Abstract
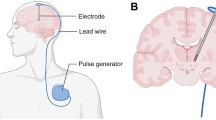
Deep brain stimulation (DBS), including optical stimulation and electrical stimulation, has been demonstrated considerable value in exploring pathological brain activity and developing treatments for neural disorders. Advances in DBS microsystems based on implantable microelectrode array (MEA) probes have opened up new opportunities for closed-loop DBS (CL-DBS) in situ. This technology can be used to detect damaged brain circuits and test the therapeutic potential for modulating the output of these circuits in a variety of diseases simultaneously. Despite the success and rapid utilization of MEA probe-based CL-DBS microsystems, key challenges, including excessive wired communication, need to be urgently resolved. In this review, we considered recent advances in MEA probe-based wireless CL-DBS microsystems and outlined the major issues and promising prospects in this field. This technology has the potential to offer novel therapeutic options for psychiatric disorders in the future.
摘要
脑深部刺激(DBS), 包括光刺激和电刺激, 对于脑重大疾病发病机理和治疗方法开发的研究具有重要的科学意义。基于植入式微电极阵列(MEA)探针的DBS微系统的发展为原位闭环DBS(CL-DBS)提供了新机遇。闭环DBS可用于监测受损的神经细胞活动, 并可根据电生理信号调整刺激参数, 以实现对神经细胞活动的精准高效调控。基于MEA探针的CL-DBS微系统虽取得了快速发展, 但仍有一些关键问题亟需解决, 包括无线通信的安全性、稳定性和电池寿命等。本综述回顾和总结了基于MEA探针的无线CL-DBS微系统的最新进展, 并探讨了该技术存在的主要问题和未来发展前景。未来, 基于MEA探针的无线CL-DBS技术的不断发展和进步将继续为神经科学和临床神经学带来创新, 并为脑重大疾病的治疗提供新策略。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdi A, Aliakbarian H, 2019. A miniaturized UHF-band rectenna for power transmission to deep-body implantable devices. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med, 7:1900311. https://doi.org/10.1109/JTEHM.2019.2910102
Abdi A, Cha HK, 2019. A regulated multiple-output highvoltage charge pump IC for implantable neural stimulators. Microelectron J, 92:104617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2019.104617
Alvarez NT, Buschbeck E, Miller S, et al., 2020. Carbon nanotube fibers for neural recording and stimulation. ACS Appl Bio Mater, 3(9):6478–6487. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.0c00861
Araki T, Bongartz LM, Kaiju T, et al., 2020. Flexible neural interfaces for brain implants—the pursuit of thinness and high density. Flex Print Electron, 5(4):043002. https://doi.org/10.1088/2058-8585/abc3ca
Aravanis AM, Wang LP, Zhang F, et al., 2007. An optical neural interface: in vivo control of rodent motor cortex with integrated fiberoptic and optogenetic technology. J Neural Eng, 4(3):S143–S156. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2560/4/3/S02
Ashok Kumar N, Chauhan M, Kandala SK, et al., 2020. Development and testing of implanted carbon electrodes for electromagnetic field mapping during neuromodulation. Magn Reson Med, 84(4):2103–2116. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.28273
Ausra J, Munger SJ, Azami A, et al., 2021. Wireless battery free fully implantable multimodal recording and neuromodulation tools for songbirds. Nat Commun, 12:1968. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-22138-8
Baek C, Kim S, Jang JW, et al., 2020. Investigation of stereotactic surgery for avian brain stimulation by a fully implanted wireless system. Neurosurg Focus, 49(1):E10. https://doi.org/10.3171/2020.4.FOCUS2025
Bahadori-Jahromi F, Salehi S, Madadi Asl M, et al., 2023. Efficient suppression of parkinsonian beta oscillations in a closed-loop model of deep brain stimulation with amplitude modulation. Front Hum Neurosci, 16:1013155. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2022.1013155
Bansal A, Shikha S, Zhang Y, 2023. Towards translational optogenetics. Nat Biomed Eng, 7(4):349–369. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-021-00829-3
Banu S, Gupta S, 2022. Power optimization of low noise amplifier (LNA) and DAC used in closed loop deep brain neuro-stimulator (CDBS) at 45nm using cadence virtuoso. Int J Health Sci, 6(S3):5491–5502. https://doi.org/10.53730/ijhs.v6nS3.7153
Becker MT, 2021. Charge injection capacity of ferroelectric microelectrodes for bioelectronic applications. AIP Adv, 11(6):065106. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0049202
Bloch E, Luo Y, da Cruz L, 2019. Advances in retinal prosthesis systems. Ther Adv Ophthalmol, 11:2515841418817501. https://doi.org/10.1177/2515841418817501
Boehler C, Vieira DM, Egert U, et al., 2020. NanoPt—a nanostructured electrode coating for neural recording and microstimulation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 12(13):14855–14865. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b22798
Bronte-Stewart HM, Petrucci MN, O’Day JJ, et al., 2020. Perspective: evolution of control variables and policies for closed-loop deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease using bidirectional deep-brain-computer interfaces. Front Hum Neurosci, 14:353. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2020.00353
Burton A, Won SM, Sohrabi AK, et al., 2021. Wireless, battery-free, and fully implantable electrical neurostimulation in freely moving rodents. Microsyst Nanoeng, 7:62. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41378-021-00294-7
Cagnan H, Denison T, McIntyre C, et al., 2019. Emerging technologies for improved deep brain stimulation. Nat Biotechnol, 37(9):1024–1033. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0244-6
Chen ZS, Pesaran B, 2021. Improving scalability in systems neuroscience. Neuron, 109(11):1776–1790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2021.03.025
Cho YU, Lim SL, Hong JH, et al., 2022a. Transparent neural implantable devices: a comprehensive review of challenges and progress. npj Flex Electron, 6:53. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41528-022-00178-4
Cho YU, Lee JY, Jeong UJ, et al., 2022b. Ultra-low cost, facile fabrication of transparent neural electrode array for electrocorticography with photoelectric artifact-free optogenetics. Adv Funct Mater, 32(10):2105568. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202105568
Choi J, Kumar K, Khazali M, et al., 2020. Optimal adaptive electrode selection to maximize simultaneously recorded neuron yield. Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2020). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Vancouver, Canada, p.6160–6171.
