Abstract
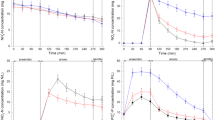
The effects of two different external carbon sources (acetate and ethanol) and electron acceptors (dissolved oxygen, nitrate, and nitrite) were investigated under aerobic and anoxic conditions with non-acclimated process biomass from a full-scale biological nutrient removal-activated sludge system. When acetate was added as an external carbon source, phosphate release was observed even in the presence of electron acceptors. The release rates were 1.7, 7.8, and 3.5 mg P/(g MLVSS·h) (MLVSS: mixed liquor volatile suspended solids), respectively, for dissolved oxygen, nitrate, and nitrite. In the case of ethanol, no phosphate release was observed in the presence of electron acceptors. Results of the experiments with nitrite showed that approximately 25 mg NO2-N/L of nitrite inhibited anoxic phosphorus uptake regardless of the concentration of the tested external carbon sources. Furthermore, higher denitrification rates were obtained with acetate (1.4 and 0.8 mg N/(g MLVSS·h)) compared to ethanol (1.1 and 0.7 mg N/(g MLVSS·h)) for both anoxic electron acceptors (nitrate and nitrite).
概 要
目 的
考察两种不同性质的外加碳源 (乙酸钠和乙醇) 在三种不同的电子受体 (溶解氧、 硝酸盐和亚硝酸盐) 条件下对聚磷菌和异养菌的影响机制。
创新点
系统研究了乙酸钠和乙醇这两种外加碳源在溶解氧、 硝酸盐和亚硝酸盐三种不同电子受体条件下的释磷、 吸磷及反硝化过程。
方 法
利用具有脱氮除磷功能的活性污泥, 开展了一系列一阶段批次试验和两阶段批次试验。 一阶段批次试验包括厌氧释磷试验、 好氧吸磷试验、 硝酸盐及亚硝酸盐利用速率 (NUR) 试验。 两阶段批次试验包括厌氧/好氧试验、 厌氧/缺氧试验。 通过改变外加碳源的投加条件, 如投加类型(乙酸 钠和乙醇)、 投加环境 (厌氧、 好氧和缺氧)、 缺氧区电子受体 (硝酸盐及亚硝酸盐), 考察两种不同类型的外加碳源在不同电子受体条件下对除磷和脱氮过程的影响。
结 论
-
(1)
当乙酸钠作为外加碳源时, 在溶解氧、 硝酸盐和亚硝酸盐三种不同电子受体条件下均发生了释磷, 释磷速率分别为 1.70、 7.80 和 3.50 mg P/(g MLVSS·h)。 当乙醇作为外加碳源时, 三种电子受体条件下均未发现有释磷。
-
(2)
无论乙酸钠还是乙醇作为外加碳源, 未经驯化的活性污泥聚磷菌均不能利用亚硝酸盐作为电子受体, 25 mg NO2-N/L 的亚硝酸盐完全抑制了吸磷过程的进行。
-
(3)
以硝酸盐作为电子受体时, 乙酸钠和乙醇的 NUR 值分别为 2.3 和 1.5 mg N/(g MLVSS·h), 比亚硝酸盐作电子受体的 NUR 值 (分别为 1.2 和 1.0 mg N/(g MLVSS·h))分别高出 92% 和 50%。 乙酸钠作为碳源的 NUR 值总是比相同条件下以乙醇作为碳源的 NUR 值高。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adouani N, Lendormi T, Limousy L, et al., 2010. Effect of the carbon source on N2O emissions during biological denitrification. Resour Conserv Recy, 54(5):299–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2009.07.011.
Ahn J, Daidou T, Tsuneda S, et al., 2001. Metabolic behavior of denitrifying phosphate-accumulating organisms under nitrate and nitrite electron acceptor conditions. J Biosci Bioeng, 92(5):442–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1389-1723(01)80293-0.
Ahn J, Daidou T, Tsuneda S, et al., 2002. Transformation of phosphorus and relevant intracellular compounds by a phosphorus accumulating enrichment culture in the presence of both the electron acceptor and electron donor. Biotechnol Bioeng, 79(1):83–93. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.10292.
