Abstract
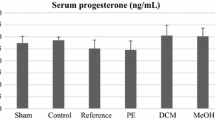
Objective: Apios americana, a plant used as a staple ingredient of native American diets, has various properties, including anti-cancer, anti-hyperglycemic, hypotensive, and anti-inflammatory activity. In Japan, Apios is used as a post-natal medication. After parturition, women undergo a period of recovery as they return to pre-pregnancy conditions. However, few health products that aid post-partum recovery are on the market. We explored whether Apios can accelerate the post-partum recovery process, in particular the involution of the uterus. Methods: Female rats kept in individual cages were mated with two male rats, with the exception of the control group (female rats without mating, on basal diet; n=6). After delivery, rats were divided into five groups based on their diet: basal diet (model; n=6); basal diet+oral intake at 5.4 g/kg of Chanfukang granules (a Chinese patent medicine preparation for post-partum lochia) (positive; n=6); basal diet containing 10% Apios powder (low; n=6); basal diet containing 20% Apios powder (medium; n=6); basal diet containing 40% Apios powder (high; n=6). Five days later, uteri and spleens were weighed. Uterus and spleen indices for each rat were calculated by dividing visceral weight by the total weight. Hormone and cytokine concentrations were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Histological analysis of uteri was completed using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases and inhibitors in uteri was measured by western blotting. Results: Our results showed that Apios treatment reduced the post-partum uterus index and regulated the hormone concentrations. Moreover, we found that the process of uterine involution was accelerated, based on morphological changes in the uterus. In addition, our results indicated that Apios alleviated the inflammatory response induced by the involution process. Transforming growth factor ß was also found to be regulated by Apios. There were significant downregulation of matrix metalloproteinases and upregulation of their inhibitors by Apios, which suggested that Apios increased the rate of the collagen clearance process. Conclusions: These results, based on experimental observations at the molecular and protein levels, verified our hypothesis that Apios can improve uterine involution, and demonstrated the potential application of Apios in post-partum care.
中文概要
目的: 研究美国豆芋(Apios americana)对产后恢复过程,特别是子宫复旧的影响。
创新点: 开发针对产后恢复的新食品。
方法: 将雌雄大鼠配种交配,对照组除外(没有交配的雌性大鼠,基础日粮,n=6)。分娩后,将雌性大鼠分为五组:基础饮食(模型组,n=6);基础饮食+灌胃给药5.4 g/kg 的产妇康颗粒(阳性组,n=6);含10%豆芋粉末的基础日粮(低剂量组,n=6);含20%豆芋粉末的基础日粮(中剂量组,n=6);含40%豆芋粉末的基础日粮(高剂量组,n=6)。实验结束后,称量子宫和脾脏质量,计算子宫和脾脏指数。并测量血清内激素和细胞因子水平,研究子宫的组织病理学变化,检测基质金属蛋白酶和抑制剂在子宫中的表达。
结论: 豆芋干预减少了产后子宫指数并调节了激素浓度,加速了子宫形态复旧的过程,减轻了分娩引起的炎症反应。同时发现,转化生长因子β 也受豆芋调节。豆芋干预使得基质金属蛋白酶显著下调,其抑制剂则显著上调,这表明豆芋增加了胶原清除过程的速度。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alan E, Liman N, 2012. Immunohistochemical localization of beta defensins in the endometrium of rat uterus during the postpartum involution period. Vet Res Commun, 36(3): 173–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-012-9529-7
Al-Bassam MA, Thomson RG, O'Donnell L, 1981. Normal postpartum involution of the uterus in the dog. Can J Comp Med, 45(3):217–232.