Cury RG, Pavese N, Aziz TZ, et al., 2022. Gaps and roadmap of novel neuromodulation targets for treatment of gait in Parkinson’s disease. npj Parkinsons Dis, 8:8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41531-021-00276-6
Cuschieri A, Borg N, Zammit C, 2022. Closed loop deep brain stimulation: a systematic scoping review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg, 223:107516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2022.107516
Dale J, Schmidt SL, Mitchell K, et al., 2022. Evoked potentials generated by deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. Brain Stimul, 15(5):1040–1047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2022.07.048
Davidson B, Giacobbe P, Mithani K, et al., 2020. Lack of clinical response to deep brain stimulation of the medial forebrain bundle in depression. Brain Stimul, 13(5):1268–1270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2020.06.010
Deisseroth K, 2015. Optogenetics: 10 years of microbial opsins in neuroscience. Nat Neurosci, 18(9):1213–1225. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4091
Ding H, Lu LH, Shi Z, et al., 2018. Microscale optoelectronic infrared-to-visible upconversion devices and their use as injectable light sources. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 115(26):6632–6637. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1802064115
Drebitz E, Rausch LP, Kreiter AK, 2020. A novel approach for removing micro-stimulation artifacts and reconstruction of broad-band neuronal signals. J Neurosci Methods, 332:108549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2019.108549
Du ZJ, Kolarcik CL, Kozai TDY, et al., 2017. Ultrasoft microwire neural electrodes improve chronic tissue integration. Acta Biomater, 53:46–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2017.02.010
Elder C, Friedman D, Devinsky O, et al., 2019. Responsive neurostimulation targeting the anterior nucleus of the thalamus in 3 patients with treatment-resistant multifocal epilepsy. Epilepsia Open, 4(1):187–192. https://doi.org/10.1002/epi4.12300
Elsanadidy E, Mosa IM, Hou BW, et al., 2022. Self-sustainable intermittent deep brain stimulator. Cell Rep Phys Sci, 3(10):101099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrp.2022.101099
Eom J, Park IY, Kim S, et al., 2021. Deep-learned spike representations and sorting via an ensemble of auto-encoders. Neural Netw, 134:131–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2020.11.009
Fan JM, Khambhati AN, Sellers KK, et al., 2023. Epileptiform discharges triggered with direct electrical stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: factors that modulate risk and treatment considerations. Brain Stimul, 16(2):462–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2023.02.006
Fang H, Zhao JN, Yu KJ, et al., 2016. Ultrathin, transferred layers of thermally grown silicon dioxide as biofluid barriers for biointegrated flexible electronic systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 113(42):11682–11687. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1605269113
Fedor FZ, Madarász M, Zátonyi A, et al., 2022. Soft, thiol-ene/acrylate-based electrode array for long-term recording of intracranial EEG signals with improved biocompatibility in mice. Adv Mater Technol, 7(5):2100942. https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.202100942
Fernandes AM, Mearns DS, Donovan JC, et al., 2021. Neural circuitry for stimulus selection in the zebrafish visual system. Neuron, 109(5):805–822.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2020.12.002
Fernandez-Leon JA, Parajuli A, Franklin R, et al., 2015. A wireless transmission neural interface system for unconstrained non-human primates. J Neural Eng, 12(5):056005. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2560/12/5/056005
Fernández-Ruiz A, Oliva A, de Oliveira EF, et al., 2019. Long-duration hippocampal sharp wave ripples improve memory. Science, 364(6445):1082–1086. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aax0758
Frank JA, Antonini MJ, Anikeeva P, 2019. Next-generation interfaces for studying neural function. Nat Biotechnol, 37(9):1013–1023. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0198-8
Ghane-Motlagh B, Sawan M, 2013. Design and implementation challenges of microelectrode arrays: a review. Mater Sci Appl, 4(8):483–495. https://doi.org/10.4236/msa.2013.48059
Gong CSA, 2022. IC-based rectification circuit techniques for biomedical energy-harvesting applications. Micromachines (Basel), 13(3):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13030411
Gottschalk S, Degtyaruk O, Mc Larney B, et al., 2019. Rapid volumetric optoacoustic imaging of neural dynamics across the mouse brain. Nat Biomed Eng, 3(5):392–401. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-019-0372-9
Guan S, Wang J, Gu X, et al., 2019. Elastocapillary self-assembled neurotassels for stable neural activity recordings. Sci Adv, 5(3):eaav2842. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aav2842
Guo YY, Jiang S, Grena BJB, et al., 2017. Polymer composite with carbon nanofibers aligned during thermal drawing as a microelectrode for chronic neural interfaces. ACS Nano, 11(7):6574–6585. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.6b07550
Habets JGV, Heijmans M, Kuijf ML, et al., 2018. An update on adaptive deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord, 33(12):1834–1843. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.115
Hart WL, Kameneva T, Wise AK, et al., 2019. Biological considerations of optical interfaces for neuromodulation. Adv Opt Mater, 7(19):1900385. https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.201900385
Hickey P, Stacy M, 2016. Deep brain stimulation: a paradigm shifting approach to treat Parkinson’s disease. Front Neurosci, 10:173. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2016.00173
Hinchet R, Yoon HJ, Ryu H, et al., 2019. Transcutaneous ultrasound energy harvesting using capacitive triboelectric technology. Science, 365(6452):491–494. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aan3997
