison D, Abrieu V, Fialip J, Dumas R, Andronikoff M, et al. Acute intestinal occlusion and calcium antagonists. Therapie 44: 201–202, 1989
Lederballe Pedersen O, Christensen CK, Mikkelsen E, Ramsch KD. Relationship between the antihypertensive effect and steady state plasma concentration of nifedipine given alone or in combination with a beta adrenoceptor blocking agent. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 18: 287–293, 1980a
Lederballe Pedersen O, Christensen NJ, Rämsch KD. Comparison of acute effects of nifedipine in normotensive and hypertensive man. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 2: 357–366, 1980b
Lederballe Pedersen O, Mikkelsen E. Acute and chronic effects of nifedipine in arterial hypertension. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 14: 375–381, 1978
Lederballe Pedersen O, Mikkelsen E, Christensen NJ, Kornerup HJ, Pedersen EB. Effect of nifedipine on plasma renin, aldosterone and catecholamines in arterial hypertension. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 15: 235–240, 1979
Lederman D, Lumerman H, Reuben S, Freedman PD. Gingival hyperplasia associated with nifedipine therapy. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology 57: 620–622, 1984
Lehtonen A, Tanskanen A, Lento H, Jarvensiven P. The effect of nifedipine on plasma lipids in patients with essential hypertension. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, Therapy and Toxicology 24: 357–358, 1986
Leier CV, Patrick TJ, Hermiller J, Dalpiaz Pacht K, Huss P, et al. Nifedipine in congestive heart failure: effects on resting and exercise hemodynamics and regional blood flow. American Heart Journal 108: 1461–1468, 1984
Leisten L, Kuhlmann J, Ebner F. Chapter II: side effects and pharmacodynamic interactions. In Kiebs (Ed.) Treatment of cardiovascular diseases with Adalat® (nifedipine), pp. 279–299, Schattauer-Verlag, 1986
Leonetti G, Cuspidi C, Sampieri L, Terzoli L, Zanchetti A. Comparison of cardiovascular, renal, and humoral effects of acute administration of two calcium channel blockers in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 4 (Suppl. 3): 319–324, 1982
Lette J, Gagnon R-M, Lemire JG, Morissette M. Rebound of vasospastic angina after cessation of long-term treatment with nifedipine. Canadian Medical Association Journal 130: 1169–1174,1984
Leucuta SE. The kinetics of nifedipine release from porous hydrophilic matrices and the pharmacokinetics in man. Pharmazie 43: 845–848, 1988
Lewis G, Ames R, Halperin A, Reeves R, Rosenbaum R, et al. Antihypertensive efficacy of nifedipine in a novel delivery system: correlation with serum nifedipine levels. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 45: 184, 1989a
Lewis GP, Ames RP, Halperin AK, Reeves RL, Rosenbaum RW, et al. Nifedipine gastrointestinal therapeutic system (NGITS) in patients with mild essential hypertension: therapeutic effects of a novel delivery system. American Journal of Hypertension 2: 18A, 1989b
Lewis JG. Adverse reactions to calcium antagonists. Drugs 25: 196–222, 1983
Lichtlen PR. Nifedipine and coronary artery disease. Lancet 336: 173–174, 1990
Lichtlen PR, Hugenholtz PG, Rafflenbeul W, Hecker H, Jost S. et al. Retardation of angiographic progression of coronary artery disease by nifedipine. Results of the International Nifedipine Trial on Antiatherosclerotic Therapy (INTACT). Lancet 335, 1109–1113,1990a
Lichtlen PR, Hugenholtz PG, Rafflenbeul W, Hecker H, Jost S, et al. Retardation of coronary artery disease in humans by the calcium-channel blocker nifedipine: results of the Intact study (International Nifedipine Trial on Antiatherosclerotic Therapy). Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy 4: 1047–1068, 1990b
Lichtlen PR, Rafflenbeul W, Amende R, Simon R, Reil G. The influence of Ca2+ -entry blockers on hemodynamics and coronary blood flow, and its importance for the treatment of angina pectoris. In Godfraind et al. (Eds) Calcium entry blockers in cardiovascular and cerebral dysfunction, pp. 161–179, Martinus Nijhoff, Boston, 1984