Alkema L, Chou D, Hogan D, et al., 2016. Global, regional, and national levels and trends in maternal mortality between 1990 and 2015, with scenario-based projections to 2030: a systematic analysis by the UN maternal mortality estimation inter-agency group. Lancet, 387(10017):462–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00838-7
Azawi OI, 2008. Postpartum uterine infection in cattle. Anim Reprod Sci, 105(3-4):187–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anireprosci.2008.01.010
Chitisankul WT, Shimada K, Omizu Y, et al., 2015. Mechanism of DDMP-saponin degradation and maltol production in soymilk preparation. LWT-Food Sci Technol, 64(1): 197–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2015.05.023
Cui J, Kim Y, Lee EB, et al., 2016. Immunostimulatory activity of Apios tuber extract on RAW264.7 macrophage cells. J Bacteriol Virol, 46(4):248–257. https://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2016.46.4.248
Curry TE Jr, Osteen KG, 2003. The matrix metalloproteinase system: changes, regulation, and impact throughout the ovarian and uterine reproductive cycle. Endocr Rev, 24(4): 428–465. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2002-0005
Elliott L, McMahon KJ, Gier HT, et al., 1968. Uterus of the cow after parturition: bacterial content. Am J Vet Res, 29(1):77–81.
Ferenczy A, Bertrand G, Gelfand MM, 1979. Studies on the cytodynamics of human endometrial regeneration: III. In vitro short-term incubation historadioautography. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 134(3):297–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(16)33036-8
Gaide Chevronnay HP, Selvais C, Emonard H, et al., 2012. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinases activity studied in human endometrium as a paradigm of cyclic tissue breakdown and regeneration. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom, 1824(1):146–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2011.09.003
Galvão KN, Santos NR, Galvão JS, et al., 2011. Association between endometritis and endometrial cytokine expression in postpartum Holstein cows. Theriogenology, 76(2): 290–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2011.02.006
Gray CA, Bartol FF, Tarleton BJ, et al., 2001. Developmental biology of uterine glands. Biol Reprod, 65(5):1311–1323. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod65.5.1311
Griffin JF, Hartigan PJ, Nunn WR, 1974. Non-specific uterine infection and bovine fertility: I. Infection patterns and endometritis during the first seven weeks post-partum. Theriogenology, 1(3):91–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/0093-691X(74)90052-1
Grota LJ, Eik-Nes KB, 1967. Plasma progesterone concentrations during pregnancy and lactation in the rat. J Reprod Fertil, 13(1):83–91. https://doi.org/10.1530/jrf.0.0130083
Harianja WY, Setiani O, Umaroh U, et al., 2017. The impact of pineapple (Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.) juice on fundal height in primigravida mothers during postpartum period. Belitung Nurs J, 3(2):134–141. https://doi.org/10.33546/bnj.76
Henell F, Ericsson JLE, Glaumann H, 1983. An electron microscopic study of the post-partum involution of the rat uterus. With a note on apparent crinophagy of collagen. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol, 42(1): 271–287. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02890390
Hoshikawa K, Juliarni 1, 1995. The growth of apios (Apios americana Medikus), a new crop, under field conditions. Jpn J Crop Sci, 64(2):323–327. https://doi.org/10.1626/jcs.64.323
Hulboy DL, Rudolph LA, Matrisian LM, 1997. Matrix metalloproteinases as mediators of reproductive function. Mol Hum Reprod, 3(1):27–45. https://doi.org/10.1093/molehr/3.1.27
Kasimanickam RK, Kasimanickam VR, Olsen JR, et al., 2013. Associations among serum pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, metabolic mediators, body condition, and uterine disease in postpartum dairy cows. Reprod Biol Endocrinol, 11:103. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7827-11-103
Kawamura J, Miura E, Kawakishi K, et al., 2015. Investigation of the safety and antihyperglycemic effect of Apios americana flower intake as a food material in normal and diabetic mice. Food Sci Technol Res, 21(3):453–462. https://doi.org/10.3136/fstr.21.453
Kikuta C, Sugimoto Y, Konishi Y, et al., 2012. Physicochemical and structural properties of starch isolated from Apios americana Medikus. J Appl Glycosci, 59(1):21–30. https://doi.org/10.5458/jag.jag.JAG-2011_011
Kinugasa H, Watanbe Y, 1992. Nutritional composition of the tubers of American groundnut (Apios americana Medikus). Sonoda Women’s Coll Stud, 26:209–218.
