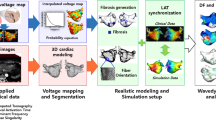
Abstract
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the most common arrhythmias, associated with high morbidity, mortality, and healthcare costs, and it places a significant burden on both individuals and society. Anti-arrhythmic drugs are the most commonly used strategy for treating AF. However, drug therapy faces challenges because of its limited efficacy and potential side effects. Catheter ablation is widely used as an alternative treatment for AF. Nevertheless, because the mechanism of AF is not fully understood, the recurrence rate after ablation remains high. In addition, the outcomes of ablation can vary significantly between medical institutions and patients, especially for persistent AF. Therefore, the issue of which ablation strategy is optimal is still far from settled. Computational modeling has the advantages of repeatable operation, low cost, freedom from risk, and complete control, and is a useful tool for not only predicting the results of different ablation strategies on the same model but also finding optimal personalized ablation targets for clinical reference and even guidance. This review summarizes three-dimensional computational modeling simulations of catheter ablation for AF, from the early-stage attempts such as Maze III or circumferential pulmonary vein isolation to the latest advances based on personalized substrate-guided ablation. Finally, we summarize current developments and challenges and provide our perspectives and suggestions for future directions.
概要
房颤(atrial fibrillation, AF)是最常见的心律失常之一, 临床危害极大. 虽然抗心律失常药物是治疗房颤最常用的策略, 但是药物治疗因其有限的疗效和潜在的副作用而面临挑战. 导管消融术作为一种替代方案被广泛用于治疗房颤患者. 然而, 由于房颤的机制还不完全清楚, 消融术后的复发率仍然很高, 尤其是持续性房颤. 因此, 何种消融策略是最优的一直是临床亟待解决的问题. 计算模型具有可重复操作、 低成本、 低风险和灵活可控等优点, 不仅可以在同一模型上预测不同消融策略的结果, 还可以找到最佳的个性化消融靶点供临床参考. 本综述总结了三维计算模型仿真房颤导管消融策略的进展, 从早期的迷宫术或环肺静脉隔离术到基于特异性底物的个性化消融方式. 最后, 我们总结了目前的发展和面临的挑战, 并对未来的发展方向提出了看法和建议.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed A, Ullah W, Hussain I, et al., 2019. Atrial fibrillation: a leading cause of heart failure-related hospitalizations; a dual epidemic. Am J Cardiovasc Dis, 9(5): 109–115.
Alessandrini M, Valinoti M, Unger L, et al., 2018. A computational framework to benchmark basket catheter guided ablation in atrial fibrillation. Front Physiol, 9:1251. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01251
Ali RL, Hakim JB, Boyle PM, et al., 2019. Arrhythmogenic propensity of the fibrotic substrate after atrial fibrillation ablation: a longitudinal study using magnetic resonance imaging-based atrial models. Cardiovasc Res, 115(12): 1757–1765. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvz083
Bayer JD, Roney CH, Pashaei A, et al., 2016. Novel radiofrequency ablation strategies for terminating atrial fibrillation in the left atrium: a simulation study. Front Physiol, 7:108. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2016.00108
Bayer JD, Boukens BJ, Krul SPJ, et al., 2019. Acetylcholine delays atrial activation to facilitate atrial fibrillation. Front Physiol, 10:1105. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.01105
Benjamin EJ, Blaha MJ, Chiuve SE, et al., 2017. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 Update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation, 135(10): e146–e603. https://doi.org/10.1161/cir.0000000000000485
Bhatti A, Oakeshott P, Dhinoja M, et al., 2019. Ablation therapy in atrial fibrillation. BMJ, 367:l6428. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l6428
Boyle PM, Hakim JB, Zahid S, et al., 2018a. Comparing reentrant drivers predicted by image-based computational modeling and mapped by electrocardiographic imaging in persistent atrial fibrillation. Front Physiol, 9:414. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00414
Boyle PM, Hakim JB, Zahid S, et al., 2018b. The fibrotic substrate in persistent atrial fibrillation patients: comparison between predictions from computational modeling and measurements from focal impulse and rotor mapping. Front Physiol, 9:1151. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01151
Boyle PM, Zghaib T, Zahid S, et al., 2019. Computationally guided personalized targeted ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation. Nat Biomed Eng, 3(11):870–879. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-019-0437-9
