Abstract
-
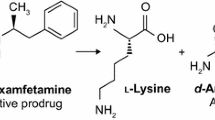
▲ Lisdexamfetamine is an amphetamine prodrug, comprising an l-lysine amino acid covalently bonded to dextroamphetamine (d-amphetamine). Lisdexamfetamine is approved in the US for the treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children aged 6–12 years.
-
▲ Lisdexamfetamine is a therapeutically inactive molecule. After oral ingestion, lisdexamfetamine is hydrolyzed to l-lysine, a naturally occurring essential amino acid, and active d-amphetamine, which is responsible for the activity of the drug.
-
▲ Ina well designed pharmacodynamic study in adult stimulant abusers, 50 or 100mg doses of oral lisdexamfetamine had less likability than d-amphetamine 40mg, suggesting a reduced abuse potential.
-
▲ Through rate-limited hydrolysis in the body, l-lysine is cleaved, gradually releasing pharmacologically active d-amphetamine. The pharmacokinetics of lisdexamfetamine suggest a reduced potential for abuse.
-
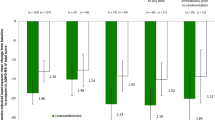
▲ In two well designed trials in children aged 6–12 years with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), the efficacy of lisdexamfetamine was superior to that of placebo in improving symptoms associated with ADHD.
-
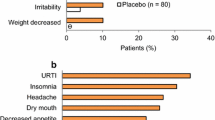
▲ Adverse events with lisdexamfetamine were, in general, mild to moderate in severity and consistent with those commonly reported with amphetamine.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The use of trade names is for product identification purposes only and does not imply endorsement.
References
Buitelaar JK, Montgomery SA, van Zwieten-Boot BJ. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: guidelines for investigating efficacy of pharmacological intervention. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2003 Aug; 13(4): 297–304
Clinical practice guideline: treatment of the school-aged child with attentiondeficit/hyperactivity disorder. American Academy of Pediatrics Subcommittee on Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Committee on Quality Improvement. Pediatrics 2001; 108(4): 1033–44
Kutcher S, Aman M, Brooks SJ, et al. International consensus statement on attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and disruptive behaviour disorders (DBDs): clinical implications and treatment practice suggestions. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2004 Jan; 14(1): 11–28
Biederman J, Krishnan S, Zhang Y, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate (NRP-104) in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a phase III, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, forced-dose, parallel-group study. Clin Ther 2007 Mar; 29(3): 1–14
Solanto MV. Neuropsychopharmacological mechanisms of stimulant drug action in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: a review and integration. Behav Brain Res 1998 Jul; 94(1): 127–52
Connor DF, Steingard RJ. New formulations of stimulants for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: therapeutic potential. CNS Drugs 2004; 18(14): 1011–30
de La Torre R, Farré M, Navarro M, et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics of amfetamine and related substances: monitoring in conventional and non-conventional matrices. Clin Pharmacokinet 2004; 43(3): 157–85
Wilens TE. Drug therapy for adults with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Drugs 2003; 63(22): 2395–411
Jasinski D, Krishnan S. A double-blind, randomized, placebo- and active-controlled, 6-period crossover study to evaluate the likability, safety, and abuse potential of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate (LDX) in adult stimulant abusers [poster]. 2006 US Psychiatric & Mental Health Congress; 2006 Nov 18; New Orleans (LA)
Jasinski D, Krishnan S. Abuse liability of intravenous lisdexamfetamine dimesylate (LDX; NRP104) [poster]. 2006 US Psychiatric and Mental Health Congress; 2006 Nov 17; New Orleans (LA)
Krishnan S, Moncrief S. An evaluation of the CYP450 inhibition potential of lisdexamfetamine in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos 2007; 35: 180–4
Boyle L, Moncrief S, Krishnan S. Pharmacokinetics of NRP 104 (lisdexamfetamine dimesylate) following administration of a single intranasal, intravenous, or oral dose in rats [poster]. 46th Annual New Clinical Drug Evaluation Unit Meeting; 2006 Jun 14; Boca Raton (FL)
Krishnan S. A multiple-dose single-arm pharmacokinetics study of oral lisdexamfetamine (LDX; NRP104) in healthy adult volunteers [poster]. 46th Annual New Clinical Drug Evaluation Unit Meeting; 2006 Jun 14; Boca Raton (FL)
Jasinski D, Krishnan S. Pharmacokinetics of oral lisdexamfetamine dimesylate (LDZ; NRP104) vs d-amphetamine in healthy adults with a history of stimulant abuse [poster]. 2006 US Psychiatric and Mental Health Congress; 2006 Nov 17; New Orleans (LA)
Krishnan S, Ermer JC, Kehner G, et al. Effect of food on lisdexamfetamine dimesylate (LDX; NRP104) pharmacokinetics [poster]. 2006 US Psychiatric & Mental Health Congress; 2006 Nov 18; New Orleans (LA)
New River Pharmaceuticals Inc. Protocol NRP104.A02. Vol. 63, Mod 5, 5.3.5.4.2: 1262. (Data on file)
Biederman J, Boellner S, Childress A, et al. Improvements in symptoms of ADHD in school-aged children with lisdexamfetamine (SPD489/NPR104) and extended-release mixed amphetamine salts versus placebo [abstract no. NR631 plus poster]. 159th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2006 May 20–25; Toronto
Lopez FA, Boellner SW, Childress A, et al. ADHD symptom improvement in children treated with lisdexamfetamine dimesylate (LDX) [poster]. 53rd Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry; 2006 28 October; San Diego (CA)
Childress AC, Krishnan S, McGough JJ, et al. Interim analysis of a long-term, open-label, single-arm study of lisdexamfetamine (LDX), an amphetamine prodrug, in children with ADHD [poster]. 53rd Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry; 2006; San Diego (CA)
Data on file, Shire Development Inc., 2007 Feb 15
US FDA. Lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse™): prescribing information (US) [online]. Available from URL: http://www.fda.gov [Accessed 2007 Mar 1]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blick, S.K.A., Keating, G.M. Lisdexamfetamine. Pediatr-Drugs 9, 129–135 (2007). https://doi.org/10.2165/00148581-200709020-00007
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00148581-200709020-00007