Krishnan HB, 1998. Identification of genistein, an anticarcinogenic compound, in the edible tubers of the American groundnut (Apios americana Medikus). Crop Sci, 38(4): 1052–1056. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1998.0011183X003800040028x
Kuramoto S, Kaneyoshi G, Morinaga Y, et al., 2013. Angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides isolated from pepsin hydrolyzate of Apios americana tuber and their hypotensive effects in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Sci Technol Res, 19(3):399–407. https://doi.org/10.3136/fstr.19.399
LeBlanc MM, Hansen PJ, Buhi WC, 1988. Uterine protein secretion in postpartum and cyclic mares. Theriogenology, 29(6):1303–1316. https://doi.org/10.1016/0093-691X(88)90010-6
Lin RY, Sullivan KM, Argenta PA, et al., 1995. Exogenous transforming growth factor-beta amplifies its own expression and induces scar formation in a model of human fetal skin repair. Ann Surg, 222(2):146–154. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-199508000-00006
Manase K, Endo T, Chida M, et al., 2006. Coordinated elevation of membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase and matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression in rat uterus during postpartum involution. Reprod Biol Endocrinol, 4:32. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7827-4-32
Morales MR, Foster JG, 2009. Forage potential of American potato bean. Proceedings of the American Forage and Grassland Council. 2009 Annual Conference, Grand Rapids, Michigan.
Murphy G, Nagase H, 2008. Progress in matrix metalloproteinase research. Mol Aspects Med, 29(5):290–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2008.05.002
Nagase H, Visse R, Murphy G, 2006. Structure and function of matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs. Cardiovasc Res, 69(3):562–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.12.002
Nara K, Nihei KI, Ogasawara Y, et al., 2011. Novel isoflavone diglycoside in groundnut (Apios americana Medik). Food Chem, 124(3):703–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.05.107
Nguyen TTT, Shynlova O, Lye SJ, 2016. Matrix metalloproteinase expression in the rat myometrium during pregnancy, term labor, and postpartum. Biol Reprod, 95(1):24. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod.115.138248
O'kane S, Ferguson MWJ, 1997. Transforming growth factor ßs and wound healing. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 29(1):63–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1357-2725(96)00120-3
Petrovitch I, Jeffrey RB, Heerema-McKenney A, 2009. Sub-involution of the placental site. J Ultrasound Med, 28(8): 1115–1119. https://doi.org/10.7863/jum.2009.28.8.1115
Reynolds B, Blackmon W, Wickremesinhe E, et al., 1988. Domestication of Apios americana. In: Janick J (Ed.), Advances in New Crops: Proceedings of the First National Symposium New Crops: Research, Development, Economics, Timber Press, p.436–442.
