Abstract
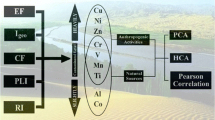
River water and sediment samples were collected at the same site in a vicinity of an abandoned mine, and the concentrations of major elements and heavy metals were determined. The chemical correlations were observed by principal component analysis (PCA), and the samples were classified by cluster analysis (CA) based on the PCA scores. The PCA results presented a macroscopic viewpoint of covariance structure, i.e., the chemical elements could be classified into three groups: 1) major elements and heavy metals in the river water, 2) Cd, Fe and Mn in the sediments, and 3) Cu and Zn in the sediments. The CA results implied a similarity of chemical compositions in most parts of the study area, except the ranges close to the abandoned copper mine. At the mixing location of mining water with natural river water, major elements and cadmium showed simple physical mixing (conservative mixing). Other heavy metals (Cu, Fe, Mn and Zn) showed the massive precipitation at the mixing event. The PCA structure was mainly interpreted in terms of the mixing process between mining water and diluted natural river water.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Wardas, L. Budek, and E. H. Rybicka, Appl. Geochem., 1996, 11, 197.
Z. Borovec, Sci. Total Environ., 1996, 177, 237.
K. C. Cheung, B. H. T. Poon, C. Y. Lan, and M. H. Wong, Chemosphere, 2003, 52, 1431.
M. Singh, G. Muller, and I. B. Singh, J. Geochem. Explor., 2003, 80, 1.
H. M. V. M. Soares, R. A. R. Boaventura, A. A. S. C. Machado, and J. C. G. E. Silva, Environ. Pollut., 1999, 105, 311.
C. K. Jain, J. Hydrology, 1996, 182, 105.
K. Loska and D. Wiechua, Chemosphere, 2003, 51, 723.
P. L. Nimis, F. Fumagalli, A. Bizzotto, M. Codogno, and N. Skert, Sci. Total Environ., 2002, 286, 233.
W. X. Liu, X. D. Li, Z. G. Shen, D. C. Wang, O. W. H. Wai, and Y. S. Li, Environ. Pollut., 2003, 121, 377.
Y. Lin, T. Teng, and T. Chang, Landsc. Urb. Plann., 2002, 62, 19.
K. Anazawa and M. Yoshida, Geochem. J., 1994, 28, 307.
K. Anazawa and M. Yoshida, Geochem. J., 1997, 30, 355.
J. E. Andrews, P. Brimblecombe, T. D. Jickells, and P. S. Liss, “An Introduction to Environmental Chemistry”, 1995, Blackwell Science, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA, 90.
D. Langmuir, “Aqueous Environmental Geochemistry”, 1997, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey, 298.
D. L. Parkhurst and C. A. J. Appelo, “User’s guide to PHREEQC (Version 2)—A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations, Water-Resources Investigations Report 99-4259”, 1999, U.S. Geological Survey, Denver, Colorado.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anazawa, K., Kaida, Y., Shinomura, Y. et al. Heavy-Metal Distribution in River Waters and Sediments around a “Firefly Village”, Shikoku, Japan: Application of Multivariate Analysis. ANAL. SCI. 20, 79–84 (2004). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.20.79
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.20.79