Lichtor T. Antiatherosclerotic activity of nifedipine in primates. Abstract. Cardiovascular Drug Reviews 6: 339, 1988
Littler WA for a UK Multicentre Hospital Group. Comparison of felodipine with nifedipine as additions to metoprolol in the treatment of hypertension. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 15(Suppl. 4): 99, 1990
Loaldi A, Polese A, Montorsi P, De Cesare N, Fabbiocchi F, et al. Comparison of nifedipine, propranolol and isosorbide dinitrate on angiographic progression and regression of coronary arterial narrowings in angina pectoris. American Journal of Cardiology 64: 433–439, 1989
Lydtin H, Lohmöller G, Lohmöller R, Walter I. Hemodynamic studies on nifedipine in man. 1st International Nifedipine Adalat Symposium, pp. 97–106, 1975
Macdonald JB. Muscle cramps during treatment with nifedipine. British Medical Journal 285: 1744, 1982
Maclean D, Mitchell ER. Felodipine compared to nifedipine in hypertension. Angiology 37: 416–417, 1986
Maclean D, Mitchell ET, Coulson RR, Fitzsimons TJ, McDevitt DG. Atenolol-nifedipine combinations compared to atenolol alone in hypertension: efficacy and tolerability. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 25: 425–431, 1988
Macphee GJA, Dutton M, Lennox IM, Williams BO. Low-dose nifedipine retard in elderly hypertensive patients. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Gerontology 11: 115–129, 1989
Malamet R, Wise RA, Ettinger WH, Wigley FM. Nifedipine in the treatment of Raynaud’s phenomenon. Evidence for inhibition of platelet activation. American Journal of Medicine 78: 602–608, 1985
Manga P, Vythilingum S. Unstable angina precipitated by nifedipine. South African Medical Journal 66: 144, 1984
Marigliano V, Ariani A, Santilli D, Meliffi L, Cacciafesta M, et al. Long-term captopril treatment in elderly hypertensive patients. Current Therapeutic Research 46: 858–865, 1989
Marley JE, Curram JB. General practice data derived tolerability assessment of antihypertensive drugs. Journal of International Medical Research 17: 473–478, 1989
Martsevich SY, Metelitsa VI, Rumiantsev DO, Piotrovskii VK, Slastnikova ID, et al. Development of tolerance to nifedipine in patients with stable angina pectoris. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 29: 339–346, 1990
Matlib MA. Relaxation of potassium chloride-induced contractions by amlodipine and its interaction with the 1,4-dihydropyridine-binding site in pig coronary artery. American Journal of Cardiology 64: 511–571, 1989
Mayhew S. Comparison of the efficacy and long-term tolerability of a combination of atenolol and nifedipine with atenolol alone in the treatment of hypertension. British Journal of Clinical Practice 44: 280–282, 1990
McLeay RAB, Stallard TJ, Watson RDS, Littler WA. The effect of nifedipine on arterial pressure and reflex cardiac control. Circulation 67: 1084–1090, 1983
Mignot G, Bernard G, Chichmanian RM. Nifedipine and nocturia. Lancet 2: 857, 1988
Millar JA, Reid JL. Decreased vascular and adrenal responses to angiotensin II after administration of nifedipine. 5th International Adalat Symposium, pp. 122–132, 1983
Mimran A, Ribstein J. Effect of chronic nifedipine in patients inadequately controlled by a converting enzyme inhibitor and a diuretic. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 7 (Suppl. 1): 92–95, 1985
Monsen L, Moisey D, Gaffney M, Fischer J, the Nifedipine GITS Study Group. Consistent blood pressure reduction without loss of diurnal variability with once-daily nifedipine GITS treatment. American Journal of Hypertension 3: 114A, 1990
Murphy C, McNamara C, Mohanty PK. The antihypertensive effects of nifedipine (GITS) in mild to moderate hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 2: 28A, 1989
Murphy MB, Scriven AJI, Dollery CT. Role of nifedipine in treatment of hypertension. British Medical Journal 287: 257–259, 1983