Rosen T, 2008. Placenta accreta and cesarean scar pregnancy: overlooked costs of the rising cesarean section rate. Clin Perinatol, 35(3):519–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clp.2008.07.003
Salamonsen LA, 2003. Tissue injury and repair in the female human reproductive tract. Reproduction, 125(3):301–311. https://doi.org/10.1530/rep.0.1250301
Sellers A, Woessner JF Jr, 1980. The extraction of a neutral metalloproteinase from the involuting rat uterus, and its action on cartilage proteoglycan. Biochem J, 189(3):521–531. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj1890521
Sheldon IM, 2004. The postpartum uterus. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract, 20(3):569–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cvfa.2004.06.008
Sheldon IM, Noakes DE, Rycroft AN, et al., 2002. Influence of uterine bacterial contamination after parturition on ovarian dominant follicle selection and follicle growth and function in cattle. Reproduction, 123(6):837–845. https://doi.org/10.1530/rep.0.1230837
Shimizu K, Furuya T, Takeo Y, et al., 1983. Clearance of materials from breakdown of uterine collagen in mice during postpartum involution. Acta Anat (Basel), 116(1): 10–13. https://doi.org/10.1159/000145720
Shkurupiy VA, Obedinskaya KS, Nadeev AP, 2011. Morphological study of the main mechanisms of myometrium involution after repeated pregnancies in mice. Bull Exp Biol Med, 150(3):378–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-011-1147-9
Soo C, Beanes SR, Hu FY, et al., 2003. Ontogenetic transition in fetal wound transforming growth factor-ß regulation correlates with collagen organization. Am J Pathol, 163(6): 2459–2476. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63601-2
Takamoto N, Leppert PC, Yu SY, 1998. Cell death and proliferation and its relation to collagen degradation in uterine involution of rat. Connec Tissue Res, 37(3-4): 163–175. https://doi.org/10.3109/03008209809002436
Takashima M, Nara K, Niki E, et al., 2013. Evaluation of biological activities of a groundnut (Apios americana Medik) extract containing a novel isoflavone. Food Chem, 138(1):298–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.10.100
Umenishi F, Umeda M, Miyazaki K, 1991. Efficient purification of TIMP-2 from culture medium conditioned by human hepatoma cell line, and its inhibitory effects on metalloproteinases and in vitro tumor invasion. J Biochem, 110(2):189–195. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123555
Wang QH, Zhang S, Qin LM, et al., 2017. Yimu San improves obstetric ability of pregnant mice by increasing serum oxytocin levels and connexin 43 expression in uterine smooth muscle. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 18(11):986–993. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1600289
WHO (World Health Organization), 2015. Childbirth: labour, delivery and immediate postpartum care. In: WHO, United Nations Population Fund, UNICEF (Eds.), Pregnancy, Childbirth, Postpartum and Newborn Care: A Guide for Essential Practice, 3rd Ed. World Health Organization, Geneva, p.85–88.
WHO, 2018. Maternal mortality. http://www.who.int/en/newsroom/fact-sheets/detail/maternal-mortality [Accessed on June 4, 2018].
Willenbrock F, Murphy G, 1994. Structure-function relationships in the tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 150(6 Pt 2):S165–S170. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm/150.6_Pt_2.S165
Wilson PW, Gorny JR, Blackmon WJ, et al., 1986. Fatty acids in the American groundnut (Apios americana). J Food Sci, 51(5):1387–1388. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.1986.tb13136.x
Woessner JF Jr, 1979. Total, latent and active collagenase during the course of post-partum involution of the rat uterus. Effect of oestradiol. Biochem J, 180(1):95–102. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj1800095
Woessner JF Jr, 1996. Regulation of matrilysin in the rat uterus. Biochem Cell Biol, 74(6):777–784. https://doi.org/10.1139/o96-084
Wolf K, Sandner P, Kurtz A, et al., 1996. Messenger ribonucleic acid levels of collagenase (MMP-13) and matrilysin (MMP-7) in virgin, pregnant, and postpartum uterus and cervix of rat. Endocrinology, 137(12):5429–5434. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.137.12.8940367
Yan FJ, Yang YY, Yu LS, et al., 2017. Effects of C-glycosides from Apios americana leaves against oxidative stress during hyperglycemia through regulating mitogenactivated protein kinases and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2. J Agric Food Chem, 65(34):7457–7466. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03163
Yoshii A, Kitahara S, Ueta H, et al., 2014. Role of uterine contraction in regeneration of the murine postpartum endometrium. Biol Reprod, 91(2):32. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod.114.117929
Zhang YZ, Zhou CS, Tang SM, et al., 2011. Effect of AATI, a bowman-birk type inhibitor from Apios americana, on proliferation of cancer cell lines. Food Chem, 128(4):909–915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.03.117
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. LZ14C200001)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Zh., Han, Y., You, Sy. et al. Improvement in post-partum uterine involution in rats treated with Apios americana. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 20, 576–587 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1800475
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1800475