Abstract
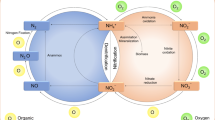
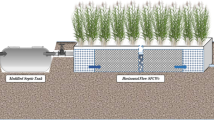
This paper describes the NiiMi process designed to treat landscape water. The main aim of the research was to investigate the feasibility of NiiMi for removing organic and nutriment materials from landscape water. During the batch-scale NiiMi operation, the removal rates of color ranged from 66.7%–80%, of turbidity from 31.7%–89.3%, of chemical oxygen demand (COD) from 7%–36.5%, of total phosphor (TP) from 43%–84.2%, of soluble phosphate from 42.9%–100%, of total nitrogen (TN) from 4.2%–46.7%, and of NH4 +-N from 39.3%–100% at the hydraulic loading of 0.2 m3/(m2·d). Results showed that the removal efficiencies of COD, TP, soluble phosphate and TN decreased with the decline in the temperature. The NiiMi process had a strong shock loading ability for the removal of the organics, turbidity, TP, soluble phosphate, TN and NH4 +-N. Three sodium chloride tracer studies were conducted, labeled as TS1, TS2, and TS3, respectively. The mean hydraulic retention times (mean HRTs) were 31 h and 28 h for TS1 and TS2, respectively, indicating the occurrence of a dead zone volume of 12% and 20% for TS1 and TS2, respectively. TS1 and TS2 displayed the occurrence of short-circuiting in the NiiMi system. The comparison results between TS1 and TS2 were further confirmed in the values obtained for some indicators, such as volumetric efficiency (e), short-circuiting (S), hydraulic efficiency (λ) and number of continuously stirred tank reactors (N).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achak, M., Mandi, L., Ouazzani, N., 2009. Removal of organic pollutants and nutrients from olive mill wastewater by a sand filter. Journal of Environmental Management, 90(8):2771–2779. [doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.03.012]
Babatunde, A.O., Zhao, Y.Q., Neill, M.O., Sullivan, B.O., 2008. Constructed wetlands for environmental pollution control: a review of developments, research and practice in Ireland. Environment International, 34(1):116–126. [doi:10.1016/j.envint.2007.06.013]
Beach, D.N.H., McCray, J.E., Lowe, S.K., Siegrist, R.L., 2005. Temporal changes in hydraulic conductivity of sand porous media biofilters during wastewater infiltration due to biomat formation. Journal of Hydrology, 311(1–4):230–243. [doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.01.024]
Beal, C.D., Gardner, E.A., Menzies, N.W., 2005. Process, performance and pollution potential: A review of septic tank-soil absorption systems. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 43(7):781–802. [doi:10.1071/SR05018]
Chen, P., 2000. The line adsorption equation: the one-dimensional counterpart of the Gibbs adsorption equation. Colloids and Surfaces, 161(1):23–30. [doi:10.1016/S0927-7757(99)00322-2]
Cheung, K.C., Venkitachalam, T.H., 2000. Improving phosphate removal of sand infiltration system using alkaline fly ash. Chemosphere, 41(1–2):243–249. [doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00417-8]
Chinese EPA, 2002. Standard Analytic Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 4th Edition. Chinese Environmental Science Publisher, Beijing, China. (in Chinese)
Eldridge, D.J., Zaady, E., Shachak, M., 2000. Infiltration through three contrasting biological soil crusts in patterned landscapes in the Negev. Israel Catena, 40(3): 323–336. [doi:10.1016/S0341-8162(00)00082-5]
El-Masry, M.H., EI-Bestawy, E., El-Adl, N.I., 2004. Bioremediation of vegetable oil and grease from polluted wastewater using a sand biofilm system. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 20(6):551–557. [doi:10.1023/B:WIBI.0000043162.17813.17]
Hamoda, M.F., Al-Ghusain, I., Al-Mutairi, N.Z., 2004. Sand filtration of wastewater for tertiary treatment and water reuse. Desalination, 164(3):203–211. [doi:10.1016/S0011-9164(04)00189-4]
He, L., 2004. Pilot Study on Treating Urban Landscape River Water by Hybrid Ecological Process. MS Thesis, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, p.25–54 (in Chinese).
He, S.B., Yan, L., Kong, H.N., Liu, Z.M., Wu, E.Y., Hu, Z.B, 2007. Treatment efficiencies of constructed wetlands for eutrophic landscape river water. Pedosphere, 17(4): 522–528. [doi:10.1016/S1002-0160(07)60062-9]
Healy, M.G., Rodgers, M., Malqueen, J., 2007. Treatment of dairy wastewater using constructed wetlands and intermittent sand filters. Bioresource Technology, 98(12): 2268–2281. [doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2006.07.036]
Hu, H.Y., Cheng, Y.L., Lin, J.Y., 2007. On-site treatment of septic tank effluent by using a soil adsorption system. Practice Periodical of Hazardous, Toxic, and Radioactive Waste Management, 11(3):197–206.
