Abstract
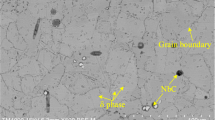
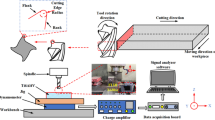
The objective of the present research is to investigate the relationship among tool wear, surface topography, and surface roughness when high-speed end milling Ti-6Al-4V alloy, and also to define an optimal flank wear criterion for the cutting tool to integrate tool life and the surface roughness requirements of the finish milling process. An annealed Ti-6Al-4V alloy was selected as the workpiece material, undergoing end milling with uncoated carbide inserts. The flank wear of the insert was observed and measured with the toolmaker’s microscope. To examine machined surfaces, 3D surface topography was provided by the white light interferometer, and the arithmetical mean roughness (R a) was calculated with the WYKO Vision32 software. The flank wear increases with cutting time, and the maximal flank wear is set as the flank wear criterion. As the cutting process progresses, tool wear is the predominant factor affecting the variation of surface roughness. According to the plots for the tool wear propagation and surface roughness variation, an optimal flank wear criterion can be defined which integrates the tool life and the surface roughness requirements for the finish milling process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin, A.K.M.N., Ismail, A.F., Khairusshima, M.K.N., 2007. Effectiveness of uncoated WC-Co and PCD inserts in end milling of titanium alloy—Ti-6Al-4V. Journal of Materials of Processing Technology, 192–193:147–158. [doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.04.095]
Corduan, N., Hirnbert, T., Poulachon, G., Dessoly, M., Lambertin, M., Vigneau, J., Payoux, B., 2003. Wear mechanisms of new tool materials for Ti-6Al-4V high performance machining. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, 52(1):73–76. [doi:10.1016/S0007-8506(07)60534-4]
Ezugwu, E.O., Wang, Z.M., 1997. Titanium alloy and their machinability—a review. Journal of Materials of Processing Technology, 68(3):262–274. [doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(96)00030-1]
Ginting, A., Nouari, M., 2009. Surface integrity of dry machined titanium alloys. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 49(3–4):325–332. [doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2008.10.011]
ISO 8688-2, 1989. Tool Life Testing in Milling—Part 2: End-milling. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland.
Jung, T.S., Yang, M.Y., Lee, K.J., 2005. A new approach to analysing machined surfaces by ball-end milling, part I: Formulation of characteristic lines of cut remainder. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 25(9-10):833–840. [doi:10.1007/s00170-003-1930-5]
Li, C.G., Dong, S., Zhang, G.X., 2000. Evaluation of the anisotropy of machined 3D surface topography. Wear, 237(2):211–216. [doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(99)00327-0]
Mativenga, P.T., Hon, K.K.B., 2003. A study of cutting forces and surface finish in high-speed machining of AISI H13 tool steel using carbide tools with TiAlN based coatings. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture, 217(2):143–151. [doi:10.1243/095440503321148786]
Oraby, S.E., Alaskari, A.M., 2008. Surface topography assessment techniques based on an in-process monitoring approach of tool wear and cutting force signature. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 15:221–230. [doi:10.1590/S1678-58782008000300007]
Rahman, M., Wang, Z.G., Wong, Y.S., 2006. A review on high-speed machining of titanium alloys. JSME International Journal, Series C, 49(1):11–20. [doi:10.1299/jsmec.49.11]
Stephenson, D.A., Agapiou, J.S., 2005. Metal Cutting Theory and Practice (2nd Ed.). Taylor & Francis, New York, USA, p.552–557.
Sun, J., Guo, Y.B., 2009. A comprehensive experimental study on surface integrity by end milling Ti-6Al-4V. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 209(8):4036–4042. [doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.09.022]
Toh, C.K., 2004. Surface topography analysis in high speed finish milling inclined hardened steel. Precision Engineering, 28(4):386–389. [doi:10.1016/j.precisioneng.2004.01.001]
Udupa, G., Singaperumal, M., Sirohi, R.S., Kothiyal, M.P., 2000. Characterization of surface topography by confocal microscopy, part I: Principles and the measurement system. Measurement Science and Technology, 11(3): 305–314. [doi:10.1088/0957-0233/11/3/320]
Venugopal, K.A., Paul, S., Chattopadhyay, A.B., 2007. Growth of tool wear in turning of Ti-6Al-4V alloy under cryogenic cooling. Wear, 262(9–10):1071–1078. [doi:10. 1016/j.wear.2006.11.010]
Zhang, S., Guo, Y.B., 2009. Taguchi method based process space for optimal surface topography by finish hard milling. ASME, Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 131(5):051003. [doi:10.1115/1.3207740]
Zoya, Z.A., Krishnamurthy, R., 2000. The performance of CBN tools in the machining of titanium alloys. Journal of Materials of Processing Technology, 100(1–3):80–86. [doi:10.1016/S0924-0136]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Key Science & Technology Specific projects (No. 2009ZX0400-032), the Taishan Scholar Program Foundation of Shandong Province, the Scientific Research Foundation for Outstanding Young Scientist of Shandong Province (No. 2007BS05001), and the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (No. 20070422033), China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Li, Jf. Tool wear criterion, tool life, and surface roughness during high-speed end milling Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 11, 587–595 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A0900776
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A0900776