Cantwell CD, Mohamied Y, Tzortzis KN, et al., 2019. Rethinking multiscale cardiac electrophysiology with machine learning and predictive modelling. Comput Biol Med, 104:339–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.10.015
Chrispin J, Gucuk Ipek E, Zahid S, et al., 2016. Lack of regional association between atrial late gadolinium enhancement on cardiac magnetic resonance and atrial fibrillation rotors. Heart Rhythm, 13(3):654–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.11.011
Cochet H, Dubois R, Yamashita S, et al., 2018. Relationship between fibrosis detected on late gadolinium-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance and re-entrant activity assessed with electrocardiographic imaging in human persistent atrial fibrillation. JACC Clin Electrophysiol, 4(1):17–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacep.2017.07.019
Conti S, Weerasooriya R, Novak P, et al., 2018. Contact force sensing for ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation: a randomized, multicenter trial. Heart Rhythm, 15(2):201–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2017.10.010
Courtemanche M, Ramirez RJ, Nattel S, 1998. Ionic mechanisms underlying human atrial action potential properties: insights from a mathematical model. Am J Physiol, 275(1):H301–H321. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.1998.275.1.H301
Cox JL, Schuessler RB, D’Agostino HJ Jr, et al., 1991. The surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation. III. Development of a definitive surgical procedure. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 101(4):569–583.
Dang L, Virag N, Ihara Z, et al., 2005. Evaluation of ablation patterns using a biophysical model of atrial fibrillation. Ann Biomed Eng, 33(4):465–474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-005-2502-7
Deng DD, Jiao PF, Ye XS, et al., 2012. An image-based model of the whole human heart with detailed anatomical structure and fiber orientation. Comput Math Methods Med, 2012:891070. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/891070
Deng DD, Murphy MJ, Hakim JB, et al., 2017. Sensitivity of reentrant driver localization to electrophysiological parameter variability in image-based computational models of persistent atrial fibrillation sustained by a fibrotic substrate. Chaos, 27(9):093932. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5003340
Dewire J, Calkins H, 2013. Update on atrial fibrillation catheter ablation technologies and techniques. Nat Rev Cardiol, 10(10):599–612. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2013.121
Fochler F, Yamaguchi T, Kheirkahan M, et al., 2019. Late gadolinium enhancement magnetic resonance imaging guided treatment of post-atrial fibrillation ablation recurrent arrhythmia. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 12(8): e007174. https://doi.org/10.1161/circep.119.007174
Ganesan AN, Kuklik P, Lau DH, et al., 2013. Bipolar electrogram Shannon entropy at sites of rotational activation: implications for ablation of atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 6(1):48–57. https://doi.org/10.1161/circep.112.976654
Gharaviri A, Pezzuto S, Potse M, et al., 2021. Left atrial appendage electrical isolation reduces atrial fibrillation recurrences: a simulation study. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 14(1):e009230. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCEP.120.009230
Giffard-Roisin S, Jackson T, Fovargue L, et al., 2017. Noninvasive personalization of a cardiac electrophysiology model from body surface potential mapping. IEEE Trans Bio-Med Eng, 64(9):2206–2218. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2016.2629849
Gong YF, Xie FG, Stein KM, et al., 2007. Mechanism underlying initiation of paroxysmal atrial flutter/atrial fibrillation by ectopic foci: a simulation study. Circulation, 115(16):2094–2102. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.106.656504
Gong YL, Gao Y, Lu ZH, et al., 2015. Preliminary simulation study of atrial fibrillation treatment procedure based on a detailed human atrial model. J Clin Trial Cardiol, 2(4): 1–9. https://doi.org/10.15226/2374-6882/2/4/00130
Ha ACT, Wijeysundera HC, Birnie DH, et al., 2017. Real-world outcomes, complications, and cost of catheter-based ablation for atrial fibrillation: an update. Curr Opin Cardiol, 32(1):47–52. https://doi.org/10.1097/hco.0000000000000348