Hong GS, Lieber CM, 2019. Novel electrode technologies for neural recordings. Nat Rev Neurosci, 20(6):330–345. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-019-0140-6
Horváth ÁC, Borbély S, Mihók F, et al., 2022. Histological and electrophysiological evidence on the safe operation of a sharp-tip multimodal optrode during infrared neuromodulation of the rat cortex. Sci Rep, 12:11434. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-15367-4
Howell B, Huynh B, Grill WM, 2015. Design and in vivo evaluation of more efficient and selective deep brain stimulation electrodes. J Neural Eng, 12(4):046030. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2560/12/4/046030
Hu DW, Yao MG, Fan Y, et al., 2019. Strategies to achieve high performance piezoelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy, 55:288–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2018.10.053
Hu SL, Ciliberti D, Grosmark AD, et al., 2018. Real-time readout of large-scale unsorted neural ensemble place codes. Cell Rep, 25(10):2635–2642.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.11.033
Huang LB, Gan L, Ling BWK, 2021. A unified optimization model of feature extraction and clustering for spike sorting. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng, 29:750–759. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2021.3074162
Idogawa S, Yamashita K, Sanda R, et al., 2021. A lightweight, wireless Bluetooth-low-energy neuronal recording system for mice. Sens Actuators B Chem, 331:129423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.129423
Jang J, Baek C, Kim S, et al., 2021. Current stimulation of the midbrain nucleus in pigeons for avian flight control. Micromachines (Basel), 12(7):788. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12070788
Jarosiewicz B, Morrell M, 2021. The RNS system: brain-responsive neurostimulation for the treatment of epilepsy. Expert Rev Med Devices, 18(2):129–138. https://doi.org/10.1080/17434440.2019.1683445
Jeong JW, McCall JG, Shin G, et al., 2015. Wireless optofluidic systems for programmable in vivo pharmacology and optogenetics. Cell, 162(3):662–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.06.058
Ji BW, Ge CF, Guo ZJ, et al., 2020. Flexible and stretchable opto-electric neural interface for low-noise electrocorticogram recordings and neuromodulation in vivo. Biosens Bioelectron, 153:112009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112009
Jia YY, Mirbozorgi SA, Lee B, et al., 2019. A mm-sized freefloating wirelessly powered implantable optical stimulation device. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst, 13(4):608–618. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBCAS.2019.2918761
Jia YY, Guler U, Lai YP, et al., 2020. A trimodal wireless implantable neural interface system-on-chip. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst, 14(6):1207–1217. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBCAS.2020.3037452
Jiang LM, Lu GX, Zeng YS, et al., 2022. Flexible ultrasound-induced retinal stimulating piezo-arrays for biomimetic visual prostheses. Nat Commun, 13:3853. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-31599-4
Jørgensen LM, Henriksen T, Mardosiene S, et al., 2021. Parkinson patients have a presynaptic serotonergic deficit: a dynamic deep brain stimulation pet study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 41(8):1954–1963. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X20982389
Kampasi K, English DF, Seymour J, et al., 2018. Dual color optogenetic control of neural populations using low-noise, multishank optoelectrodes. Microsyst Nanoeng, 4:10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41378-018-0009-2
Khan IS, D’Agostino EN, Calnan DR, et al., 2019. Deep brain stimulation for memory modulation: a new frontier. World Neurosurg, 126:638–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.12.184
Khodagholy D, Ferrero JJ, Park J, et al., 2022. Large-scale, closed-loop interrogation of neural circuits underlying cognition. TrendsNeurosci, 45(12):968–983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2022.10.003
Kim CY, Ku MJ, Qazi R, et al., 2021. Soft subdermal implant capable of wireless battery charging and programmable controls for applications in optogenetics. Nat Commun, 12:535. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20803-y
Kim JH, Lee GH, Kim S, et al., 2018. Flexible deep brain neural probe for localized stimulation and detection with metal guide. Biosens Bioelectron, 117:436–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.06.035
Kim K, Vöröslakos M, Seymour JP, et al., 2020. Artifact-free and high-temporal-resolution in vivo opto-electrophysiology with microLED optoelectrodes. Nat Commun, 11:2063. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15769-w
Kim T, Kadji H, Whalen AJ, et al., 2022. Thermal effects on neurons during stimulation of the brain. J Neural Eng, 19(5):056029. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/ac9339
Kim TI, McCall JG, Jung YH, et al., 2013. Injectable, cellular-scale optoelectronics with applications for wireless optogenetics. Science, 340(6129):211–216. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1232437
Király B, Balazsfi D, Horvath I, et al., 2020. In vivo localization of chronically implanted electrodes and optic fibers in mice. Nat Commun, 11:4686. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18472-y
Krauss JK, Lipsman N, Aziz T, et al., 2021. Technology of deep brain stimulation: current status and future directions. Nat Rev Neurol, 17(2):75–87. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-020-00426-z
Kuan YC’ Lo YK, Kim Y, et al., 2015. Wireless gigabit data telemetry for large-scale neural recording. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, 19(3):949–957. https://doi.org/10.1109/jbhi.2015.2416202
Kumari LS, Kouzani AZ, 2023. Electrophysiology-based closed loop optogenetic brain stimulation devices: recent developments and future prospects. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng, 16:91–108. https://doi.org/10.1109/RBME.2022.3141369
