Abstract
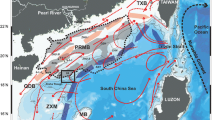
The Tainan Basin is one of the set of Cenozoic extensional basins along northern margin of the South China Sea that experienced extension and subsequently thermal subsidence. The Tainan Basin is close to the Taiwan Arc-Trench System and straddles a transition zone between oceanic and continental crust. A new regional multi-channel seismic profile (973-01) across the region of NE South China Sea is introduced in this paper. In seismic stratigraphy and structural geology, a model of Cenozoic tectono-sedimentation of the Tainan Basin is established. The results show that three stages can be suggested in Tainan Basin; In Stage A (Oligocene (?)-Lower Miocene) the stratigraphy shows restricted rifting, indicating crustal extension. Terrestrial sediments mostly filled the faulted sags of the North Depression on the continental shelf. Structural highs, including the Central Uplift, blocked material transportation to the South Depression in abyssal basin. In Stage B the Tainan Basin (Middle-Upper Miocene) exhibits a broad subsidence resulting from the post-rifting thermal cooling. The faulted-sags in North Depression had been filled up. Terrestrial materials were transported over the structural highs and deposited directly in the South Depression through submarine gullies or canyons. This sedimentation resulted in a crucial change in the slope to a modern shape. In Stage C (Latest Miocene-Recent) a phase change from extension to compression took place due to the orogeny caused by the overthrusting of the Luzon volcanic arc. Many inverse structures, such as thrusts, fault bend folds, and a regional unconformity were formed. Forland basin began developing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves, T.M., Motta, C., Sandnes, F., Cunha, T., Monteiro, J.H. Pinheiro, L.M., 2006. Mesozoic-Cenozoic evolution of North Atlantic continental-slope basins: the Peniche basin, western Iberian margin. AAPG Bulletin, 90(1):31–60.[doi:10.1306/08110504138]
Briais, A., Pautot, G., 1990. Reconstructions of the South China Sea from Structural Data and Magnetic Anomalies. In: Jin, X., Kudrass, H.R., Pautot, G. (Eds.), Marine Geology and Geophysics of the South China Sea. Proc. Symp. on Recent Contributions to the Geological History of the South China Sea. China Ocean Press, Hangzhou, p.60–70.
Chen, S., Lei, Z., Zhou, Y., 1987. Major oil accumulation characteristics and exploration direction in the Pearl River Mouth Basin. China Oil, Winter, p.17–23.
Clift, P., Lin, J., 2001. Preferential mantle lithospheric extension under the South China margin. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 18(8):929–945. [doi:10.1016/S0264-8172(01)00037-X]
Ding, W.W., Wang, Y.M., Chen, H.L., Yang, S.F., Wu, N.Y., 2004. Deformation characters and its tectonic evolution of the Southwest Taiwan Basin. Journal of Zhejiang University (Science Edition), 31(2):216–220 (in Chinese).
Du, D.L., 1994. Tectonic evolution and analysis of oil-gas accumulation in Southwest Taiwan Basin. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 14(3):5–18 (in Chinese).
ECPGC (Editiorial Committee of Petroleum Geology of Oil and Gas Bearing Areas on the Continental Shelf and Its Neighbouring Regions), 1990. Oil and Gas Bearing Areas on the Continental Shelf and Its Neighbouring Regions, Petroleum Geology of China. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing (in Chinese).
Ercilla, G., Alonso, B., Wynn, R.B., Baraza, J., 2002. Turbidity current sediment waves on irregular slopes: Observations from the Orinoco sediment-wave field. Marine Geology, 192:171–187.
Hall, R., 2002. Cenozoic geological and plate tectonic evolution of SE Asia and the SW Pacific: computer-based reconstructions, model and animations. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 20(4):353–431. [doi:10.1016/S1367-9120(01)00069-4]
Hall, R., Ali, J.R., Anderson, C.D., Baker, S.J., 1995. Origin and motion history of the Philippine Sea Plate. Tectonophysics, 251(1–4):229–250. [doi:10.1016/0040-1951(95)00038-0]
Hamilton, W., 1979. Tectonics of the indonesian region. U.S. Geol. Surv., Prof. Paper, 1078:345.