Anthonisen AC, Loehr RC, Prakasam TBS, et al., 1976. Inhibition of nitrification by ammonia and nitrous acid. J Water Pollut Contr Fed, 48(5):835–852.
APHA (American Public Health Association), 1998. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th Ed. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC, USA.
Constantin H, Fick M, 1997. Influence of C-sources on the denitrification rate of a high-nitrate concentrated industrial wastewater. Water Res, 31(3):583–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(96)00268-0.
Council of the European Union, 1991. Council Directive 91/271/EEC of 21 May 1991 concerning urban wastewater treatment. Off J Eur Union, 135:40-52.
Guerrero J, Guisasola A, Baeza JA, 2011. The nature of the carbon source rules the competition between PAO and denitrifiers in systems for simultaneous biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal. Water Res, 45(16):4793–4802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.06.019.
Guerrero J, Taya C, Guisasola A, et al., 2012. Understanding the detrimental effect of nitrate presence on EBPR systems: effect of the plant configuration. J Chem Technol Biotechnol, 87(10):1508–1511. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.3812.
Guisasola A, Pijuan M, Baeza JA, et al., 2004. Aerobic phosphorus release linked to acetate uptake in bio-P sludge: process modelling using oxygen uptake rate. Biotechnol Bioeng, 85(7):722–733. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.10868.
Hagman M, Nielsen JL, Nielsen PH, et al., 2008. Mixed carbon sources for nitrate reduction in activated sludgeidentification of bacteria and process activity studies. Water Res, 42(6-7):1539–1546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.10.034.
Hu JY, Ong SL, Ng WJ, et al., 2003. A new method for characterizing denitrifying phosphorus removal bacteria by using three different types of electron acceptor. Water Res, 37(14):3463–3471. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00205-7.
Isaacs SH, Henze M, 1995. Controlled carbon source addition to an alternating nitrification-denitrification wastewater treatment process including biological P removal. Water Res, 29(1):77–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(94)E0119-Q.
Kampas P, Parsons SA, Pearce P, et al., 2009. An internal carbon source for improving biological nutrient removal. Bioresour Technol, 100(1):149–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.05.023.
Kristensen GH, Jørgensen PE, Henze M, 1992. Characterization of functional microorganism groups and substrate in activated sludge and wastewater by AUR, NUR and OUR. Water Sci Technol, 25(6):43–57.
Kujawa K, Klapwijk B, 1999. A method to estimate denitrification potential for predenitrification systems using NUR batch tests. Water Res, 33(10):2291–2300. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00459-X.
Li QH, Li P, Zhu PP, et al., 2008. Effects of exogenous organic carbon substrates on nitrous oxide emissions during the denitrification process of sequence batch reactors. Environ Eng Sci, 25(8):1221–1228. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2007.0172.
Meinhold J, Arnold E, Isaacs S, 1999. Effect of nitrite on anoxic phosphorus uptake in biological phosphorus removal activated sludge. Water Res, 33(8):1871–1883. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00411-4.
Metcalf & Eddy Inc., Tchobanoglous G, Burton FL, et al., 2003. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment and Reuse, 4th Ed. McGraw-Hill Higher Education, New York.
Morgan-Sagastume F, Nielsen JL, Nielsen PH, 2008. Substratedependent denitrification of abundant probe-defined denitrifying bacteria in activated sludge. FEMS Microbiol Ecol, 66(2):447–461. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2008.00571.x.
Peng YZ, Ma Y, Wang SY, 2007. Denitrification potential enhancement by addition of external carbon sources in a pre-denitrification process. J Environ Sci, 19(3):284–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(07)60046-1.
Pijuan M, Guisasola A, Baeza JA, et al., 2005. Aerobic phosphorus release linked to acetate uptake: influence of PAO intracellular storage compounds. Biochem Eng J, 26(2-3):184–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2005.04.014.