Myers MG, Raemsch KD. Comparative pharmacokinetics and antihypertensive effects of the nifedipine tablet and capsule. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 10 (Suppl. 10): 76–78, 1987
Mysliwiec M, Rydzewski A, Bulhak W. Calcium antagonist withdrawal syndrome. British Journal 286: 1898, 1983
Nakanishi T, Nishimura M, Kubota S, Hirabayashi M. Effect of nifedipine retard tablets in hypertension: evaluation using a noninvasive portable automatic sphygmomanometer and a new method of assessment. Current Therapeutic Research 46: 681–691, 1989
Nehring J, Camm AJ. Calcium antagonist withdrawal syndrome. British Medical Journal 286: 1057, 1983
Nobile-Orazio E, Sterzi R. Cerebral ischaemia after nifedipine treatment. British Medical Journal 283: 948, 1981
Nyberg GF, Nilsson JE, Blomqvist N, Prager G. Double blind cross-over comparison of an extended release formulation and conventional nifedipine capsules in angina pectoris patients. Abstract no. 3. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology 17 (Suppl. 16): 1990
Oates NS, Feher MD, Perry HE, Schmid BJ, Sever PS, et al. Influence of quinidine on nifedipine plasma pharmacokinetics. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 25: 675P, 1988
Odar-Cederlöf I, Anderson P, Bondesson U. Nifedipine as an antihypertensive drug in patients with renal failure — pharmacokinetics and effects. Journal of Internal Medicine 227: 329–337, 1990
Olutade BO, Hall WD, Hildebrandt K, et al. Efficacy of nifedipine GITS vs hydrochlorthiazide in the management of moderate hypertension in the black hypertensive. Southern Medical Journal 82: 121, 1989
Onoda JM, Nelson KK, Jones CL, Chen B, Piechocki MP, et al. Combination chemotherapy with the calcium channel blocker nifedipine and cisplatin. Investigational New Drugs 7: 443, 1989
Oren R, Polak A, Goldenhersh M, Heyman A, Naparstek Y. Nifedipine-induced nonthrombocytopenic purpura. DICP: Annals of Pharmacotherapy 23: 88, 1989
Oviasu VO, Obasohan AO. Use of nifedipine in the management of systemic hypertension in Nigerian patients. Current Therapeutic Research 39: 455–459, 1986
Pabst G, Lutz D, Molz KH, Dahmen W, Jaeger H. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of three different galenic nifedipine preparations. Arzneimittel-Forschung — Drug Research 36: 256–260, 1986
Palma-Aguirre JA, Rosas-Alcazar G, Rodriguez JM, Leon-Urrea F, Montoya-Cabrera MA. Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of nifedipine administered by different routes in healthy volunteers. Archivos de Investigacion Medica 20: 129–135, 1989
Palmer A, Fletcher A, Hamilton G, Muriss S, Bulpitt C. A comparison of verapamil and nifedipine on quality of life. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 30: 365–370, 1990
Palumbo G, Barantani E, Pozzi F, Azzolini V, Gronda D. et al. Long-term nifedipine treatment and glucose homeostasis in hypertensive patients. Current Therapeutic Research 43: 171–179, 1988
Pancera P, Arosio E, Arcaro G, Priante F, Montesi G, et al. Haemodynamic parameters in hypertensive patients: changes induced by lacidipine and nifedipine. Journal of Hypertension 7 (Suppl. 6): 284–285, 1989
Parent R, Chiasson JL, Larochelle P. Hemodynamic and endocrine effects of acute and chronic administration of nifedipine. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 29: 59–64, 1989
Pasanisi F, Ferrara AL, Iovine C, Mancini M. Effects of nifedipine on insulin secretion and plasma lipids in hypertensive patients. Current Therapeutic Research 39: 894–899, 1986
Patrick KS. Gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis of plasma nifedipine. Journal of Chromatography 495: 123–130, 1989
Pfisterer M, Müller-Brand J, Burkart F. Combined acebutolol/ nifedipine therapy in patients with chronic coronary artery disease: additional improvement of ischaemic-induced left ventricular dysfunction. American Journal of Cardiology 49: 1259–1266, 1982
