Abstract
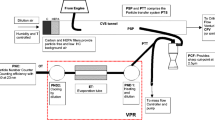
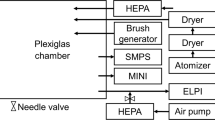
The purpose of this study is to clarify the chemical characterization of PM2. 5 and PM10 in diesel exhaust particles (DEP). Sampling of PM2. 5 and PM10 in DEP was carried out in November 1999 using an automobile exhaust testing system at the National Traffic Safety and Environment Laboratory, with a diesel truck (engine type: direct injection, displacement: 7961 cc, carrying weight: 2020 kg, equivalent inertia weight: 5600 kg) placed on a chassis dynamometer. Sampling conditions included idling, constant speed of 40 km/h, M-15 test pattern and 60%-revolution/40%-load of maximum power. Samples were collected on a polycarbonate membrane filter (Nuclepore®, pore size: 0. 8 µm) using a MiniVol Portable Air Sampler (Airmetrics Co., Inc.). The concentrations of several elemental and ionic species in the PM2. 5 and PM10 samples were determined by particle induced X-ray emission (PIXE) and ion chromatography analysis. PIXE analysis of the PM2.5 and PM10 samples revealed 15 elements, of which Na, Mg, Si, S, Cl, Ca, Fe and Zn were found to be the major components. Ionic species were Cl–, NO2–, NO3–, SO42–, Na+, NH4+, K+ and Ca2+. Concentrations of elements and ionic species under the sampling condition of 60%-revolution/40%-load were highest in comparison with those of the other sampling conditions. The elemental and ionic species data were compared for PM2. 5 and PM10; PM2. 5 concentrations were 70% or more of PM10 concentrations for the majority of elements, and concentrations of ionic species in PM2. 5 and PM10 were almost identical.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Environment Agency Government of Japan, “Quality of The Envronment n Japan 197T, 2000, Environment Agency, Tokyo, 120–128.
K. Yoshizumi, T. Watanabe, K. Ishii, H. Yoshida, K. Asakuno, T. Tamura, M. Kan, and N. Yoshino, “The source apportionment evaluation o ambient particulate matter in the Tokyo mtropolitan area by a receptor oriented modell”, 1989, Annual Report of the Tokyo Metropolitan Research Institute for Environmental Protection 1989, Tokyo, 3–10.
K. Sakamoto, in Proceedings of the International Symposium on Ambient Fine Particles and Health, ed. Japan Society for Atmospheric Environment, 1999, Tokyo, Japan, 70–80.
A. Mizohata, N. Ito, and Y. Kusuya, J. Jpn Soc. Atmos. Environ., 2000, 35, 77.
R. D. McClellan, Ann. Rev. Phamaol. Toxicol., 1989, 27, 279.
T. Ichinose, A. Furuyama, and M. Sagai, Toxicol, 1995, 99, 153.
H. Takano, T. Yoshikawa, Y. Miyabara, K. Imaoka, T. Ichiose, and M. Sagai, Am. J. Rspir. Crit. Care Med., 1997, 156, 36.
K. Iwai and I. Utiyama, J. Jpn Soc. Atmos. Environ., 2000, 35, 229.
JACP Diesel Vehicle Working Group, “Study of Crrent Diesel Vehicle and uel Influence on Emissionss”, JACP Technical Report 1–3–1, 2000, Petroleum Energy Center.
S. Hayakari and R. Hanaisi, J. Jpn Soc. Atmos. Environ., 2001, 36, 39.
K. Sera, T. Yanagisawa, H. Tsunoda, S. Hutatukawa, Y. Saitoh, S. Suzuki, and H. Orihara, Intern. J. PXE, 1992, 2, 325.
K. Sera, S. Futatsugawa, and K. Saitoh, Intern. J. PXE, 1997, 7, 71.
K. Saitoh, K. Sera, T. Gotoh, and M. Nakamura, Nuclear Instrum. Methods Pys. B, 2002, 189, 86.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saitoh, K., Sera, K., Shirai, T. et al. Determination of Elemental andIonic Compositions for Diesel Exhaust Particles by Particle Induced X-ray Emission and Ion Chromatography Analysis. ANAL. SCI. 19, 525–528 (2003). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.19.525
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.19.525