

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
DOI: 10.17485/IJST/v15i21.2401
Year: 2022, Volume: 15, Issue: 21, Pages: 1059-1066
Original Article
Poulami Chatterjee1,*, Amaresh Dubey2
1 Department of Economics, St. Xavier’s University, Kolkata, India
2 Centre for the Study of Regional Development, School of Social Sciences Jawaharlal, Nehru University, New Delhi, India
*Corresponding author email: [email protected]
Received Date:23 December 2021, Accepted Date:30 April 2022, Published Date:21 June 2022
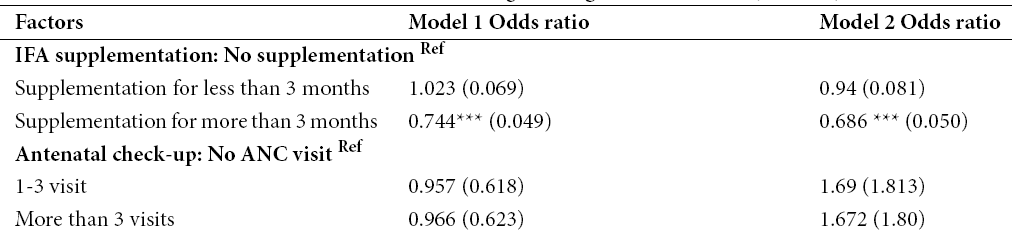
Objective: To evaluate the association between Iron Folic Acid (IFA) supplementation during pregnancy and children’s birth weights in India. Methods: We have used India Human Development Survey-2, 2011-12 data to verify this relation. This is a nationally representative survey of 42,152 households in 1503 villages and 971 urban localities across India. The association between the child’s birth weight and IFA intake during pregnancy along with other potential factors are analysed using logistic regression. Findings: Approximately 24 percent of women were found to be never consuming IFA during pregnancy and 31 percent of pregnant women took IFA for less than three months which is below the prescribed limit in 2011-12. This study finds that IFA supplementation has significantly associated with 23 percent (and 31 percent in Model 2) reduction in odds of low-birth-weight outcome when it is consumed for more than 3 months during pregnancy. However, this association is not significant for less than 3 months supplementation. Our study has also shown that factors like maternal nutrition (BMI taken as a proxy), maternal education, mother’s age and wealth quintile are likely to impact birth weight after adjustment for other covariates. Novelty: To our knowledge, there are just handful of studies which attempted to find out the association between IFA supplementation during pregnancy and birth weight outcome using population level data in India. We need sufficient evidence to establish the relationship for this developing country where almost 58 percent of pregnant women were anaemic. Our study tries to find out the magnitude of association between Iron and Folic Acid (IFA) supplementation during pregnancy and children’s birth weights in India using nationally representative IHDS data. This study also examines the socio-economic and demographic factors associated with birth outcome. From this analysis, we can emphasis on some potential policy interventions to reduce prevalence of low birth weight. The useful policies to ensure nutritious food to pregnant women and also to women who are likely to conceive will be highly effective.
Keywords: Low birth weight, Antenatal care, Iron supplementation, Determinants of low birth-weight, IHDS data
© 2022 Chatterjee & Dubey. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.