OPEN-ACCESS PEER-REVIEWED
LETTER TO EDITOR
Samiksha Ghimire1,*, Erwin M. Jongedijk1, Simone H.J. van den Elsen1, Mireille A. Wessels1, Daan J. Touw1,2, Jan-Willem C. Alffenaar 1,3,4
1University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, Department of Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology, Groningen, The Netherlands; 2University of Groningen, Groningen Research Institute of Pharmacy, Department of Pharmacokinetics Toxicology and Targeting, Groningen, The Netherlands; 3University of Sydney, Faculty of Medicine and Health, School of Pharmacy, Sydney, Australia; 4Westmead hospital, Sydney, Australia.
Journal of Applied Bioanalysis. Vol.6. No.2. pages 68-70 (2020).
Published 15 June 2020. https://doi.org/10.17145/jab.20.008 | (ISSN 2405-710X).
Correspondence: Ghimire S . Samiksha Ghimire, PhD, University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology, Groningen, The Netherlands.
Citation:
Ghimire S, Jongedijk EM, van den Elsen SH, Wessels MA, Touw DJ, Alffenaar JW. Cross-validation of Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry method for quantification of Levofloxacin in saliva. J Appl Bioanal 6(2), 56-58 (2020).
Open-access and Copyright:
©2020 Ghimire S et al. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Funding/Manuscript writing assistance:
The authors have no financial support or funding to report and they also declare that no writing assistance was utilized in the production of this article.
Competing interest:
The authors have declared that no competing interest exist.
Article history:
Received: 17 February 2020, Revised 27 May 2020, Accepted 02 June 2020.
Keywords: levofloxacin, saliva, liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry, tuberculosis.
Levofloxacin belongs to the Group A drug for treating multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) but exhibits considerable pharmacokinetic variability. For a 750-1000 mg once daily dosing, the desired levofloxacin plasma/serum concentration range is 8-12 mg/L and the area under the concentration time curve from 0 to 24h is 75 if MIC is 0.5 mg/L and 150 if MIC is 1 mg/L. Saliva too could be a potential patient friendly alternative sampling matrix for levofloxacin quantification [1,2]. However, levofloxacin quantification in saliva using a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method developed for plasma or serum requires cross validation. Moreover, the handling of infectious saliva samples from TB patients puts health care workers at risk of contagion. Membrane filtration was found to be suitable for sterilization of saliva samples [3]. The aims of this study were: a) to assess if drug concentrations in human saliva could be reliably determined with calibration samples prepared in human serum; and b) to perform a recovery test for levofloxacin concentrations in saliva after using sorbent material such as cotton rolls and/or filtering through a membrane filter.
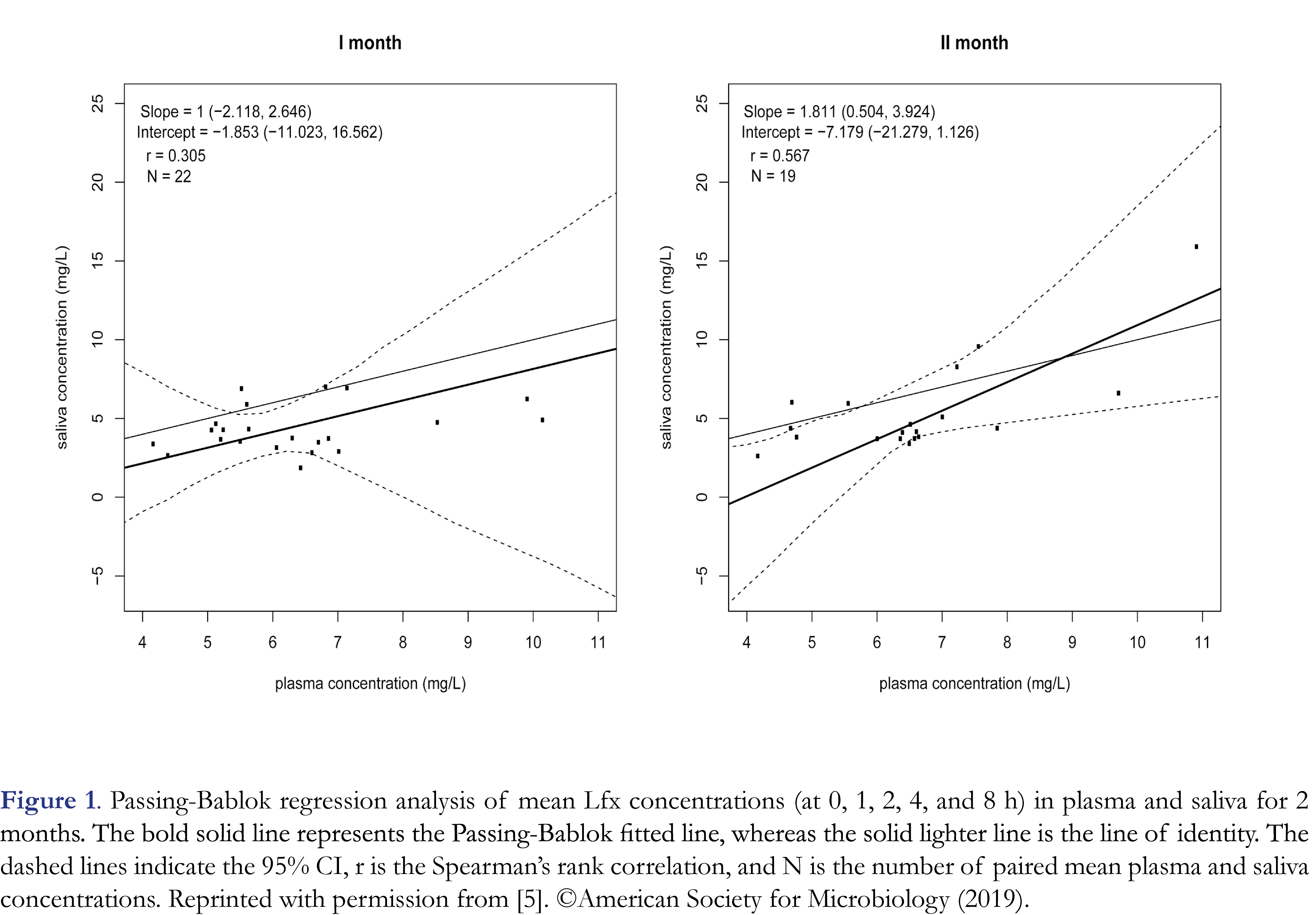