Kwarteng E, Cebe M, 2022. A survey on security issues in modern Implantable Devices: solutions and future issues. Smart Health, 25:100295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smhl.2022.100295
Lanzio V, Telian G, Koshelev A, et al., 2021. Small footprint optoelectrodes using ring resonators for passive light localization. Microsyst Nanoeng, 7:40. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41378-021-00263-0
Lecomte A, Descamps E, Bergaud C, 2018. A review on mechanical considerations for chronically-implanted neural probes. J Neural Eng, 15(3):031001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/aa8b4f
Lee B, Koripalli MK, Jia YY, et al., 2018. An implantable peripheral nerve recording and stimulation system for experiments on freely moving animal subjects. Sci Rep, 8:6115. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-24465-1
Lee B, Jia YY, Mirbozorgi SA, et al., 2019. An inductively-powered wireless neural recording and stimulation system for freely-behaving animals. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst, 13(2):413–424. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBCAS.2019.2891303
Lee D, Jeong SH, Yun S, et al., 2021. Totally implantable enzymatic biofuel cell and brain stimulator operating in bird through wireless communication. Biosens Bioelectron, 171:112746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112746
Lee J, Ozden I, Song YK, et al., 2015. Transparent intracortical microprobe array for simultaneous spatiotemporal optical stimulation and multichannel electrical recording. Nat Methods, 12(12):1157–1162. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3620
Lee JM, Lin DC, Kim HR, et al., 2021. All-tissue-like multifunctional optoelectronic mesh for deep-brain modulation and mapping. Nano Lett, 21(7):3184–3190. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c00425
Lee KJ, Hong D, Jang JW, et al., 2023. A wireless ECoG recording system to detect brain responses to tactile stimulation. IEEE Sens J, 23(12):13692–13701. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2023.3272630
Lee S, Cortese AJ, Gandhi AP, et al., 2018. A 250 µm×57 µm microscale opto-electronically transduced electrodes (MOTEs) for neural recording. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst, 12(6):1256–1266. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBCAS.2018.2876069
Lehto LJ, Canna A, Wu L, et al., 2020. Orientation selective deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in rats. Neuroimage, 213:116750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.116750
Leibig C, Wachtler T, Zeck G, 2016. Unsupervised neural spike sorting for high-density microelectrode arrays with convolutive independent component analysis. J Neurosci Methods, 271:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2016.06.006
Li DF, Wang W, Wang HJ, et al., 2008. Polyaniline films with nanostructure used as neural probe coating surfaces. Appl Surf Sci, 255(2):581–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.06.150
Li JN, Cheng YH, Gu ML, et al., 2023. Sensing and stimulation applications of carbon nanomaterials in implantable brain-computer interface. Int J Mol Sci, 24(6):5182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065182
Li RH, Hosseini H, Saggar M, et al., 2023. Current opinions on the present and future use of functional near-infrared spectroscopy in psychiatry. Neurophotonics, 10(1):013505. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.NPh.10.1.013505
Li ZH, Wang YT, Zhang N, et al., 2020. An accurate and robust method for spike sorting based on convolutional neural networks. Brain Sci, 10(11):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10110835
Libbrecht S, Hoffman L, Welkenhuysen M, et al., 2018. Proximal and distal modulation of neural activity by spatially confined optogenetic activation with an integrated high-density optoelectrode. J Neurophysiol, 120(1):149–161. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00888.2017
Ling W, Yu JX, Ma N, et al., 2020. Flexible electronics and materials for synchronized stimulation and monitoring in multi-encephalic regions. Adv Funct Mater, 30(32):2002644. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202002644
Liu CB, Zhao Y, Cai X, et al., 2020. A wireless, implantable optoelectrochemical probe for optogenetic stimulation and dopamine detection. Microsyst Nanoeng, 6:64. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41378-020-0176-9
Liu SJ, Liu L, Zhao Y, et al., 2022. A high-performance electrode based on van der Waals heterostructure for neural recording. Nano Lett, 22(11):4400–4409. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c00848
Liu X, Lu YC, Iseri E, et al., 2018. A compact closed-loop optogenetics system based on artifact-free transparent graphene electrodes. Front Neurosci, 12:132. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00132
Liu XL, Zhu HJ, Qiu T, et al., 2021. A fully integrated sensor-brain-machine interface system for restoring somatosensation. IEEE Sens J, 21(4):4764–4775. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2020.3030899
Lo MC, Widge AS, 2017. Closed-loop neuromodulation systems: next-generation treatments for psychiatric illness. Int Rev Psychiatry, 29(2):191–204. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540261.2017.1282438
Luan L, Robinson JT, Aazhang B, et al., 2020. Recent advances in electrical neural interface engineering: minimal invasiveness, longevity, and scalability. Neuron, 108(2):302–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2020.10.011
Lyu HM, Wang JG, La JH, et al., 2018. An energy-efficient wirelessly powered millimeter-scale neurostimulator implant based on systematic codesign of an inductive loop antenna and a custom rectifier. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst, 12(5):1131–1143. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBCAS.2018.2852680