Heiniö, P., Dacies, R.J., 2006. Degradation of compressional fold belt: Deep-water Niger Delta. AAPG Bulletin, 90(5):753–770. [doi:10.1306/11210505090]
Hinz, K., Fritsh, J., Kempter, E.H.K., Mohammad, A.M., Mohamed, D., Vosberg, H., Weber, J., Benavidez, J., 1989. Thrust tectonics along the northwestern continental margin of Sabah/Borneo. Geologische Rundschau, 78(3):705–730. [doi:10.1007/BF01829317]
Hilde, T.W.C., Uyeda, S., Kroenke, L., 1977. Evolution of the western Pacific and its margin. Tectonophysics, 38:145–165. [doi:10.1016/0040-1951(77)90205-0]
Hinz, K., Schlünter, H.U., 1985. Geology of the dangerous grounds, South China Sea, and the continental margin off southwest Palawan: results of SONNE cruises SO-23 and SO-27. Energy, 10:297–315.
Holloway, N.H., 1982. North Palawan block, Philippines-Its relation to Asian mainland and role in evolution of South China Sea. AAPG Bulletin, 66 (9):1355–1383.
Huang, C.H., Wu, W.Y., Chang, C.P., 1997. Tectonic evolution of accretionary prism in the arc-continent collision terrane of Taiwan. Tectonophysics, 281(1–2):31–51. [doi:10.1016/S0040-1951(97)00157-1]
Huang, C.H., Xia, K.Y., Perter, B., 2001. Structural evolution from Paleogene extention to Latest Miocene-Recent arc-continent collision offshore Taiwan: comparison with on land geology. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 19(5):619–639. [doi:10.1016/S1367-9120(00)00065-1]
Hutchison, C.S., 2004. Marginal basin evolution: the southern South China Sea. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 21(9):1129–1148. [doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2004.07.002]
Lapierre, H., Jahn, B.M., Charvet, J., Yu, Y.W., 1997. Mesozoic felsic arc magmatism and continental olivine tholeiites in Zhejiang Province and their relationship with the tectonic activity in southeastern China. Tectonophysics, 274(4):321–338. [doi:10.1016/S0040-1951(97) 00009-7]
Letouzey, J., Sage, L., Müller, C., 1988. Geological and Structural Map of Eastern Asia, 1:2,500,000: Introductory Notes. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bookstore, USA, p.52.
Li, C.F., Zhou, Z.Y., Li, J.B., Hao, H.J., Geng, J.H., 2007. Structure of the northeasternmost South China Sea continental margin and ocean basin: geophysical constraints and tectonic implications. Marginal Geophysical Research, 28(1):59–79. [doi:10.1007/s11001-007-9014-9]
Li, J.B., Jin, X., Gao, J.Y., 2002. Morpho-tectonic study on late-stage spreading of the eastern subbasin of South China Sea. Science in China (Series D), 49(12): 1279–1288.
Li, M.B., Jin, X.L., Li, J.B., Chu, F.Y., Fang, Y.X., Tang, Y., 2005. Miocene deposition and palaeo-slope evolvement of the middle part of northern continental slope in the South China Sea. Acta Oceanologica Sinaca, 27(3):73–79 (in Chinese).
Lin, A.T., Watts, A.B., Hesselbo, S.P., 2003. Cenozoic stratigraphy and subsidence history of the South China Sea margin in the Taiwan region. Basin Research, 15(4):453–478. [doi:10.1046/j.1365-2117.2003.00215.x]
Lu, H., Fulthorpe, C.S., Mann, P., 2003. Three-dimensional architecture of shelf-building sediment drifts in the offshore Canterbury Basin. New Zealand: Marine Geology, 193:19–47.
Lüdmann, T., Wong, H.K. 1999. Neotectonic regime on the passive continental margin of the northern South China Sea. Tectonophysics, 311(1–4):113–138.
Mann, R.G., Bryant, W.R., Rabinowitz, P.D., 1992. Seismic Facies Interpretation of the Northern Green Canyon area, Gulf of Mexico. In: Watkins, J.S., Feng, Z.Q., McMillen, K.J. (Eds.), Geology and Geophysics of Continental Margins. AAPG Memoir, 53:343–360.
Northrup, C.J., Royden, L.H., Burchfiel, B.C., 1995. Motion of the Pacific plate relative to Eurasia and its potential relation to Cenozoic extension along the eastern margin of Eurasia. Geology, 23(8):719–722. [doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0719:MOTPPR>2.3.O;2]
Seno, T., Stein, S., Gripp, A.E., 1993. A model for the motion of the Philippine Sea plate consistent with NUVEL-1 and geologic data. Journal of Geophysical Research, 98(B10):17941–17948. [doi:10.1029/93JB00782]
Shanmugam, G., Moiola, R.J., 1988. Submarine fans: Characteristics, models, classification, and reservoir potential: Earth Science Reviews, 24:383–428.