Phillips RA, Ardeljan M, Goldman ME, Eison HB, Krakoff LR. Cardiac and hemodynamic adjustments to rapid and sustained blood pressure reduction. American Journal of Hypertension 2: 196S–199S, 1989
Picca M, Azzollini F, Cereda A, Pelosi G. Comparison of the antianginal efficacy of four calcium antagonists and propranolol in stable angina pectoris. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 37: 325–331, 1989
Pitlik S, Manor RS, Lipshitz I, Perry G, Rosenfeld J. Transient retinal ischaemia reduced by nifedipine. British Medical Journal 287: 1845–1846, 1983
Plotkin CN, Eckenbrecht PD, Waldo DA. Consecutive cardiac arrests on induction of anesthesia associated with nifedipine-induced carotid sinus hypersensitivity. Anesthesia and Analgesia 68: 402–405, 1989
Potter JF, Beevers DG. Comparison of nifedipine and captopril as third-line agents in hypertensive patients uncontrolled with beta-blocker and diuretic therapy. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 27: 410–414, 1987
Poulter N, Thompson AV, Sever PS. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial to investigate the additive hypotensive effect of a diuretic (mefruside) to that produced by nifedipine. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 10 (Suppl. 10): 53–55, 1987
Qureshi S, Laganière S, McGilveray IJ, Lacasse Y, Caillé G. Ni-fedipine-alcohol interaction. Journal of the American Medical Association 264: 1660–1661, 1990
Quyyumi AA, Wright CM, Mockus LJ, Fox KM. How important is a history of chest pain in determining the degree of ischaemia in patients with angina pectoris? British Heart Journal 54: 22–26, 1985
Raemsch KD, Sommer J. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of nifedipine. Hypertension 5: II18–1124, 1983
Raffestin B, Boillot J, Derrieux C, Comoy E, Martre H. Exercise and the calcium-blocker, nifedipine, in normal subjects. Abstract. Scientific Meeting of the European Society for Clinical Investigation, Milan 17–19 April, 1984
Ramon Y, Behar S, Kishon Y, Engelberg IS. Gingival hyperplasia caused by nifedipine - a preliminary report. International Journal of Cardiology 5: 195–204, 1984
Reams GP, Hamory A, Lau A, Bauer JH. Effect of nifedipine on renal function in patients with essential hypertension. Hypertension 11: 452–456, 1988
Rees-Jones DI, Oliver IM. A fixed combination of atenolol 50mg and nifedipine 20mg in the long term treatment of hypertension. Acta Therapeutica 16: 151–162, 1990
Reitberg DP, Love SJ, Quercia GT, Zinny MA. Effect of food on nifedipine pharmacokinetics. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 42: 72–75, 1987
Resnick LM, Sealey JE, Laragh JH. Calcium metabolism and the renin-aldosterone system determine the acute blood pressure response to calcium channel blockade. Circulation 66 (Suppl. 2): II107, 1982
Reynolds NJ, Jones SK, Crossley J, Harman RRM. Exfoliative dermatitis due to nifedipine. British Journal of Dermatology 121: 401–404, 1989
Rice KR, Gervino E, Jarisch WR, Stone PH. Effects of nifedipine on myocardial perfusion during exercise in chronic stable angina pectoris. American Journal of Cardiology 65: 1097–1101, 1990
Richardson PJ, Meany B, Breckenridge AM, Grimmer SFM, Johnston GD, et al. Lisinopril in essential hypertension: a six month comparative study with nifedipine. Journal of Human Hypertension 1: 175–179, 1987
Richter JE, Dalton CB, Bradley LA, Castell DO. Oral nifedipine in the treatment of noncardiac chest pain in patients with the nutcracker esophagus. Gastroenterology 93: 21–28, 1987
Rimoy GH, Idle JR, Bhaskar NK, Rubin PC. The influence of food on the pharmacokinetics of ‘biphasic’ nifedipine at steady state in normal subjects. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 28: 612–615, 1989
Robertson DRC, Waller DG, Renwick AG, George CF. Age-related changes in the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of nifedipine. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 25: 297–305, 1988
