Trends in Renal Replacement Therapy in Bosnia and Herzegovina 2002-2008
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2010.2641Keywords:
RRT, epidemiology, ESRD, hemodialysisAbstract
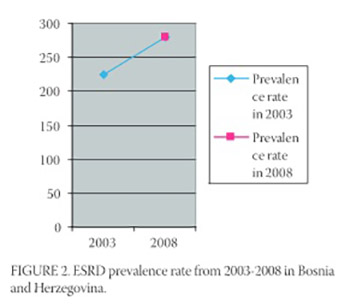
Renal Registry (RR) of Bosnia and Herzegovina was established in 2002, with aim to follow up the trends of Renal Replacement Therapy in Bosnia and Herzegovina. The prevalence of Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT) in Bosnia and Herzegovina is rising steadily. One reason for this is an increasing number of patients starting RRT. The aim is to present the epidemiology and treatment of all aspects of RRT in Bosnia and Herzegovina in period 2002-2008. Centre-related and patient-related questionnaires were sent to all 25 dialysis centres in Bosnia and Herzegovina. The demographic data, prevalence and incidence, type of renal replacement therapy, cause of ESRD, erythropoietin administration, cause of death, and type of vascular access were obtained from the questionnaires. Collected data were analysed using SPSS statistics. The number of patients treated by Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT) increased steadily from 1,531 patients in 2002 to the 2,206 at the 2008 (43%). The prevalence has increased from 399 pmp in 2002 to 696 pmp. in 2008. Incidence (new patients) in 2002 was 110 pmp and incidence rate in 2008 was 163, and there were 249 new patients (day 1). The mean age for new patients increased from 60 years in 2002 to 63.5 years in 2008 and the population over 75 years rate from 8.79% to 11.3%. Most ESRD patients in Bosnia and Herzegovina are undergoing intermittent hemodialysis (92%), while some patients (8%) are treated by peritoneal dialysis and transplantation. The most significant cause of ESRD in 2008 was chronic glomerulonephritis (421 patients, 19.2%), followed by pyelonephritis (414 patients, 18.9%), BEN (14.7%) and Diabetes mellitus (12.2%). Hepatitis B and C virus infections had 397 (16.3%) patients, out of them 22 had both type of infections and 98 patients had B type infection. Only 10.5% of patients were tested on MRSA and 3 patients were positive on MRSA. There were no HIV-positive patients on RRT. The most common type of vascular access was AV fistula in 85% patients, AV graft 2% and catheters in 13%. Out of hemodialysis patients, 85.7% received ESA almost s.c. The median weekly dose was 4,000 UI. Cardiovascular diseases were the leading cause of death, gross mortality rate of dialysis patients being 13.01% in 2008. The need for RRT in Bosnia and Herzegovina is increasing and the number of patients increased by 43% since 2002. Hemodialysis is still the most common modality of treatment (92%), while proportion of PD and transplantation is slowly increasing. The preventive measures are necessary to prevent ESRD and also to decrease the number of patients on dialysis.
Downloads