Haïssaguerre M, Jaïs P, Shah DC, et al., 1998. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N Engl J Med, 339(10):659–666. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199809033391003
Haissaguerre M, Shah AJ, Cochet H, et al., 2016. Intermittent drivers anchoring to structural heterogeneities as a major pathophysiological mechanism of human persistent atrial fibrillation. J Physiol, 594(9):2387–2398. https://doi.org/10.1113/jp270617
Hakalahti A, Biancari F, Nielsen JC, et al., 2015. Radiofrequency ablation vs. antiarrhythmic drug therapy as first line treatment of symptomatic atrial fibrillation: systematic review and meta-analysis. Europace, 17(3):370–378. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euu376
Hakim JB, Murphy MJ, Trayanova NA, et al., 2018. Arrhythmia dynamics in computational models of the atria following virtual ablation of re-entrant drivers. Europace, 20(S3): iii45–iii54. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euy234
Heijman J, Algalarrondo V, Voigt N, et al., 2016. The value of basic research insights into atrial fibrillation mechanisms as a guide to therapeutic innovation: a critical analysis. Cardiovasc Res, 109(4):467–479. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvv275
Ho SY, Sánchez-Quintana D, 2009. The importance of atrial structure and fibers. Clin Anat, 22(1):52–63. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.20634
Hwang M, Kwon SS, Wi J, et al., 2014. Virtual ablation for atrial fibrillation in personalized in-silico three-dimensional left atrial modeling: comparison with clinical catheter ablation. Prog Biophys Mol Biol, 116(1):40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2014.09.006
Hwang M, Song JS, Lee YS, et al., 2016. Electrophysiological rotor ablation in in-silico modeling of atrial fibrillation: comparisons with dominant frequency, Shannon entropy, and phase singularity. PLoS ONE, 11(2):e0149695. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0149695
Kaboudian A, Cherry EM, Fenton FH, 2019. Real-time interactive simulations of large-scale systems on personal computers and cell phones: toward patient-specific heart modeling and other applications. Sci Adv, 5(3):eaav6019. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aav6019
Kim IS, Lim B, Shim J, et al., 2019. Clinical usefulness of computational modeling-guided persistent atrial fibrillation ablation: updated outcome of multicenter randomized study. Front Physiol, 10:1512. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.01512
Kim TH, Uhm JS, Kim JY, et al., 2017. Does additional electrogram-guided ablation after linear ablation reduce recurrence after catheter ablation for longstanding persistent atrial fibrillation? A prospective randomized study. J Am Heart Assoc, 6(2):e004811. https://doi.org/10.1161/jaha.116.004811
Latchamsetty R, Morady F, 2018. Atrial fibrillation ablation. Annu Rev Med, 69:53–63. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-med-041316-090015
Li Y, Wu YF, Chen KP, et al., 2013. Prevalence of atrial fibrillation in China and its risk factors. Biomed Environ Sci, 26(9):709–716. https://doi.org/10.3967/0895-3988.2013.09.001
Lim B, Hwang M, Song JS, et al., 2017. Effectiveness of atrial fibrillation rotor ablation is dependent on conduction velocity: an in-silico 3-dimensional modeling study. PLoS ONE, 12(12):e0190398. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0190398
Lim B, Park JW, Hwang M, et al., 2020a. Electrophysiological significance of the interatrial conduction including cavotricuspid isthmus during atrial fibrillation. J Physiol, 598(17):3597–3612. https://doi.org/10.1113/jp279660
Lim B, Kim J, Hwang M, et al., 2020b. In situ procedure for high-efficiency computational modeling of atrial fibrillation reflecting personal anatomy, fiber orientation, fibrosis, and electrophysiology. Sci Rep, 10:2417. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-59372-x
Luo CH, Rudy Y, 1991. A model of the ventricular cardiac action potential. Depolarization, repolarization, and their interaction. Circ Res, 68(6):1501–1526. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.res.68.6.1501
Mărgulescu AD, Nuñez-Garcia M, Alarcón F, et al., 2019. Reproducibility and accuracy of late gadolinium enhancement cardiac magnetic resonance measurements for the detection of left atrial fibrosis in patients undergoing atrial fibrillation ablation procedures. Europace, 21(5):724–731. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euy314