Robinson BF, Dobbs RJ, Kelsey CR. Effects of nifedipine on resistance vessels, arteries and veins in man. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 10: 433–438, 1980
Robles NR, Lobos JM, Seguido P, Lahoz F. Tolerability of sustained release nifedipine. Medicina Clinica 92: 438, 1989
Romeo R, Sorace R, Alessandria I, Finocchiaro ML, Raciti GA, et al. Efficacy of nifedipine and nicardipine in hypertensive patients at rest and during stress testing. Current Therapeutic Research 47: 314–320, 1990
Rotmensch HH, Roth A, Liron M, Rubinstein A, Gefel A, et al. Lymphocyte sensitisation in nifedipine-induced hepatitis. British Medical Journal 281: 976–977, 1980
Rubin PC, Butters L, McCabe R. Nifedipine and platelets in preeclampsia. American Journal of Hypertension 1: 175–177, 1988
Rustin MHA, Newton JA, Smith NP, Dowd PM. The treatment of chilblains with nifedipine: the results of a pilot study, a double-blind placebo-controlled randomized study and a long-term open trial. British Journal of Dermatology 120: 267–275, 1989
Saano V, Raatikainen O, Paronen P, Komulainen H. Pharmacokinetics and acute side-effects of nifedipine given as slow-release tablets or liquid-filled capsules. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 10: 247–254, 1989
Salvetti A, Innocenti PF, Iardella M, Pambianco F, Saba GC, et al. Captopril and nifedipine interactions in the treatment of essential hypertensives: a crossover study. Journal of Hypertension 5 (Suppl. 4): 139–142, 1987
Sando H, Katagiri H, Okada M, Shoda R, Arai Y, et al. The effect of nifedipine and nicardipine on glucose tolerance, insulin and C-peptide. Diabetes 32: 66A, 1983
Sasaki J, Arakawa K. Effect of nifedipine on serum lipids, lipoproteins, and apolipoproteins in patients with essential hypertension. Current Therapeutic Research 41: 845–851, 1987
Schanzenbächer P, Deeg P, Liebau G, Kochsiek K. Paradoxical angina after nifedipine: angiographic documentation. American Journal of Cardiology 53: 345–346, 1984
Schnapp P. Acute natriuretic effect of nifedipine in elderly males with essential hypertension. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, Therapy and Toxicology 27: 442–444, 1989
Schnapp P, Hermann H, Cernak P, Kahay J. Nifedipine monotherapy in the hypertensive elderly: a placebo-controlled clinical trial. Current Medical Research and Opinion 10: 407–413, 1987
Schulte K-L, Meyer-Sabellek WA, Haertenberger A, Thiede H-M, Roecker L, et al. Antihypertensive and metabolic effects of diltiazem and nifedipine. Hypertension 8: 859–865, 1986
Schwartz A. Calcium antagonists: review and perspective on mechanism of action. American Journal of Cardiology 64: 31–91, 1989
Schwartz JB, Upton RA, Lin ET, Williams RL, Benét LZ. Effect of cimetidine or ranitidine administration on nifedipine pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics 43: 673–680, 1988
Schwartz M, Naschitz JE, Yeshurun D, Sharf D. Oral nifedipine in the treatment of hypertensive urgency: cerebrovascular accident following a single dose. Archives of Internal Medicine 150: 686–687, 1990
Scoble JE, Uff JS, Eastwood JB. Nifedipine nephritis. Correspondence. Clinical Nephrology 21: 302, 1984
Seuter F. Antiatherosclerotic effects of nifedipine and nitrendipine in rats with experimental atherosclerosis. Cardiovascular Drug Reviews 6: 337, 1988
Shettigar UR, Loungani R. Adverse effects of sublingual nifedipine in acute myocardial infarction. Critical Care Medicine 17: 196–197, 1989
Singer DRJ, Markandu ND, Shore AC, MacGregor GA. Captopril and nifedipine in combination for moderate to severe essential hypertension. Hypertension 9: 629–633, 1987
Singh BN. The mechanism of action of calcium antagonists relative to their clinical applications. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 21: 109S–121S, 1986
