Abstract
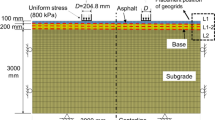
Top-down crack in asphalt pavements has been reported as a widespread mode of failure. A solid understanding of the mechanisms of crack growth is essential to predict pavement performance in the context of thickness design, as well as in the design and optimization of mixtures. Using the coupled element free Galerkin (EFG) and finite element (FE) method, top-down crack propagation in asphalt pavements is numerically simulated on the basis of fracture mechanics. A parametric study is conducted to isolate the effects of overlay thickness and stiffness, base thickness and stiffness on top-down crack propagation in asphalt pavements. The results show that longitudinal wheel loads are disadvantageous to top-down crack because it increases the compound stress intensity factor (SIF) at the tip of top-down crack and shortens the crack path, and thus the fatigue life descends. The SIF experiences a process “sharply ascending—slowly descending—slowly ascending—sharply ascending again” with the crack propagating. The thicker the overlay or the base, the lower the SIF; the greater the overlay stiffness, the higher the SIF. The crack path is hardly affected by stiffness of the overlay and base.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belytschko, T., Lu, Y.Y., Gu, L., 1994. Element free Galerkin methods. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 37(2):229–256. [doi:10.1002/nme.1620370205]
Belytschko, T., Organ, D., Krongauz, Y., 1995. A coupled finite element-element free Galerkin method. Computational Mechanics, 17(3):186–195. [doi:10.1007/BF00364080]
Belytschko, T., Krongauz, Y., Organ, D., 1996. Meshless methods: an overview and recent developments. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 139(1–4):3–47. [doi:10.1016/S0045-7825(96)01078-X]
de Freitas, D., Paulo, P., Luis, P., Thomas, A., 2005. Effect of construction quality, temperature, and rutting on initiation of top-down cracking. Transportation Research Record, Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 1929(1):174–182. [doi:10.3141/1929-21]
Erdogan, F., Sih, G.C., 1963. On the crack extension in plates under plate loading and transverse shear. Journal of Basic Engineering, 85:519–525.
Jacobs, M.M., 1995. Crack Growth in Asphalt Mix. MS Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, Holand.
Mao, C., Qiu, Y.J., Li, Y.P., 2004. Simulation of surface crack propagation in asphalt pavements and analysis of its influential factors. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 39(4):437–441 (in Chinese).
Myers, L.A., Roque, R., Birgisson, B., 2001. Propagation mechanisms for surface-initiated longitudinal wheelpath cracks. Transportation Research Record Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 1778(1):113–122. [doi:10.3141/1778-14]
Paris, P., Erdogan, F., 1963. A critical analysis of crack propagation laws. Journal of Basic Engineering, Series D, 85D(4):528–535.
Rabczuk, T., Xiao, S.P., Sauer, M., 2006. Coupling of mesh-free methods with finite elements: basic concepts and test results. Communications in Numerical Methods in Engineering, 22(10):1031–1065. [doi:10.1002/cnm.871]
Sangpetngam, B., Birgisson, B., Roque, R., 2004. Multilayer boundary-element method for evaluating top-down cracking in hot-mix asphalt pavements. Transportation Research Record Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 1896(1):129–137. [doi:10.3141/1896-13]
Siddharthan, R.V., Yao, J., Sebaaly, P.E., 1998. Pavement strain from dynamic 3D load distribution. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 124(6):557–566. [doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-947X(1998)124:6(557)]
Song, S.H., Paulino, G.H., Buttlar, W.G., 2006. Simulation of crack propagation in asphalt concrete using an intrinsic cohesive zone model. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 132(11):1215–1223. [doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(2006)132:11(1215)]
Svasdisant, T., Schorsch, M., Baladi, G.Y., Pinyosunun, S., 2002. Mechanistic analysis of top-down cracks in asphalt pavements. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 1809(1):126–136. [doi:10.3141/1809-15]
Wang, L.B., Myers, L.A., Mohammad, L.N., Fu, Y.R., 2003. Micromechanics study on top-down cracking. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 1853(1):121–133. [doi:10.3141/1853-14]
Yang, X.X., Fan, J.Q., Kuang, Z.B., 1996. A contour integral method for stress intensity factors of mixed-mode crack. Computational Structural Mechanics and Applications, 13(1):84–86 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project (Nos. 50908093 and 50778077) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, H., Zhu, Hp., Miao, Y. et al. Simulation of top-down crack propagation in asphalt pavements. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 11, 223–230 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A0900248
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A0900248
Key words
- Road engineering
- Top-down crack
- Coupled element free Galerkin (EFG) and finite element (FE) method
- Stress intensity factor (SIF)
- Crack propagating path