Sibuet, J.C., Hsu, S.K., 2004. How was Taiwan created. Tectonophysics, 379(1–4):159–181. [doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2003.10.022]
Sun, Z., Zhong, Z.H., Zhou, D., Xia, B., Qiu, X.L., Zeng, Z.X., Jiang, J.Q., 2006. Research on the dynamics of the South China Sea opening: Evidence from analogue modeling. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 49(10): 1053–1069.
Suppe, J., 1984. Kinematics of arc-continent collision, flipping of subduction and back-arc spreading near Taiwan. Mem. Geol. Soc. China, 6:21–33.
Tapponnier, P., Peltzer, G..L., le Dain, A.Y., Armijo, R., Cobbold, P., 1982. Propagaring extrusion tectonics in Asia: New insights from simple experiments with plasticine. Geology, 10(12):611–616. [doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1982)10<611:PETIAN>2.0.CO;2]
Tapponnier, P., Peltzer, G., Armijo, R., 1986. On the Mechanics of the Collision between India and Asia. In: Coward, M.P., Ries, A.C. (Eds.), Collision Tectonics. Geol. Soc. London Spec., 19:115–157.
Taylor, B., Hayes, D.E., 1980. The Tectonic Evolution of the South China Basin. In: Hayes, D.E. (Eds.), the Tectonic and Geologic Evolution of Southeast Asian Seas and Islands, Part 1. Am. Geophys. Union Geophys. Monogr., 23:89–104.
Taylor, B., Hayes, D.E., 1983. Origin and History of the South China Sea basin. In: Hayes, D.E. (Ed.), the Tectonic and Geologic Evolution of Southeast Asian Seas and Islands, Part 2. Am. Geophys. Union Geophys. Monogr., 27:23–56.
Teng, L.S., 1990. Geotectonic evolution of late Cenozoic arc-continental collision in Taiwan. Tectonophysics, 183(1–4):57–76. [doi:10.1016/0040-1951(90)90188-E]
Tzeng, J., 1994. Tertiary Seismic Stratigraphic Analysis of the Tainan Basin. M.S. Thesis, National Taiwan University, p.5–17 (in Chinese).
Weimer, P., 1990. Sequence stratigraphy, facies geometries, and depositional history of the Mississippi Fan, Gulf of Mexico. AAPG Bulletin, 74:425–453.
Williams, P.R., Johnston, C.R., Almond, R.A., Simamora, W.H., 1988. Late Cretaceous to Early Tertiary structural elements of West Kalimantan. Tectonophysics, 148(3–4):279–297. [doi:10.1016/0040-1951(88)90135-7]
Yu, H.X., Lin, X.Z., 1992. The seismic-stratigraphic analysis of the late Cenozoic stratum, Tainan Basin. Acta Oceanographica Taiwanica, 9(2):6–12.
Zhong, J.Q., Huang, C.L., Zang, W.H., 1993. Geologic evolution analyse of Taixinan Basin in late Cenozoic Era. Marine Sciences, 12(4):34–38 (in Chinese).
Zhou, D., 2002. Mesozoic strata and sedimentary environment in SW Taiwan Basin of NE South China Sea and Peikang High of western Taiwan. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 21(2):50–57 (in Chinese).
Zhou, D., Ru, K., Chen, H.Z., 1995. Kinematics of Cenozoic extension on the South China Sea continental margin and its implications for the tectonic evolution of the region. Tectonophysics, 251(1–4):161–177. [doi:10.1016/0040-1951(95)00018-6]
Zhou, X.M., Li, W.X., 2000. Origin of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in southeastern China: implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas. Tectonophysics, 326(3–4):269–287. [doi:10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00120-7]
Zhou, Z., Lao, Q., Chen, H., Ding, S., Liao, Z., 1996. Early Mesozoic Orogeny in Fujian, Southeast China. In: Hall, R., Blundell, D. (Eds.), Tectonics Evolution of Southeast Asia. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ., 106:549–556.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Projected supported by the National Basic Research Program (973) of China (No. 2007CB411704), Key Laboratory of Marginal Sea Geology, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Nos. KZCX3-SW-234 and MSGL0609), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40676024)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Ww., Li, Jb., Li, Mb. et al. A Cenozoic tectono-sedimentary model of the Tainan Basin, the South China Sea: evidence from a multi-channel seismic profile. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 9, 702–713 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A071572
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A071572