Singlas E, Martre H, Taburet A-M, Jacobs C, Sari R. Effet de l’hemodialyse sur les taux plasmatiques de nifedipine. Presse Médicale 13: 943–944, 1984
Sirnes PA, Overskeid K, Pedersen TR, Bathen J, Drivenes A, et al. Evolution of infarct size during the early use of nifedipine in patients with acute myocardial infarction: the Norwegian nifedipine multicenter trial. Circulation 70: 638–644, 1984
Smith SR, Kendall MJ, Lobo J, Beerahee A, Jack DB, et al. Ranitidine and cimetidine; drug interactions with single dose and steady-state nifedipine administration. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 23: 311–315, 1987b
Smith SR, Wiggins J, Stableforth DE, Skinner C, Kendall MJ. Effect of nifedipine on serum theophylline concentrations and asthma control. Thorax 42: 794–796, 1987a
Sooriyamoorthy M, Gower DB, Eley BM. Androgen metabolism in gingival hyperplasia induced by nifedipine and cyclosporin. Journal of Periodontol Research 25: 25–30, 1990
Soret Ph, Waeber B, Lüscher TF. Efficacy and tolerability of isradipine and sustained release nifedipine in the management of hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 3: 119A, 1990
Sorkin EM, Clissold SP, Brogden RN. Nifedipine: a review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy, in ischaemic heart disease, hypertension and related cardiovascular disorders. Drugs 30: 182–274, 1985
Soward AL, Vanhaleweyk GLJ, Serruys PW. The haemodynamic effects of nifedipine, verapamil and diltiazem in patients with coronary artery disease: a review. Drugs 32: 66–101, 1986
Spital A, Scandling JD. Nifedipine in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Archives of International Medicine 143: 2025, 1983
Stanley NN, Thirkettle JL, Varma MPS, Larkin H, Heath ID. Efficacy and tolerability of atenolol, nifedipine and their combination in the management of hypertension. Drugs 35 (Suppl. 4): 29–35, 1988
Stessman J, Leibel B, Yagil Y, Eliakim R, Ben-Ishay D. Nifedipine in the treatment of hypertension in the elderly. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 25: 193–196, 1985
Stone PH, Muller JE, Turi ZG, Geltman E, Jaffe AS, et al. Efficacy of nifedipine therapy in patients with refractory angina pectoris: significance of the presence of coronary vasospasm. American Heart Journal 106: 644–652, 1983
Streifler J, Wittenberg C, Rosenfeld JB. Effects of different single doses of nifedipine on blood pressure, renal function, plasma aldosterone and renin in hypertensive subjects. 5th International Adalat Symposium, pp. 164–174, 1983
Strickland WG, Blackmore PF, Exton JH. Nifedipine and alpha-adrenergic blockade. New England Journal of Medicine 307: 757–758, 1982
Svetkey LP, Weinberger MH, Gavras H, Gavras I, Brown TS, et al. Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of twice-daily nifedipine as a step-2 agent in mild essential hypertension. Journal of Clinical Hypertension 3: 579–588, 1987
Swanson DR, Barclay BL, Wong PSL, Theeuwes F. Nifedipine gastrointestinal therapeutic system. American Journal of Medicine 83 (Suppl. 6B): 3–9,1987
Taburet AM, Singlas E, Colin J-N, Benzet O, Thibonnier M, et al. Pharmacokinetic studies of nifedipine tablet. Correlation with antihypertensive effects. Hypertension 5: II29–II33, 1983
Takahashi S, Nakai T, Fujiwara R, Kutsumi Y, Tamai T, et al. Effectiveness of long-acting nifedipine in pheochromocytoma. Japanese Heart Journal 30: 751–757, 1989
Terry RW. Nifedipine therapy in angina pectoris: evaluation of safety and side effects. American Heart Journal 104: 681–689, 1982
Thiery J. The beneficial influence of nifedipine on the regression of cholesterol-induced atherosclerosis in rabbits. Abstract. Cardiovascular Drug Reviews 6: 338–339, 1988
Tonolo G, Troffa C, Pazzola A, Melis MG, Manunta P, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of a new once daily nifedipine formulation in mild to moderate essential hypertension. Current Therapeutic Research 47: 76–80, 1990