McDowell KS, Zahid S, Vadakkumpadan F, et al., 2015. Virtual electrophysiological study of atrial fibrillation in fibrotic remodeling. PLoS ONE, 10(2):e0117110. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0117110
Miller CAS, Maron MS, Estes NAM III, et al., 2019. Safety, side effects and relative efficacy of medications for rhythm control of atrial fibrillation in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol, 123(11):1859–1862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2019.02.051
Morgan R, Colman MA, Chubb H, et al., 2016. Slow conduction in the border zones of patchy fibrosis stabilizes the drivers for atrial fibrillation: insights from multi-scale human atrial modeling. Front Physiol, 7:474. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2016.00474
Nademanee K, McKenzie J, Kosar E, et al., 2004. A new approach for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: mapping of the electrophysiologic substrate. J Am Coll Cardiol, 43(11):2044–2053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2003.12.054
Narayan SM, Krummen DE, Shivkumar K, et al., 2012. Treatment of atrial fibrillation by the ablation of localized sources: CONFIRM (Conventional Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation With or Without Focal Impulse and Rotor Modulation) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol, 60(7):628–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2012.05.022
Nattel S, Harada M, 2014. Atrial remodeling and atrial fibrillation: recent advances and translational perspectives. J Am Coll Cardiol, 63(22):2335–2345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2014.02.555
Nattel S, Heijman J, Zhou LP, et al., 2020. Molecular basis of atrial fibrillation pathophysiology and therapy: a translational perspective. Circ Res, 127(1):51–72. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.120.316363
Nguyen TP, Qu ZL, Weiss JN, 2014. Cardiac fibrosis and arrhythmogenesis: the road to repair is paved with perils. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 70:83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.10.018
Nishida K, Nattel S, 2014. Atrial fibrillation compendium: historical context and detailed translational perspective on an important clinical problem. Circ Res, 114(9): 1447–1452. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.114.303466
Pallisgaard JL, Gislason GH, Hansen J, et al., 2018. Temporal trends in atrial fibrillation recurrence rates after ablation between 2005 and 2014: a nationwide Danish cohort study. Eur Heart J, 39(6):442–449. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehx466
Pashakhanloo F, Herzka DA, Ashikaga H, et al., 2016. Myofiber architecture of the human atria as revealed by submillimeter diffusion tensor imaging. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 9(4):e004133. https://doi.org/10.1161/circep.116.004133
Patel NJ, Atti V, Mitrani RD, et al., 2018. Global rising trends of atrial fibrillation: a major public health concern. Heart, 104(24):1989–1990. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2018-313350
Pedrotty DM, Klinger RY, Kirkton RD, et al., 2009. Cardiac fibroblast paracrine factors alter impulse conduction and ion channel expression of neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Res, 83(4):688–697. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvp164
Pontecorboli G, Figueras i Ventura RM, Carlosena A, et al., 2017. Use of delayed-enhancement magnetic resonance imaging for fibrosis detection in the atria: a review. Europace, 19(2): 180–189. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euw053
Rahman F, Kwan GF, Benjamin EJ, 2014. Global epidemiology of atrial fibrillation. Nat Rev Cardiol, 11(11):639–654. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2014.118
Reumann M, Bohnert J, Osswald B, et al., 2007. Multiple wavelets, rotors, and snakes in atrial fibrillation—a computer simulation study. J Electrocardiol, 40(4):328–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2006.12.016
Reumann M, Bohnert J, Seemann G, et al., 2008. Preventive ablation strategies in a biophysical model of atrial fibrillation based on realistic anatomical data. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 55(2):399–406. https://doi.org/10.1109/tbme.2007.912672
