Abstract
Objective
The pharmacokinetics of cilostazol were studied in patients with mild, moderate and severe renal impairment and in healthy volunteers after administration of 50mg single and multiple doses of cilostazol.
Design
This was an open-label, single and multiple dose study administering 50mg cilostazol every 12 hours to healthy volunteers and patients with varying degrees of renal impairment.
Participants
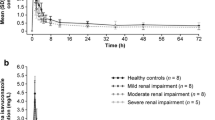
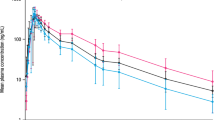
6 normal volunteers [creatinine clearance (CLCR) ≥90 ml/min]; 6 patients with mild (CLCR 50 to 89 ml/min), 5 with moderate (CLCR 26 to 49 ml/min) and 6 with severe (CLCR 5 to 25 ml/min) renal impairment.
Outcome Measures
Noncompartmental pharmacokinetic parameters were determined for each study participant.
Results
At steady state, in the severe renal disease group, cilostazol and OPC-13015 peak concentrations (Cmax) were 29 and 41% lower and the areas under the concentration-time curve over the dosage interval (AUCτ) 39 and 47% lower than in the healthy volunteers. Cmax and AUCτ of OPC-13213 were significantly higher, 173 and 209%, respectively, than those in the healthy volunteers. The accumulation ratios were not significantly different between the various renal function groups for cilostazol and its metabolites. The estimated pharmacological activity of cilostazol and its metabolites was similar between the normal volunteers and those with severe renal impairment.
Conclusions
A dosage reduction in renally impaired patients is not supported by the pharmacokinetics of cilostazol and its metabolites in this patient group.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Talbert RL. Drug dosing in renal insufficiency. J Clin Pharmacol 1994; 34: 99–110.
Bramer SL, Tata PNV, Mallikaarjun S, et al. Disposition of 14C-cilostazol after single dose administration to healthy human subjects. Pharm Res 1997; 14 Suppl. 11: S–612.
Fu CJ, Tata PNV, Bramer SL. Simultaneous quantitative determination of cilostazol and its metabolites in plasma by high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 1999; 728(2): 251–62.
Bramer SL, Forbes WP. Effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of a single dose of cilostazol. Clin Pharmacokinet 1999; 37 Suppl. 2: 25–32.
Gibaldi M, Perrier D. Pharmacokinetics. 2nd ed. New York: Marcel Dekker, 1982: 332–6.
Bramer SL, Forbes WP, Mallikaarjun S. Cilostazol pharmacokinetics after single and multiple oral doses in healthy males and patients with intermittent claudication resulting from peripheral arterial disease. Clin Pharmacokinet 1999; 37 Suppl. 2: 1–11.
Tata PNV, Bramer SL. Plasma protein binding and displacement studies of cilostazol. American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists Annual Meeting; 1997 Nov 2–6; Boston. Pharm Res 1997; 14 Suppl. 11: S555–6.
Suri A, Forbes WP, Bramer SL. Effects of CYP3A inhibition on the metabolism of cilostazol. Clin Pharmacokinet 1999; 37 Suppl. 2: 61–8.
PLETAL® (Cilostazol) Package Insert, 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mallikaarjun, S., Forbes, W.P. & Bramer, S.L. Effect of Renal Impairment on the Pharmacokinetics of Cilostazol and its Metabolites. Clin Pharmacokinet 37 (Suppl 2), 33–40 (1999). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199937002-00004
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199937002-00004