Mager T, de la Morena DL, Senn V, et al., 2018. High frequency neural spiking and auditory signaling by ultrafast red-shifted optogenetics. Nat Commun, 9:1750. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04146-3
Maimon BE, Sparks K, Srinivasan S, et al., 2018. Spectrally distinct channelrhodopsins for two-colour optogenetic peripheral nerve stimulation. Nat Biomed Eng, 2(7):485–496. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-018-0255-5
Martínez S, Garcia-Violini D, Belluscio M, et al., 2023. Dynamical models in neuroscience from a closed-loop control perspective. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng, 16:706–721. https://doi.org/10.1109/RBME.2022.3180559
Matsushita K, Hirata M, Suzuki T, et al., 2018. A fully implantable wireless ECoG 128-channel recording device for human brain-machine interfaces: W-HERBS. Front Neurosci, 12:511. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00511
McIntyre CC, Chaturvedi A, Shamir RR, et al., 2015. Engineering the next generation of clinical deep brain stimulation technology. Brain Stimul, 8(1):21–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2014.07.039
Menchón JM, Real E, Alonso P, et al., 2021. A prospective international multi-center study on safety and efficacy of deep brain stimulation for resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder. Mol Psychiatry, 26(4):1234–1247. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-019-0562-6
Mendrela AE, Kim K, English D, et al., 2018. A high-resolution opto-electrophysiology system with a miniature integrated headstage. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst, 12(5):1065–1075. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBCAS.2018.2852267
Meng L, Jin MY, Zhu XD, et al., 2022. Peripherical electrical stimulation for Parkinsonian tremor: a systematic review. Front Aging Neurosci, 14:795454. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2022.795454
Moghaddasi M, Shoorehdeli MA, Fatahi Z, et al., 2020. Unsupervised automatic online spike sorting using reward-based online clustering. Biomed Signal Process Control, 56:101701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2019.101701
Mohanty A, Li Q, Tadayon MA, et al., 2020. Reconfigurable nanophotonic silicon probes for sub-millisecond deep-brain optical stimulation. Nat Biomed Eng, 4(2):223–231. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-020-0516-y
Molina R, Hass CJ, Cernera S, et al., 2021. Closed-loop deep brain stimulation to treat medication-refractory freezing of gait in Parkinson’s disease. Front Hum Neurosci, 15:633655. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2021.633655
Ng KA, Greenwald E, Xu YP, et al., 2016. Implantable neurotechnologies: a review of integrated circuit neural amplifiers. Med Biol Eng Comput, 54:45–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-015-1431-3
Nordi TM, Gounella RH, Luppe M, et al., 2022. Low-noise amplifier for deep-brain stimulation (DBS). Electronics, 11(6):939. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11060939
Normann RA, Fernandez E, 2016. Clinical applications of penetrating neural interfaces and Utah Electrode Array technologies. J Neural Eng, 13(6):061003. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2560/13/6/061003
Obaid S, Lu LY, 2019. Highly efficient microscale gallium arsenide solar cell arrays as optogenetic power options. IEEE Photonics J, 11(1):8400108. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPHOT.2019.2896005
Obien MEJ, Deligkaris K, Bullmann T, et al., 2015. Revealing neuronal function through microelectrode array recordings. Front Neurosci, 8:423. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2014.00423
Ohta Y, Guinto MC, Tokuda T, et al., 2021. Micro-LED array-based photo-stimulation devices for optogenetics in rat and macaque monkey brains. IEEE Access, 9:127937–127949. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3111666
Oldroyd P, Malliaras GG, 2022. Achieving long-term stability of thin-film electrodes for neurostimulation. Acta Biomater, 139:65–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2021.05.004
Ouyang H, Liu Z, Li N, et al., 2019. Symbiotic cardiac pacemaker. Nat Commun, 10:1821. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09851-1
Pang N, Meng W, Zhong YS, et al., 2022. Ultrasound deep brain stimulation modulates body temperature in mice. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng, 30:1851–1857. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2022.3188516
Parastarfeizabadi M, Kouzani AZ, 2017. Advances in closed-loop deep brain stimulation devices. J Neuroeng Rehabil, 14:79. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12984-017-0295-1
Park S, Heo SW, Lee W, et al., 2018. Self-powered ultra-flexible electronics via nano-grating-patterned organic photovoltaics. Nature, 561(7724):516–521. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0536-x
Patel B, Chiu S, Wong JK, et al., 2021. Deep brain stimulation programming strategies: segmented leads, independent current sources, and future technology. Expert Rev Med Devices, 18(9):875–891. https://doi.org/10.1080/17434440.2021.1962286
Paz JT, Davidson TJ, Frechette ES, et al., 2013. Closed-loop optogenetic control of thalamus as a tool for interrupting seizures after cortical injury. Nat Neurosci, 16(1):64–70. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3269
Petrucci MN, Anderson RW, O’Day JJ, et al., 2020. A closed-loop deep brain stimulation approach for mitigating burst durations in people with Parkinson’s disease. Proceedings of the 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society. IEEE, Montreal, QC, Canada, p.3617–3620. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC44109.2020.9176196
Pfau J, Ganatra D, Weltin A, et al., 2019. Electrochemical stability of thin-film platinum as suitable material for neural stimulation electrodes. 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). Berlin, Germany, p.3762–3765. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2019.8856621.
