Abstract
-
▴ Olmesartan medoxomil/amlodipine is a fixeddose combination of olmesartan medoxomil and amlodipine, both established antihypertensive agents. Dose titration with the individual constituent drugs is recommended before switching to the equivalent fixed-dose combination.
-
▴ In a randomized, double-blind, factorial trial in patients with mild to severe hypertension, 8 weeks of olmesartan medoxomil/amlodipine was more effective in reducing diastolic BP (DBP) and systolic BP (SBP) than placebo or equivalent dosages of olmesartan medoxomil or amlodipine as monotherapy.
-
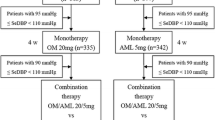
▴ In two randomized, double-blind trials in patients with moderate to severe hypertension not adequately treated with amlodipine or olmesartan medoxomil monotherapy, 8 weeks of olmesartan medoxomil/amlodipine 20 mg/5 mg, 40 mg/5 mg or 40 mg/10 mg per day was more effective in reducing DBP and SBP than continuing treatment with olmesartan medoxomil 20 mg/day or amlodipine 5 mg/day monotherapy.
-
▴ More patients receiving olmesartan medoxomil/amlodipine at approved dosages than monotherapy recipients at equivalent dosages reached BP goals (42.5–51.0% vs 21.1–36.3% in the factorial trial and 44.5–54% vs 28.5–30% in the monotherapy comparisons).
-
▴ In the comparison with amlodipine monotherapy, >70% of olmesartan medoxomil/amlodipine recipients, some requiring upwards dosage adjustment, met BP goals.
-
▴ Olmesartan medoxomil/amlodipine was generally well tolerated in clinical trials. Peripheral oedema was significantly less common in olmesartan medoxomil/amlodipine 40 mg/10 mg per day than amlodipine monotherapy 10 mg/day recipients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolf-Maier K, Cooper RS, Banegas JR, et al. Hypertension prevalence and blood pressure levels in 6 European countries, Canada, and the United States. JAMA 2003 May 14; 289(18): 2363–9
Whitworth JA. 2003 World Health Organization (WHO) International Society of Hypertension (ISH) statement on management of hypertension (World Health Organization, International Society of Hypertension Writing Group). J Hypertens 2003 Nov; 21(11): 1983–92
Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, et al. 2007 guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 2007 Jun; 28(12): 1462–536
Daiichi Sankyo Inc. Marketing approval for Sevikar granted [media release 2008 Nov 13] [online]. Available from URL: http://www.daiichi-sankyo.eu/site_eu/index.php?node_id=2683 [Accessed 2008 Nov 24]
Daiichi Sankyo, Netherlands. Sevikar®: summary of product characteristics [online]. Available from URL: http://www.artsenapotheker.nl/geneesmiddel/sevikar [Accessed 2009 Mar 23]
Daiichi Sankyo Inc. Azor™ (amlodipine and olmesartan medoxomil): prescribing information [online]. Available from URL: http://www.fda.gov/cder/foi/label/2007/022100lbl.pdf [Accessed 2008 Dec 3]
Bakris GL. Combined therapy with a calcium channel blocker and an angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker. J Clin Hypertens 2008 Jan; 10 Suppl. 1: 27–32
Scott LJ, McCormack PL. Olmesartan medoxomil: a review of its use in the management of hypertension. Drugs 2008; 68(9): 1239–72
Haria M, Wagstaff AJ. Amlodipine: a reappraisal of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use in cardiovascular disease. Drugs 1995; 50(3): 560–86
Epstein BJ, Vogel K, Palmer BF. Dihydropyridine calcium channel antagonists in the management of hypertension. Drugs 2007; 67(9): 1309–27
Martinez-Martin FJ, Macias-Batista A, Rodriguez-Rosas H, et al. Treatment with a combination of olmesartan plus amlodipine vs. olmesartan plus hydrochlorothiazide in hypertensive patients with metabolic syndrome increases insulin sensitivity and adiponectin and reduces inflammation markers [abstract no. PS23/TUE/02]. J Hypertension 2008; 26 Suppl. 1: 331. Plus poster presented at the 18th Scientific Meeting, European Society of Hypertension and the 22nd Scientific Meeting, International Society of Hypertension; 2008 Jun 14–19; Berlin
Rohatagi S, Lee J, Shenouda M, et al. Pharmacokinetics of amlodipine and olmesartan after administration of amlodipine besylate and olmesartan medoxomil in separate dosage forms and as a fixed-dose combination. J Clin Pharmacol 2008 Nov; 48(11): 1309–22
Rohatagi S, Carrothers TJ, Kshirsagar S, et al. Evaluation of population pharmacokinetics and exposure-response relationship with coadministration of amlodipine besylate and olmesartan medoxomil. J Clin Pharmacol 2008 Jul; 48(7): 823–36
Chrysant SG, Melino M, Karki S, et al. The Combination of Olmesartan Medoxomil and Amlodipine Besylate in Controlling High Blood Pressure: COACH, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 8-week factorial efficacy and safety study. Clin Ther 2008; 30(4): 587–604
Volpe M, Brommer P, Haag U, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of olmesartan medoxomil combined with amlodipine in patients with moderate to severe hypertension after amlodipine monotherapy: a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, multicentre study. Clin Drug Invest 2009 Jan; 29(1): 11–25
Barrios V, Laies P, Ammentorp B, et al. Olmesartan medoxomil (OLM) plus amlodipine (AML) provides BP reduction and improves BP goal rate attainment in patients (pts) with moderate-to-severe hypertension [abstract no. PS33/Thu/32]. J Hypertens 2008; 26 Suppl.1: 472–73. Plus poster presented at the 18th Scientific Meeting, European Society of Hypertension and the 22nd Scientific Meeting, International Society of Hypertension; 2008 Jun 14–19; Berlin