Rolf S, Kircher S, Arya A, et al., 2014. Tailored atrial substrate modification based on low-voltage areas in catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 7(5):825–833. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCEP.113.001251
Roney CH, Williams SE, Cochet H, et al., 2018. Patient-specific simulations predict efficacy of ablation of inter-atrial connections for treatment of persistent atrial fibrillation. Europace, 20(S3):iii55–iii68. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euy232
Roney CH, Beach ML, Mehta AM, et al., 2020. In silico comparison of left atrial ablation techniques that target the anatomical, structural, and electrical substrates of atrial fibrillation. Front Physiol, 11:1145. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.572874
Roney CH, Bendikas R, Pashakhanloo F, et al., 2021. Constructing a human atrial fibre atlas. Ann Biomed Eng, 49(1):233–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-020-02525-w
Rotter M, Dang L, Jacquemet V, et al., 2007. Impact of varying ablation patterns in a simulation model of persistent atrial fibrillation. Pace-Pacing Clin Electrophysiol, 30(3):314–321. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-8159.2007.00671.x
Roy A, Varela M, Chubb H, et al., 2020. Identifying locations of re-entrant drivers from patient-specific distribution of fibrosis in the left atrium. PLoS Comput Biol, 16(9): e1008086. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008086
Ruchat P, Virag N, Dang L, et al., 2007a. A biophysical model of atrial fibrillation ablation: what can a surgeon learn from a computer model? Europace, 9(S6):vi71–vi76. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/eum209
Ruchat P, Dang L, Virag N, et al., 2007b. A biophysical model of atrial fibrillation to define the appropriate ablation pattern in modified maze. Eur J Cardio-Thorac Surg, 31(1):65–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcts.2006.10.015
Ruchat P, Dang L, Schlaepfer J, et al., 2007c. Use of a biophysical model of atrial fibrillation in the interpretation of the outcome of surgical ablation procedures. Eur J Cardio-Thorac Surg, 32(1):90–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcts.2007.02.031
Saha M, Roney CH, Bayer JD, et al., 2018. Wavelength and fibrosis affect phase singularity locations during atrial fibrillation. Front Physiol, 9:1207. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01207
Sanders P, Berenfeld O, Hocini M, et al., 2005. Spectral analysis identifies sites of high-frequency activity maintaining atrial fibrillation in humans. Circulation, 112(6):789–797. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.104.517011
Schade A, Nentwich K, Costello-Boerrigter LC, et al., 2016. Spatial relationship of focal impulses, rotors and low voltage zones in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 27(5):507–514. https://doi.org/10.1111/jce.12913
Seemann G, Höper C, Sachse FB, et al., 2006. Heterogeneous three-dimensional anatomical and electrophysiological model of human atria. Philos Trans Roy Soc A-Math Phys Eng Sci, 364(1843): 1465–1481. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2006.1781
Seitz J, Horvilleur J, Lacotte J, et al., 2011. Correlation between AF substrate ablation difficulty and left atrial fibrosis quantified by delayed-enhancement cardiac magnetic resonance. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol, 34(10):1267–1277. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-8159.2011.03148.x
Seitz J, Bars C, Théodore G, et al., 2017. AF ablation guided by spatiotemporal electrogram dispersion without pulmonary vein isolation: a wholly patient-tailored approach. J Am Coll Cardiol, 69(3):303–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2016.10.065
Shade JK, Ali RL, Basile D, et al., 2020. Preprocedure application of machine learning and mechanistic simulations predicts likelihood of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation recurrence following pulmonary vein isolation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 13(7):e008213. https://doi.org/10.1161/circep.119.008213
Shim J, Hwang M, Song JS, et al., 2017. Virtual in-silico modeling guided catheter ablation predicts effective linear ablation lesion set for longstanding persistent atrial fibrillation: multicenter prospective randomized study. Front Physiol, 8:792. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00792