Pimenta S, Rodrigues JA, Machado F, et al., 2021. Double-layer flexible neural probe with closely spaced electrodes for high-density in vivo brain recordings. Front Neurosci, 15:663174. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.663174
Pisanello F, Sileo L, Oldenburg IA, et al., 2014. Multipointemitting optical fibers for spatially addressable in vivo optogenetics. Neuron, 82(6):1245–1254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.04.041
Pol S, Temel Y, Jahanshahi A, 2021. A custom made electrode construct and reliable implantation method that allows for long-term bilateral deep brain stimulation in mice. Neuromodulation, 24(2):212–219. https://doi.org/10.1111/ner.13165
Poojari Y, 2017. Silicones for encapsulation of medical device implants. Silicon, 9(5):645–649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-017-9603-4
Pool JL, 1954. Psychosurgery in older people. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2(7):456–466. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.1954.tb02138.x
Pranti AS, Schander A, Bödecker A, et al., 2017. Highly stable PEDOT: PSS coating on gold microelectrodes with improved charge injection capacity for chronic neural stimulation. Proceedings, 1(4):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040492
Price JB, Rusheen AE, Barath AS, et al., 2020. Clinical applications of neurochemical and electrophysiological measurements for closed-loop neurostimulation. Neurosurg Focus, 49(1):E6. https://doi.org/10.3171/2020AFOCUS20167
Provenza NR, Sheth SA, Dastin-van Rijn EM, et al., 2021. Long-term ecological assessment of intracranial electrophysiology synchronized to behavioral markers in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Nat Med, 27(12):2154–2164. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-021-01550-z
Qian X, Chen Y, Feng Y, et al., 2017. A method for removal of deep brain stimulation artifact from local field potentials. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng, 25(12):2217–2226. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2016.2613412
Rácz M, Liber C, Németh E, et al., 2020. Spike detection and sorting with deep learning. J Neural Eng, 17(1):016038. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/ab4896
Rahman A, Siddik AB, Ghosh TK, et al., 2020. A narrative review on clinical applications of fNIRS. J Digit Imaging, 33(5):1167–1184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-020-00387-1
Ramot M, Martin A, 2022. Closed-loop neuromodulation for studying spontaneous activity and causality. Trends Cogn Sci, 26(4):290–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2022.01.008
Rhew HG, Jeong J, Fredenburg JA, et al., 2014. A fully self-contained logarithmic closed-loop deep brain stimulation SoC with wireless telemetry and wireless power management. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 49(10):2213–2227. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSSC.2014.2346779
Riva-Posse P, Choi KS, Holtzheimer PE, et al., 2018. A connectomic approach for subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation surgery: prospective targeting in treatment-resistant depression. Mol Psychiatry, 23(4):843–849. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2017.59
Roca E, Gobetti A, Cornacchia G, et al., 2023. An expandable chamber for safe brain retraction: new technologies in the field of transcranial endoscopic surgery. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 24(4):326–335. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200557
Ryvlin P, Jehi LE, 2022. Neuromodulation for refractory epilepsy. Epilepsy Curr, 22(1):11–17. https://doi.org/10.1177/15357597211065587
Scangos KW, Makhoul GS, Sugrue LP, et al., 2021a. State-dependent responses to intracranial brain stimulation in a patient with depression. Nat Med, 27(2):229–231. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-01175-8
Scangos KW, Khambhati AN, Daly PM, et al., 2021b. Closed-loop neuromodulation in an individual with treatment-resistant depression. Nat Med, 27(10):1696–1700. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-021-01480-w
Schwarz DA, Lebedev MA, Hanson TL, et al., 2014. Chronic, wireless recordings of large-scale brain activity in freely moving rhesus monkeys. Nat Methods, 11(6):670–676. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2936
Seo D, Neely RM, Shen K, et al., 2016. Wireless recording in the peripheral nervous system with ultrasonic neural dust. Neuron, 91(3):529–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.06.034
Shabbir I, Lee DM, Choo DC, et al., 2022. A graphene nanoplatelets-based high-performance, durable triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting the energy of human motion. Energy Rep, 8:1026–1033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2021.12.020
Shi ZF, Zheng FM, Zhou ZT, et al., 2019. Silk-enabled conformal multifunctional bioelectronics for investigation of spatiotemporal epileptiform activities and multimodal neural encoding/decoding. Adv Sci, 6(9):1801617. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201801617
Shim E, Chen Y, Masmanidis S, et al., 2016. Multisite silicon neural probes with integrated silicon nitride waveguides and gratings for optogenetic applications. Sci Rep, 6:22693. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22693
Shim S, Yun S, Kim S, et al., 2020. A handheld neural stimulation controller for avian navigation guided by remote control. Biomed Mater Eng, 30(5–6):497–507. https://doi.org/10.3233/BME-191070
Shin G, Gomez AM, Al-Hasani R, et al., 2017. Flexible near-field wireless optoelectronics as subdermal implants for broad applications in optogenetics. Neuron, 93(3):509–521.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.12.031
Sierra RO, Pedraza LK, Barcsai L, et al., 2023. Closed-loop brain stimulation augments fear extinction in male rats. Nat Commun, 14:3972. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-39546-7