Chrysant SG, Rhyne J, Melino M, et al. Combination of amlodipine besylate and olmesartan medoxomil significantly reduces blood pressure in patients with hypertension independent of age [abstract no. PS26/Wed/21]. J Hypertens 2008; 26 Suppl. 1: 375. Plus poster presented at the 18th Scientific Meeting, European Society of Hypertension and the 22nd Scientific Meeting, International Society of Hypertension; 2008 Jun 14–19; Berlin
Chrysant SG, Patron A, Karki S, et al. Combination of amlodipine besylate plus olmesartan medoxomil provides greater reductions in seated diastolic and systolic blood pressure compared with monotherapy in men and women [abstract no. PS26/Wed/15]. J Hypertens 2008; 26 Suppl. 1: 374. Plus poster presented at the 18th Scientific Meeting, European Society of Hypertension and the 22nd Scientific Meeting, International Society of Hypertension; 2008 Jun 14–19; Berlin
Bakris G, Mion-Bet S, Karki S, et al. Combination of amlodipine besylate and olmesartan medoxomil provides greater reduction in blood pressure compared with monotherapy in subjects with and without diabetes [abstract no. p-12]. J Clin Hypertens 2008 May; 10 (5; Suppl. A): 10
Oparil S, Ramstad D, Melino M, et al. The combination of amlodipine besylate plus olmesartan medoxomil provides numerically greater reductions in blood pressure compared with component monotherapies in race and ethnic subgroups [abstract no. PS26/Wed/14]. J Hypertens 2008; 26 Suppl. 1: 373–4. Plus poster presented at the 18th Scientific Meeting, European Society of Hypertension and the 22nd Scientific Meeting, International Society of Hypertension; 2008 Jun 14–19; Berlin
Bakris G, Eads Jr S, Karki S, et al. Does body mass index influence blood pressure reduction among subjects treated with combination of amlodipine besylate and olmesartan medoxomil versus component monotherapy? [abstract no. PS26/Wed/16]. J Hypertens 2008 Suppl 1; 374. Plus poster presented at the 18th Scientific Meeting, European Society of Hypertension and the 22nd Scientific Meeting, International Society of Hypertension; 2008 Jun 14–19; Berlin
Oparil S, Herron J, Melino M, et al. The combination of amlodipine besylate and olmesartan medoxomil safely reduces blood pressure compared with monotherapy in both patients with stage 1 and 2 hypertension [abstract no. PS26/Wed/22]. J Hypertens 2008; Suppl. 1: 375–6. Plus poster presented at the 18th Scientific Meeting, European Society of Hypertension and the 22nd Scientific Meeting, International Society of Hypertension; 2008 Jun 14–19; Berlin
Oparil S, Sandoval J, Karki S, et al. Combination of amlodipine besylate and olmesartan medoxomil provides greater reduction in blood pressure compared with monotherapy in naive and non-naive subjects [abstract no. PS26/Wed/23]. J Hypertens 2008; 26 Suppl. 1: 376. Plus poster presented at the 18th Scientific Meeting, European Society of Hypertension and the 22nd Scientific Meeting, International Society of Hypertension; 2008 Jun 14–19; Berlin
Chrysant SG, Melino M, Karki S, et al. Long term efficacy and safety of amlodipine besylate and olmesartan medoxomil in achieving BP thresholds in patients with mild to severe hypertension [abstract no. PS26/Wed/29]. J Hypertens 2008 26 Suppl. 1: 377. Plus poster presented at the 18th Scientific Meeting, European Society of Hypertension and the 22nd Scientific Meeting, International Society of Hypertension; 2008 Jun 14–19; Berlin
Chrysant SG, Oparil S, Bakris G, et al. Combination of amlodipine plus olmesartan medoxomil (OM) is effective and safe with long term dosing while treating patients (pts) to blood pressure goal [abstract no. PS26/Wed/17]. J Hyper tens 2008; 26 Suppl. 1: 374. Plus poster presented at the 18th Scientific Meeting, European Society of Hypertension and the 22nd Scientific Meeting, International Society of Hypertension; 2008 Jun 14–19; Berlin
Brommer P, Laeis P, Ammentorp B, et al. Olmesartan medoxomil plus amlodipine is well tolerated in patients with moderate-to-severe hypertension [abstract no. PS33/Thu/33]. J Hypertens 2008; 26 Suppl. 1: 473. Plus poster presented at the 18th Scientific Meeting, European Society of Hypertension and the 22nd Scientific Meeting, International Society of Hypertension; 2008 Jun 14–19; Berlin
Acknowledgements and Disclosures
The manuscript was reviewed by: F. Anan, Department of Cardiology, Oita Red Cross Hospital, Oita, Japan; G.D. Johnston, Department of Therapeutic Pharmacology, Queens University of Belfast, Belfast, Northern Ireland, UK; M. Volpe, Cardiology, II Faculty of Medicine, University of Rome ‘La Sapienza’, Sant’ Andrea Hospital, Rome, Italy.
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding. During the peer review process, the manufacturers of the agent under review were offered an opportunity to comment on this article. Changes resulting from any comments received were made on the basis of scientific and editorial merit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanford, M., Keam, S.J. Olmesartan Medoxomil/Amlodipine. Drugs 69, 717–729 (2009). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200969060-00005
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200969060-00005