A slight modification was done to our previously published LC-MS/MS method for levofloxacin quantification in human serum/plasma [4]. The assay was adjusted to simultaneously detect ciprofloxacin, moxifloxacin and levofloxacin in plasma/serum. First, for cross validation, levofloxacin stock solution of 2.5 mg/mL was prepared in dimethyl sulfoxide (Merck, NJ, USA). Nine different concentrations of the calibration samples in blank human serum were made: 0.20, 0.50, 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 40, and 50 mg/L. In addition, four different concentrations of quality control samples (QC) in saliva, with a lower limit of quantification at 0.2 mg/L, low QC at 1 mg/L, medium at 20 mg/L, and high at 40 mg/L were prepared. The internal standard solution was prepared from a 1 mg/ml stock solution of [2H4]-levofloxacin in DMSO by diluting 50 µl to 250 ml with methanol (0.2 mg/L). For cross validation, all samples were analyzed in quintuplicate. The analysis was performed on a triple quadrupole LC-MS/MS (Thermo Scientific TSQ Quantiva, San Jose, CA, USA). A Thermo Accucore C18 analytical column of particle size 2.6 µm, 50 mm length, and internal diameter of 2.1 mm was used. The column temperature during analysis was 60°C. The linearity of the calibration curve was 0.20-50 mg/L for levofloxacin in both serum and saliva. QC samples in saliva at four concentration levels (0.20, 1, 20, 40 mg/L) were quantified using a calibration curve in serum. All QC samples were prepared and measured in 5-fold during a single day. The LC-MS/MS method had a run time of 2 min and levofloxacin eluted at a retention time of 0.7 min. Accepted bias and coefficient of variation (CV) were ≤15% for QC samples at low (at -0.9% and 1.0%), medium (at -0.3% and 0.9%), and high (at 2.0% and 1.3%) concentrations and ≤ 20% for LLOQ (at -1.0% and 2.3%) in saliva. This method was clinically applied for the analysis of levofloxacin concentrations in saliva samples at the laboratory of the department of Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology in the University Medical Center Groningen for a clinical trial (identifier number NCT 03000517) on the pharmacokinetics of levofloxacin in saliva of 23 MDR-TB patients. The median observed AUC0-24 and Cmax in saliva were 67.09 mg*h/L and 7.03 mg/L [5]. Levofloxacin concentrations in plasma and saliva of 23 MDR-TB patients is shown (Figure 1).
Figures
[Click to enlarge]
References
- Gröschl M. Saliva: a reliable sample matrix in bioanalytics. Bioanalysis 9, 655-668 (2017). [CrossRef]
- van den Elsen, Simone HJ, Oostenbrink LM, Heysell SK, et al. Systematic Review of Salivary Versus Blood Concentrations of Antituberculosis Drugs and Their Potential for Salivary Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Ther Drug Monit 40, 17-37 (2018). [CrossRef]
- van den Elsen SHJ, van der Laan T, Akkerman OW, et al. Membrane Filtration Is Suitable for Reliable Elimination of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from Saliva for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. J Clin Microbiol 55, 3292-3293 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Ghimire S, van Hateren K, Vrubleuskaya N, et al. Determination of levofloxacin in human serum using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Appl Bioanal 4(1), 16-25 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Ghimire S, Maharjan B, Jongedijk EM et al. Evaluation of Saliva as a Potential Alternative Sampling Matrix for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Levofloxacin in Patients with Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 23 (5) e02379-18 (2019). [CrossRef]
All site content, except where otherwise noted, is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License