Abstract
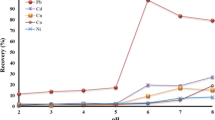
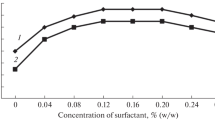
A very simple, ultra-sensitive and fairly selective direct spectrophotmetric method is presented for the rapid determination of lead(II) at ultra-trace level using 1,5-diphenylthiocarbazone (dithizone) in micellar media. The presence of the micellar system avoids the previous steps of solvent extraction and reduces the cost and toxicity while enhancing the sensitivity, selectivity and the molar absorptivity. The molar absorptivities of the lead-dithizone complex formed in the presence of the cationic cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) surfactants are almost ten times the value observed in the standard method, resulting in an increase in the sensitivity of the method. The reaction is instantaneous and the absorbance remains stable for over 24 h. The average molar absorption coefficient was found to be 3.99 x 105 L mol-1 cm-1 and Sandell’s sensitivity was 30 ng cm-2 of Pb. Linear calibration graphs were obtained for 0.06 - 60 mg L-1 of Pb(II); the stoichiometric composition of the chelate is 1:2 (Pb:dithizone). The interference from over 50 cations, anions and complexing agents has been studied at 1 mg L-1 of Pb(II). The method was successfully used in the determination of lead in several standard reference materials (alloys and steels), environmental water samples (potable and polluted), biological samples (human blood and urine), soil samples and solutions containing both lead(II) and lead(IV) and complex synthetic mixtures. The method has high precision and accuracy (σ= ±0.01 for 0.5 mg L-1).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. D. Clayton and F. E. Clayton, “Pathy’s Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology”, 3rd ed., 1981, Wiley, New York, 1687.
R. A. Goyer and T. W. Clarkson, in “Casarett and Doull’s Toxicology: The Basic Science of Poisons,” C. D. Klaassen, 6th ed., 2001, Macmillan Publishing Company, 827.
L. H. Hurney, in “Trace Element Analytical Chemistry in Medicine and Biology etc.”, ed. P. Pratter and P. Scharmel, 1984, Vol. 3, Walter de Gruyter, Berlin, 375.
L. R. Beecks, Anal. Chem., 1986, 58, 975A.
M. M. Key, A. F. Henschel, J. Butter, R. N. Ligo, and I. R. Tebershed, “Occupational Diseases: A Guide to their Recognition”, 1977, US Department of Health, Education and Welfare, U.S. Govt. Printing, Washington, D.C.
A. K. De, “Environmental Chemistry”, 3rd ed., 1996, New Age International (P) Limited, New Delhi, 263.
J. Fries and H. Getrost, “Organic Reagents for Trace Analysis”, 1977, E. Merck, Darmstadt, 243.
L. Hageman, L. Torma, and B. E. Ginther, J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1975, 58, 990.
B. Kumar, H. B. Singh, M. Katyal, and R. L. Sharma, Mikrochim. Acta [Wien], 1991, 79.
EPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency), “Proposed Guidelines for Carcinogen Risk Assessment”, 1999, Office of Research and Development, NCEA-F-0644.
H. Tani, T. Kamidate, and H. Watanabe, Anal. Sci., 1998, 14, 875.
M. E. D. Garcia and A. S. Medel, Talanta, 1986, 33, 255.
H. Khan, M. J. Ahmed, and M. I. Bhanger, Anal. Sci., 2005, 21, 507.
L. C. Willemsons, “Handbook of Lead Chemicals”, Project LC-116, International Lead-Zinc Research Organization, 1986, New York.
M. J. Ahmed and M. Moniruzzaman, Ultra Scientist of Physical Sciences, 2001, 13, 25.
A. L. D. Comitre and B. V. F. Reis, Talanta, 2005, 65, 846.
M. J. Ahmed and M.-Al Mamun, Talanta, 2001, 55, 43.
S. L. C. Ferreira, M. G. M. Andrade, I. P. Lobo, and A. C. Costa, Anal. Lett., 1991, 24, 1675.
J. M. Pan, Y. S. Chen, and H. T. Yan, “Chromagenic Reagent and Their Application in Spectrophotometric Analysis, Shanghai Science and Technology”, 1981, 411–413.
Z. J. Li, Z. Z. Zhu, Y. P. Chen, C. G. Xu, and J. M. Pan, Talanta, 1999, 48, 511.
K. Kilian and K. Pyrzynska, Talanta, 2003, 60, 669.
M. J. Ahmed and M.-Al Momun, Talanta, 2001, 55, 43.
B. K. Pal and B. Chowdhury, Mikrochim. Acta [Wien], 1984, 121.
N. S. Murcia, E. G. Lundquist, R. O. Russo, and D. G. Peters, J. Chem. Educ., 1990, 67, 7.
E. B. Sandell, “Colorimetric Determination of Traces of Metals”, 1965, Interscience, New York, 269.
C. B. Ojeda, A. G. de Torres, F. S. Rojas, and J. M. C. Pavon, Analyst, 1987, 112, 1499.
I. Nukatsuka, A. Nashirmura, and K. Ohzeki, Anal. Chim. Acta, 1995, 304, 243.
P. Job, Ann. Chim. [Paris], 1928, 9, 113.
J. A. Yoe and A. L. Jones, Ind. Eng. Chem. Anal. Ed., 1944, 16, 11.
J. Fries and H. Getrost, “Organic Reagents for Trace Analysis”, 1977, E. Merck, Dramstadt, 207.
H. D. Fiedler, J. L. Westrup, A. J. Souza, A. D. Pavei, C. U. Chagas, and F. Nome, Talanta, 2004, 64, 190.
S. Mitra (ed.), “Sample Preparation Techniques in Analytical Chemistry”, 2003, Wiley-Interscience, New Jersey, 14.
E. A. Greenberg, S. L. Clesceri, and D. A. Eaton (ed.), “Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater”, 18th ed., 1992, American Public Health Association, Washington, D.C., 3.
R. L. Boecks, Anal. Chem., 1986, 58(2), 275A.
M. L. Jackson, “Soil Chemical Analysis”, 1965, Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 326.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, H., Ahmed, M.J. & Bhanger, M.I. A Rapid Spectrophotometric Method for the Determination of Trace Level Lead Using 1,5-Diphenylthiocarbazone in Aqueous Micellar Solutions. ANAL. SCI. 23, 193–199 (2007). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.23.193
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.23.193