Jarboui, R., Sellami, F., Kharroubi, A., Gharsallah, N., Ammar, E., 2008. Olive mill wastewater stabilization in open-air ponds: Impact on clay-sandy soil. Bioresource Technology, 99(16):7699–7708. [doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2008. 01.074]
Jiang, X., Jin, X.K., Yao, Y., Li, L.H., Wu, F.C., 2008. Effects of biological activity, light, temperature and oxygen on phosphorus release processes at the sediment and water interface of Taihu Lake, China. Water Research, 42(8–9): 2251–2259. [doi:10.1016/j.watres.2007.12.003]
Jing, S.R., Lin, Y.F., Lee, D.Y., Wang, T.W., 2001. Nutrient removal from polluted river water by using constructed wetlands. Bioresource Technology, 76(2):131–135. [doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(00)00100-0]
Kadlec, R.H., Knight, R.L., 1996a. Phosphorus Treatment Wetlands. Lewis Publishers, Michigan, p.443–480.
Kadlec, R.H., Knight, R.L., 1996b. Treatment Wetlands. Lewis-CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, p.443–480.
Kruzic, A.P., 1997. Natural treatment and on-site processes. Water Environment Research, 69(4):522–526. [doi:10.2175/106143097X134812]
Kuschk, P., Wießner, A., Kappelmeyer, U., Weißbrodt, E., Kästner, M., Stottmeister, U., 2003. Annual cycle of nitrogen removal by a pilot-scale subsurface horizontal flow in a constructed wetland under moderate climate. Water Research, 37(17):4236–4242. [doi:10.1016/S0043-1354 (03)00163-5]
Li, B., Qian, W.M., Lu, J.L., 2007. Enhanced denitrogenation for decentralized wastewater by diffluent subsurface infiltration. Technology of Water Treatment, 33(8):34–37 (in Chinese).
Lowe, K.S., Siegrist, R.L., 2008. Controlled field experiment for performance evaluation of septic tank effluent treatment during soil infiltration. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 134(2): 93–101. [doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2008)134:2(93)]
Mulligan, C.N., Davarpanah, N., Fukue, M., Inoue, T., 2009. Filtration of contaminated suspended solids for the treatment of surface water. Chemosphere, 74(6):779–786. [doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.10.055]
Munoz, P., Drizo, A., Hession, W.C., 2006. Flow patterns of dairy wastewater constructed wetlands in a cold climate. Water Research, 40(17):3209–3218. [doi:10.1016/j.watres.2006.06.036]
Persson, J., Somes, N.L.G., Wong, T.H.F., 1999. Hydraulics efficiency of constructed wetlands and ponds. Water Science & Technology, 40(3):291–300. [doi:10.1016/S0273-1223(99)00448-5]
Persson, J., Wittgren, H.B., 2003. How hydrological and hydraulic conditions affect performance of ponds. Ecological Engineering, 21(4–5):259–269. [doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2003.12.004]
Sakadevan, K., Bavor, H.J., 1998. Phosphate adsorption characteristics of soils, slags and zeolite to be used as substrates in constructed wetland systems. Water Research, 32(2):393–399. [doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(97) 00271-6]
Siriwardene, N.R., Deletic, A., Fletcher, T.D., 2007. Clogging of stormwater gravel infiltration systems and filters: Insights from a laboratory study. Water Research, 41(7): 1433–1440. [doi:10.1016/j.watres.2006.12.040]
Suliman, F., French, H., Haugen, L.E., Kløve, B., Jenssen, P., 2005. The Effect of the Scale of Horizontal Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands on Flow and Transport Parameters Q. IWA Publishing, 51(9):259–266.
Sun, T., He, Y., 1998. Treatment of domestic wastewater by underground capillary seepage system. Ecological Engineering, 11(1–4):111–119. [doi:10.1016/S0925-8574 (98)00027-5]
Tanık, A., Comakoğlu, B., 1996. Nutrient removal from domestic wastewater by rapid infiltration system. Journal of Arid Environments, 34(3):379–390. [doi:10.1006/jare.1996.0118]
US EPA, 2002. Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems Manual. EPA/625/R-00/008. US Environmental Protection Agency.
Wang, X., Meng, Z.M., Chen, B., Yang, Z.F., Li, C., 2009. Simulation of nitrogen contaminant transportation by a compact difference scheme in the downstream Yellow River, China. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 14(3):935–945. [doi:10.1016/j.cnsns.2007.07.018]
Werner, T., Kadlec, R., 2000. Wetland residence time distribution modeling. Ecological Engineering, 15(1–2):77–90. [doi:10.1016/S0925-8574(99)00036-1]
Yamaguchi, T., Moldrup, P., Rolston, S.I., Tearnishi, S., 1996. Nitrification in porous media during rapid, unsaturated water flow. Water Research, 30(3):531–540. [doi:10.1016/0043-1354(95)00206-5]
Zhang, J., Huang, X., Liu, C.X., Shi, H.C., Hu, H.Y., 2005. Nitrogen removal enhanced by intermittent operation in a subsurface wastewater infiltration system. Ecological Engineering, 25:419–428. [doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2005.06.011]
Zhang, J., Huang, X., Shao, C.F., Liu, C.X., Shi, H.C., Hu, H.Y., Liu, Z.Q., 2004. Influence of packing media on nitrogen removal in a subsurface infiltration system. Journal of Environmental Science, 16(1):153–156.
Zhao, Q.L., Xue, S., You, S.J., Wang, L.N., 2007. Removal and transformation of organic matter during soil-aquifer treatment. Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE A, 8(5):712–718. [doi:10.1631/jzus.2007.A0712]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Zhang, Lb., Wu, Yf. et al. Treatment and hydraulic performances of the NiiMi process for landscape water. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 11, 132–142 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A0900437
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A0900437