Traube M, Dubovik S, Lange RC, McCallum RW. The role of nifedipine therapy in achalasia: results of a randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled study. American Journal of Gastroenterology 84: 1259–1262, 1989
Triggle DJ. Calcium antagonists in atherosclerosis: a review and commentary. Cardiovascular Drug Reviews 6: 320–335, 1989
Ueno K, Kawashima S, Uemoto K, Ikada T. Effect of food on nifedipine sustained-release preparation. DICP, Annals of Pharmacotherapy 23: 662–665, 1989
Verheught FWA. Nifedipine and coronary artery disease. Lancet 336: 172, 1990
Vetrovec GW. Once-daily therapy for angina pectoris with nifedipine gastrointestinal therapeutic system. Dosing and clinical efficacy. American Journal of Medicine 86 (Suppl. 1A): 28–32, 1989
Vinceneux Ph, Canal M, Domart Y, Roux A, Cascio B, et al. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interactions between nifedipine and propranolol or betaxolol. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, Therapy and Toxicology 24: 153–158, 1986
von Arnim T, Erath A. Nitrates and calcium antagonists for silent myocardial ischemia. American Journal of Cardiology 61: 1SE–ISE, 1988
van Zwieten PA. Vascular effects of calcium antagonists: implications for hypertension and other risk factors for coronary heart disease, American Journal of Cardiology 64: 1171–1211, 1989
Wallace WA, Wellington KL, Murphy GW, Liang C-S. Comparison of antianginal efficacies and exercise hemodynamic effects of nifedipine and diltiazem in stable angina pectoris. American Journal of Cardiology 63: 414–418, 1989
Waller DG, Challenor VF, Francis DA, Roath OS. Clinical and Theological effects of nifedipine in Raynaud’s phenomenon. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 22: 449–454, 1986
Waller DG, Ren wick AG, Gruchy BS, George CF. The first pass metabolism of nifedipine in man. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 18: 951–954, 1984
Walley TJ, Woods KL, Barnett DB. The effects of intravenous and oral nifedipine on ex vivo platelet function. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 37: 449–452, 1989
Waters D, Lespérance J, Francetich M, Causey D, Théroux P, et al. A controlled clinical trial to assess the effect of a calcium channel blocker on the progression of coronary atherosclerosis. Circulation 82: 1940–1953, 1990
Weber F, Anlauf M. Vasodilation in the vascular bed of skeletal muscle after intravenous nifedipine in normotensives and hypertensives. Journal of Hypertension 7 (Suppl. 6): 286–287, 1989
Weinstein DB, Heider JG. Antiatherogenic properties of calcium antagonists. American Journal of Cardiology 59: 163B-172B, 1987
Welzel D, Burger KJ, Weidinger G. Calcium antagonists as firstline antihypertensive agents: a placebo-controlled, comparative trial of isradipine and nifedipine. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 15 (Suppl. 1): 70–74, 1990
Wilkinson R, Mansy S. A dose finding study of the combination of atenolol and nifedipine in hypertension. Current Medical Research and Opinion 12: 108–113, 1990
Wing LMH, Chalmers JP, West MJ, Bune AJC. Slow-release nifedipine as a single or additional agent in the treatment of essential hypertension — a placebo-controlled crossover study. Clinical and Experimental Hypertension Part A-Theory and Practice A7: 1173–1185, 1985
Winocour PH, Waldek S, Cohen H, Anderson DC, Gordon C. Glycaemic control and exercise tolerance in hypertensive insulin-treated diabetes during nifedipine therapy. British Journal of Clinical Practice 41: 772–778, 1987
Witchitz S, Serradimigni A for the Cooperative Study Group. Lisinopril versus slow-release nifedipine in the treatment of mild to moderate hypertension: a multicentre study. Journal of Human Hypertension 3: 29–33, 1989
Wollersheim H, Berden J, Thien T. Decreased rectal body temperature induced by different vasodilatory drugs. Netherlands Journal of Medicine 34: 189–193, 1989