Sim I, Razeghi O, Karim R, et al., 2019. Reproducibility of atrial fibrosis assessment using CMR imaging and an open source platform. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging, 12(10): 2076–2077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmg.2019.03.027
Slawuta A, Jacek P, Mazur G, et al., 2020. Quality of life and frailty syndrome in patients with atrial fibrillation. Clin Interv Aging, 15:783–795. https://doi.org/10.2147/cia.s248170
Sohns C, Lemes C, Metzner A, et al., 2017. First-in-man analysis of the relationship between electrical rotors from non-invasive panoramic mapping and atrial fibrosis from magnetic resonance imaging in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 10(8): e004419. https://doi.org/10.1161/circep.116.004419
Steinbeck G, Sinner MF, Lutz M, et al., 2018. Incidence of complications related to catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter: a nationwide in-hospital analysis of administrative data for Germany in 2014. Eur Heart J, 39(45):4020–4029. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehy452
Takahashi Y, O’Neill MD, Hocini M, et al., 2008. Characterization of electrograms associated with termination of chronic atrial fibrillation by catheter ablation. J Am Coll Cardiol, 51(10):1003–1010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2007.10.056
Trayanova NA, Popescu DM, Shade JK, 2021. Machine learning in arrhythmia and electrophysiology. Circ Res, 128(4): 544–566. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317872
Vandersickel N, van Nieuwenhuyse E, van Cleemput N, et al., 2019. Directed networks as a novel way to describe and analyze cardiac excitation: directed graph mapping. Front Physiol, 10:1138. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.01138
Verma A, Jiang CY, Betts TR, et al., 2015. Approaches to catheter ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med, 372(19):1812–1822. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1408288
Virag N, Jacquemet V, Henriquez CS, et al., 2002. Study of atrial arrhythmias in a computer model based on magnetic resonance images of human atria. Chaos, 12(3):754–763. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1483935
Weimar T, Schena S, Bailey MS, et al., 2012. The Cox-Maze procedure for lone atrial fibrillation: a single-center experience over 2 decades. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 5(1):8–14. https://doi.org/10.1161/circep.111.963819
Woods CE, Olgin J, 2014. Atrial fibrillation therapy now and in the future: drugs, biologicals, and ablation. Circ Res, 114(9):1532–1546. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.302362
Zahid S, Whyte KN, Schwarz EL, et al., 2016. Feasibility of using patient-specific models and the “minimum cut” algorithm to predict optimal ablation targets for left atrial flutter. Heart Rhythm, 13(8):1687–1698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2016.04.009
Zhao JC, Hansen BJ, Wang YF, et al., 2017. Three-dimensional integrated functional, structural, and computational mapping to define the structural “fingerprints” of heart-specific atrial fibrillation drivers in human heart ex vivo. J Am Heart Assoc, 6(8):e005922. https://doi.org/10.1161/jaha.117.005922
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81901841 and 61527811), the Key Research and Development Program of Zhejiang Province (No. 2020C03016), and the Dalian University of Technology (No. DUT18RC(3)068), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Author contributions
Zhenghong WU and Yunlong LIU wrote the manuscript. Zhenghong WU created the figure and tables. Zhenghong WU, Lv TONG, and Diandian DONG edited the manuscript. Dongdong DENG and Ling XIA contributed the framework of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Compliance with ethics guidelines
Zhenghong WU, Yunlong LIU, Lv TONG, Diandian DONG, Dongdong DENG, and Ling XIA declare that they have no conflict of interest.
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Z., Liu, Y., Tong, L. et al. Current progress of computational modeling for guiding clinical atrial fibrillation ablation. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 22, 805–817 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000727
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000727