Silverå Ejneby M, Jakesová M, Ferrero JJ, et al., 2022. Chronic electrical stimulation of peripheral nerves via deep-red light transduced by an implanted organic photocapacitor. Nat Biomed Eng, 6(6):741–753. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-021-00817-7
Sitã L, Brondi M, de Leon Roig PL, et al., 2022. A deep-learning approach for online cell identification and trace extraction in functional two-photon calcium imaging. Nat Commun, 13:1529. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29180-0
Slopsema JP, Canna A, Uchenik M, et al., 2021. Orientation-selective and directional deep brain stimulation in swine assessed by functional MRI at 3T. NeuroImage, 224:117357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117357
Solanki S, Gupta AK, Saha U, et al., 2023. Triboelectric Nanogenerator-based smart biomedical sensors for healthcare. Sustain Energy Technol Assess, 57:103233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2023.103233
Su F, Kumaravelu K, Wang J, et al., 2019. Model-based evaluation of closed-loop deep brain stimulation controller to adapt to dynamic changes in reference signal. Front Neurosci, 13:956. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00956
Su F, Chen M, Zu LL, et al., 2021. Model-based closed-loop suppression of parkinsonian beta band oscillations through origin analysis. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng, 29:450–457. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2021.3056544
Su Y, Routhu S, Moon KS, et al., 2016. A wireless 32-channel implantable bidirectional brain machine interface. Sensors, 16(10):1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16101582
Tala F, Leiber J, Fisher H, et al., 2021. A low-cost, wireless, multi-channel deep brain stimulation system for rodents. Proceedings of the 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC). IEEE, Mexico, p.7526–7529. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC46164.2021.9629826
Telkes I, Viswanathan A, Jimenez-Shahed J, et al., 2018. Local field potentials of subthalamic nucleus contain electro-physiological footprints of motor subtypes of Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 115(36):E8567–E8576. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1810589115
Thiele S, Sörensen A, Weis J, et al., 2020. Deep brain stimulation of the medial forebrain bundle in a rodent model of depression: exploring dopaminergic mechanisms with raclopride and micro-PET. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg, 98(1):8–20. https://doi.org/10.1159/000504860
Thunemann M, Lu YC, Liu X, et al., 2018. Deep 2-photon imaging and artifact-free optogenetics through transparent graphene microelectrode arrays. Nat Commun, 9:2035. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04457-5
Tinkhauser G, Pogosyan A, Little S, et al., 2017. The modulatory effect of adaptive deep brain stimulation on beta bursts in Parkinson’s disease. Brain, 140(4):1053–1067. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awx010
Topalovic U, Aghajan ZM, Villaroman D, et al., 2020. Wireless programmable recording and stimulation of deep brain activity in freely moving humans. Neuron, 108(2):322–334.e9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2020.08.021
Topalovic U, Barclay S, Ling CK, et al., 2023. A wearable platform for closed-loop stimulation and recording of single-neuron and local field potential activity in freely moving humans. Nat Neurosci, 26(3):517–527. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-023-01260-4
Tremblay S, Acker L, Afraz A, et al., 2020. An open resource for non-human primate optogenetics. Neuron, 108(6):1075–1090.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2020.09.027
van der Wal JM, Bergfeld IO, Lok A, et al., 2020. Long-term deep brain stimulation of the ventral anterior limb of the internal capsule for treatment-resistant depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 91(2):189–195. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2019-321758
Walker EY, Sinz FH, Cobos E, et al., 2019. Inception loops discover what excites neurons most using deep predictive models. Nat Neurosci, 22(12):2060–2065. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-019-0517-x
Wang L, Fei ZX, Wu ZT, et al., 2023. Wearable bending wireless sensing with autonomous wake-up by piezoelectric and triboelectric hybrid nanogenerator. Nano Energy, 112:108504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2023.108504
Wang LC, Ge CF, Wang MH, et al., 2020. An artefact-resist optrode with internal shielding structure for low-noise neural modulation. J Neural Eng, 17(4):046024. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/aba41f
Wang YD, Song YL, Dai YC, et al., 2022. The burst of electrophysiological signals in the suprachiasmatic nucleus of mouse during the arousal detected by microelectrode arrays. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 10:970726. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.970726
White M, Mackay M, Whittaker RG, 2020. Taking optogenetics into the human brain: opportunities and challenges in clinical trial design. Open Access J Clin Trials, 2020:33–41. https://doi.org/10.2147/OAJCT.S259702
Wright JP, Mughrabi IT, Wong J, et al., 2022. A fully implantable wireless bidirectional neuromodulation system for mice. Biosens Bioelectron, 200:113886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113886
Xu HJ, Scholten K, Jiang WX, et al., 2022. Acute in vivo recording with a generic parylene microelectrode array implanted with dip-coating method into the rat brain. Proceedings of the 44th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC). Glasgow, Scotland, United Kingdom, p. 214–217. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC48229.2022.9870987
Yang X, Zhou T, Zwang TJ, et al., 2019. Bioinspired neuronlike electronics. Nat Mater, 18(5):510–517. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-019-0292-9
Yao G, Kang L, Li J, et al., 2018. Effective weight control via an implanted self-powered vagus nerve stimulation device. Nat Commun, 9:5349. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07764-z
