Abstract
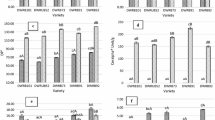
The effect of sowing date on grain protein, hordein fraction content and malting quality of two-rowed spring barley was invesitigated by using ten commercial cultivars with different grain protein content and the relationships among these traits were examined. The results showed that grain protein content and B hordein content increases as the sowing date postponed and were significantly affected by sowing date, while C and D hordein contents were less influenced by sowing date. There were significant differences in grain protein and hordein fraction content among the ten cultivars. The coefficient of variation of D hordein content was much larger than that of B and C hordein contents, suggesting its greater variation caused by different sowing dates. Beta-amylase activity and diastatic power were also significantly affected by sowing date, with malt extract being less affected. Significant differences in measured malt quality were found among the ten cultivars. Grain protein was significantly correlated with B hordein and malt extract positively and negatively, respectively. There was no significant correlation between beta-amylase activity or diastatic power and grain protein content. B hordein was negatively and significantly correlated with malt extract, but no significant correlations between C hordein, D hordein and malting quality traits.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC (American Association of Cereal Chemists), 2000. Approved Methods of American Association of Cereal Chemists, 10th Ed. The Association, St Paul, MN.
Ahokas, H., Naskali, L., 1990. Geographic variation of α-amylase, β-amylase, β-glucanase, pullulanase and chitinase activity in germinatingHordeum spontaneum barley from Israel and Jordan.Genetica,82:73–78.
Arends, A.M., Fox, G.P., Henry, R.J., Marschke, R.J., Symons, M.H., 1995. Genetic and environmental variation in the diastatic power of Australian barley.J. Cereal Sci.,21:63–70.
Baxter, E.D., Wainwright, T., 1979. Hordein and malting quality.J. Amer. Soc. Brew. Chemist,37:8–12.
Birch, C.J., Long, K.E., 1990. Effect of nitrogen on the growth, yield and grain protein content of barley (Hordeum vulgare).Aust. J. Exp. Agric.,30:237–242.
Bishop, L.R., Day, F.E., 1993. The effect of variety on the relation between nitrogen content and extract.J. Inst. Brew.,39:545–551.
Brennan, C.S., Smith, D.B., Harris, N., Shewry, P.R., 1998. The production and characterization of Hor3 null lines of barley provides new information on the relationship of D hordein to malting performance.J. Cereal Sci.,28:291–299.
Coles, G.D., Jamieson, P.D., Haslemore, R.M., 1991. Effects of moisture stress on malting quality in Triumph barley.J. Cereal Sci.,14:161–177.
Delcour, J.A., Verschaeve, S.G., 1987. Malt diastatic power. Part I. A modified EBC diastatic power assay for the selective estimation of β-amylase activity. Time and temperature dependence of the release of reducing sugars.J. Inst. Brew.,93:296–301.
Eagles, H.A., Bedggood, A.G.J., Panozzo, F., Martin, P.J., 1995. Cultivar and environmental effects on malting quality in barley.Aust. J. Agric. Res.,46:831–844.
EBC (European Brewery Convention), 1975. Analytica EBC, 3rd Ed. Verlag Hans Carl, Nurnberg, Germany.
Georg-Kraemer, J.E., Mundstock, E.C., Cavalli-Molina, L., 2001. Developmental expression of amylase during barley malting.J. Cereal Sci.,33:279–288.
Gibson, T.S., Solah, V., Glenni-Homes, M.R., Taylor, H.R., 1995. Diastatic power in malted barley: contributions of malt parameters to its development and the potential of barley grain beta-amylase to predict malt diastatic power.J. Inst. Brew.,101:277–280.
Grant, C.A., Gauer, L.E., Gehl, D.T., Bailey, L.D., 1991. Protein production and nitrogen utilization by barley cultivars in response to nitrogen fertilization under varying moisture conditions.Can. J. Plant Sci.,71:997–1009.