Puig S, Coma M, van Loosdrecht MCM, et al., 2007. Biological nutrient removal in a sequencing batch reactor using ethanol as carbon source. J Chem Technol Biotechnol, 82(10):898–904. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.1754.
Puig S, Coma M, Monclusa H, et al., 2008. Selection between alcohols and volatile fatty acids as external carbon sources for EBPR. Water Res, 42(3):557–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.07.050.
Rodríguez L, Villasenor J, Fernandez FJ, 2007. Use of agro-food wastewaters for the optimisation of the denitrification process. Water Sci Technol, 55(10):63–70. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2007.307.
Saito T, Brdjanovic D, van Loosdrecht MCM, 2004. Effect of nitrite on phosphate uptake by phosphate accumulating organisms. Water Res, 38(17):3760–3768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.05.023.
Sin G, Niville K, Bachis G, et al., 2008. Nitrite effect on the phosphorus uptake activity of phosphate accumulating organisms (PAOs) in pilot-scale SBR and MBR reactors. Water SA, 34:249–260.
Smolders GJF, van der Meij J, van Loosdrecht MCM, et al., 1994. Model of the anaerobic metabolism of the biological phosphorus removal process; stoichiometry and pH influence. Biotechnol Bioeng, 43(6):461–470. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.260430605.
Swinarski M, Makinia J, Czerwionka K, et al., 2009. Comparison of the effects of conventional and alternative external carbon sources for enhancing the denitrification process. Water Environ Res, 81(9):896–906. https://doi.org/10.2175/106143009X407438.
Swinarski M, Makinia J, Stensel HD, et al., 2012. Modeling external carbon addition in biological nutrient removal processes with an extension of the International Water Association Activated Sludge Model. Water Environ Res, 84(8):646–655. https://doi.org/10.2175/106143012X13373550426670.
Wang DB, Zheng W, Li XM, et al., 2013. Evaluation of the feasibility of alcohols serving as external carbon sources for biological phosphorus removal induced by the oxic/extended-idle regime. Biotechnol Bioeng, 110(3):827–837. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24753.
Yuan Q, Oleszkiewicz J, 2010. Interaction between denitrification and phosphorus removal in a sequencing batch reactor phosphorus removal system. Water Environ Res, 82(6):536–540. https://doi.org/10.2175/106143009X12529484815476.
Zhou Y, Pijuan M, Yuan Z, 2007. Free nitrous acid inhibition on anoxic phosphorus uptake and denitrification by polyphosphate accumulating organisms. Biotechnol Bioeng, 98(4):903–912. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.21458.
Zhou Y, Pijuan M, Yuan Z, 2008. Development of a 2-sludge, 3-stage system for nitrogen and phosphorous removal from nutrient-rich wastewater using granular sludge and biofilms. Water Res, 42(12):3207–3217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2008.04.012.
Zhou Y, Oehme A, Lim M, et al., 2011. The role of nitrite and free nitrous acid (FNA) in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res, 45(15):4672–4682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.06.025
Acknowledgements
During the time of the study at Gdansk University of Technology, Ms. Xiang HU was a researcher supported by the project “CARbon BALAncing for Nutrient Control in Wastewater Treatment (CARBALA)” (PIRSES-GA-2011-295176) under the International Research Staff Exchange Scheme FP7-PEOPLE-2011-IRSES.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the European Regional Development Fund within the Framework of the Innovative Economy Operational Program 2007-2013 (No. UDA-POIG.01.03.01-22-140/09-04), the CARbon BALAncing for Nutrient Control in Wastewater Treatment (CARBALA) (No. PIRSES-GA-2011-295176), and the National Water Pollution Control and Management of Science and Technology in China (No. 2015ZX07218001)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Sobotka, D., Czerwionka, K. et al. Effects of different external carbon sources and electron acceptors on interactions between denitrification and phosphorus removal in biological nutrient removal processes. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 19, 305–316 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1700064
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1700064
Key words
- Biological nutrient removal (BNR)
- Denitrification
- Enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR)
- External carbon source
- Electron acceptor