Yu NB, Liang SQ, Lu JW, et al., 2021. Quantified assessment of deep brain stimulation on Parkinson’s patients with task fNIRS measurements and functional connectivity analysis: a pilot study. Chin Neurosurg J, 7:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-021-00251-3
Yun S, Koh CS, Jeong J, et al., 2019. Remote-controlled fully implantable neural stimulator for freely moving small animal. Electronics, 8(6):706. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8060706
Zaaimi B, Turnbull M, Hazra A, et al., 2023. Closed-loop optogenetic control of the dynamics of neural activity in non-human primates. Nat Biomed Eng, 7(4):559–575. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-022-00945-8
Zaer H, Deshmukh A, Orlowski D, et al., 2021. An intracortical implantable brain-computer interface for telemetric real-time recording and manipulation of neuronal circuits for closed-loop intervention. Front Hum Neurosci, 15:618626. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2021.618626
Zanos S, 2019. Closed-loop neuromodulation in physiological and translational research. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med, 9(11):a034314. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a034314
Zátonyi A, Orban G, Modi R, et al., 2019. A softening laminar electrode for recording single unit activity from the rat hippocampus. SciRep, 9:2321. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-39835-6
Zeng Q, Yu SJ, Fan ZH, et al., 2022. Nanocone-array-based platinum-iridium oxide neural microelectrodes: structure, electrochemistry, durability and biocompatibility study. Nanomaterials, 12(19):3445. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193445
Zhang CC, Zhang YY, Zhan SK, et al., 2018. Telemedical deep brain stimulation: merits and limitations. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg, 96(4):272–273. https://doi.org/10.1159/000491603
Zhang F, Aghagolzadeh M, Oweiss K, 2012. A fully implantable, programmable and multimodal neuroprocessor for wireless, cortically controlled brain-machine interface applications. J Signal Process Syst, 69(3):351–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-012-0670-x
Zhang QS, Hu SL, Talay R, et al., 2023. A prototype closed-loop brain-machine interface for the study and treatment of pain. Nat Biomed Eng, 7(4):533–545. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-021-00736-7
Zhang S, Zhang XP, Zhong HL, et al., 2022. Hypothermia evoked by stimulation of medial preoptic nucleus protects the brain in a mouse model of ischaemia. Nat Commun, 13:6890. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-34735-2
Zhang SY, Yoshida W, Mano H, et al., 2020. Pain control by co-adaptive learning in a brain-machine interface. Curr Biol, 30(20):3935–3944.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2020.07.066
Zhang Z, Li YF, Mouthaan K, et al., 2018. A miniature mode reconfigurable inductorless IR-UWB transmitter-receiver for wireless short-range communication and vital-sign sensing. IEEE J Emerg Sel Top Circuits Syst, 8(2):294–305. https://doi.org/10.1109/JETCAS.2018.2799930
Zhang ZH, Russell LE, Packer AM, et al., 2018. Closed-loop all-optical interrogation of neural circuits in vivo. Nat Methods, 15(12):1037–1040. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-018-0183-z
Zhao D, Sun Q, Cheng S, et al., 2018. Extraction of Parkinson’s disease-related features from local field potentials for adaptive deep brain stimulation. Neurophysiology, 50(1):57–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-018-9717-3
Zhao SY, Li G, Tong CJ, et al., 2020. Full activation pattern mapping by simultaneous deep brain stimulation and fMRI with graphene fiber electrodes. Nat Commun, 11:1788. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15570-9
Zhao Y, Liu CB, Liu ZX, et al., 2019. Wirelessly operated, implantable optoelectronic probes for optogenetics in freely moving animals. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 66(1):785–792. https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2018.2882397
Zhou A, Santacruz SR, Johnson BC, et al., 2019. A wireless and artefact-free 128-channel neuromodulation device for closed-loop stimulation and recording in non-human primates. Nat Biomed Eng, 3(1):15–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-018-0323-x
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. T2293730, T2293731, 62121003, 61960206012, 61973292, 62171434, 61975206, and 61971400), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Nos. 2022YFC2402501 and 2022YFB3205602), the Major Program of Scientific and Technical Innovation 2030 (No. 2021ZD02016030), and the Scientific Instrument Developing Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. GJJSTD20210004). We thank Dr. Yilin SONG (State Key Laboratory of Transducer Technology, Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China) for her advice on grammar revisions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qianli JIA, Xinxia CAI, and Mixia WANG investigated the literature, and conceived and wrote the manuscript and drew figures. Xinxia CAI, Mixia WANG, Yaoyao LIU, Shiya LV, Yiding WANG, Peiyao JIAO, Wei XU, and Zhaojie XU checked the paper and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved to the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Qianli JIA, Yaoyao LIU, Shiya LV, Yiding WANG, Peiyao JIAO, Wei XU, Zhaojie XU, Mixia WANG, and Xinxia CAI declare that they have no conflict of interest.
This review does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Q., Liu, Y., Lv, S. et al. Wireless closed-loop deep brain stimulation using microelectrode array probes. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B (2024). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2300400
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2300400
Key words
- Deep brain stimulation (DBS)
- Wireless closed-loop deep brain stimulation (CL-DBS) microsystem
- Microelectrode array (MEA) probe
- Optical stimulation
- Electrical stimulation