Woo KS, Pun CO. Long-acting nifedipine versus metoprolol as monotherapy for essential hypertension. A randomized, controlled crossover study. Western Journal of Medicine 152: 149–152, 1990
Yagil Y, Kobrin I, Leibel B, Ben-Ishay, D. Ischémie ECG changes with initial nifedipine therapy of severe hypertension. Correspondence. American Heart Journal 103: 310–311, 1982
Yamasaki M, Morikawa H, Deguchi M, Chui XL, Mizutori M, et al. Treatment of hypertensive pregnant patients with the long-acting preparation of nifedipine. Clinical and Experimen-tal Hypertension B8: 382, 1989
Yokoyama S, Kaburagi T. Clinical effects of intravenous nifedipine on renal function. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 5: 67–71, 1983
Zar MA, Gooptu D. Effect of nifedipine on the contractile responses of human colonic muscle. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 16: 339–340, 1983
Zlotogorski A, Nyska M, Sela M, Nyska A, Gotsman M. Nifedipine-induced gingival hyperplasia: case reports and literature review. Israel Journal of Medical Sciences 25: 453–455, 1989
Zusman R, Christensen D, Federman E, Kochar MS, McCarron D. et al. Comparison of nifedipine and propranolol used in combination with diuretics for the treatment of hypertension. American Journal of Medicine 82 (Suppl. 3B): 37–41, 1987
Zusman RM, Christensen DM, Federman EB, Ruddy TD, Miller DD, et al. Nifedipine, but not propranolol, improves left ventricular systolic and diastolic function in patients with hypertension. American Journal of Cardiology 64: 51F-61F, 1989
Zylber-Katz E, Turetz-Abramovitch M, Koren G, Levy M. Pharmacokinetic interaction between nifedipine and propranolol. Fundamental Clinical Pharmacology 2: 29–35, 1988
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Various sections of the manuscript reviewed by: N. Bittar, Department of Medicine, University of Wisconsin-Madison Medical School, Madison, Wisconsin, USA; D.D. Breimer, Center for Biopharmaceutical Sciences, Sylvius Laboratories, Leiden, The Netherlands; V.F. Challenor, Clinical Pharmacology Group, University of Southampton, Southampton General Hospital, Southampton, England; P.F. Cohn, Cardiology Division, Health Sciences Center, Stonybrook, New York, USA; W.H. Frishman, Montefiore Medical Center, The Jack D. Weiler Hospital of the Albert Einstein College of Medicine Division, Bronx, New York, USA; S. Fujii, Third Department of Internal Medicine, Yamaguchi University School of Medicine, Ube, Yamaguchi, Japan; M.R. Goldstein, Crozer Cottage, Crozer-Chester Medical Center, Chester, Pennsylvania, USA; A.M. Heagerty, University of Leicester School of Medicine, Department of Medicine, Clinical Sciences Building, Leicester Royal Infirmary, Leicester, England; C. Hoyo-Vadillo, Division of Pharmacology, Center for Biopharmaceutical Sciences, Sylvius Laboratories, Leiden, The Netherlands; P.R. Lichtlen, Division of Cardiology, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Federal Republic of Germany; G.P. Reams, Department of Medicine, University of Missouri-Columbia School of Medicine, Medical Sciences Building, Columbia, Missouri, USA; A.G. Renwick, Clinical Pharmacology Group, University of Southampton, Southampton General Hospital, Southampton, England; P.C. Rubin, Department of Therapeutics, University Hospital, Queen’s Medical Centre, Nottingham, England; M.H.A. Rustin, The Royal Free Hospital, Hampstead, London, England; F.W.A. Verbeugt, Academisch Ziekenhuis, Vrije Universiteit, Afdeling Cardiologie, Amsterdam, The Netherlands; D.G. Waller, Clinical Pharmacology Group, University of Southampton, Southampton General Hospital, Southampton, England.
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF03257484.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murdoch, D., Brogden, R.N. Sustained Release Nifedipine Formulations. Drugs 41, 737–779 (1991). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199141050-00006
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199141050-00006