Howard, K.A., Gayler, K.R., Eagles, H.A., Halloran, G.M., 1996. The relationship between D hordein and malting quality in barley.J. Cereal Sci.,24:47–53.
Kaczmarek, K., Adamski, T., Surma, M., Jezowski, S., Lseniewska-Erstczak, M., 1999. Genotype-environment interaction of barley doubled haploids with regard to malting quality.Plant Breeding,118:243–247.
Macnicol, P.K., Jacobsen, J.V., Keys, M.M., Stuart, I.M., 1993. Effects of heat and water stress on malt quality and grain parameters of Schooner barley grown in cabinets.J. Cereal Sci.,18:61–68.
McCleary, B.V., Codd, R., 1989. Measurement of β-amylase in cereal flours and commercial enzyme preparations.J. Cereal Sci.,9:17–33.
Molina-Cano, J.L., Francesch, M., Perez-Vendrell, A.M., Ramo, T., Voltas, J., Brufau, J., 1997. Genetic and environmental variation in malting and feed quality of quality.J. Cereal Sci.,25:37–47.
Molina-Cano, J.L., Polo, J.P., Romera, E., Araus, J.L., Zarco, J., Swanston, J.S., 2001. Relationships between barley hordeins and malting quality in a mutant of cv. Triumph I. Genotype by environment interaction of hordein content.J. Cereal Sci.,34:285–294.
Morgan, A.G., Riggs, T.J., 1981. Effects of drought on yield and grain and malt characters in spring barley.J. Sci. Food Agric.,32:339–346.
Peltonen, J., Rita, H., Aikasalo, R., Home, S., 1994. Hordein and malting quality in northern barleys.Hereditas,120:231–239.
Rahman, S., Shewry, P.R., Miflin, B.J., 1982. Differential protein accumulation during barley grain development.J. Exper. Bot.,33:717–728.
Riggs, T.J., Sanada, M., Morgan, A.G., Smith, D.B., 1983. Use of acid gel electrophoresis in the characterization of “B” hordein protein in relation to mating quality and mildew resistance of barley.J. Sci. Food Agric.,34:576–586.
Savin, R.S., Nicolas, M.E., 1996. Effects of short periods of drought and high temperature on grain growth and starch accumulation of two malting barley cultivars.Aust. J. Plant Physiol.,23:201–210.
Shewry, P.R., Faulks, A.J., Parmar, S., Miflin, B.J., 1980. Hordein polypeptide pattern in relation to malting quality and the varietal identification of malted barley grain.J. Inst. Brew.,86:138–141.
Shewry, P.R., Franklin, J., Parmar, S., Smith, S.J., Miflin, B.J., 1983. The effects of sulphur starvation on the amino acid and protein compositions of barley grain.J. Cereal Sci.,1:21–31.
Shewry, P.R., Kreis, M., Parmar, S., Lew, E.J.L., Kasarda, D.D., 1985. Identification of γ-type hordeins in barley.FEBS Lett.,190:61–64.
Smith, D.B., 1990. Barley seed protein and its effects on malting and brewing quality.Plant Varieties Seeds,3:63–80.
Swanston, J.S., 1980. Use of electrophoresis in testing for high diastatic power in barley.J. Inst. Brew.,86:81–83.
Swanston, J.S., Molina-Cano, J.L., 2001. Beta-amylase activity and thermostability in two mutants derived from the malting barley cv. Triumph.J. Cereal Sci.,33:155–162.
Varvel, G.E., Severson, R.K., 1987. Evaluation of cultivar and nitrogen management's options for malting barley.Agron. J.,79:459–463.
Wang, J.M., Zhang, G.P., Chen, J.X., Shen, Q.Q., Wu, F.B., 2003. Genotypic and environmental variation in barley beta-amylase activity and its relation to protein content.Food Chem.,83:163–165.
Weston, D.T., Horsley, R., Schwarz, P.B., Goos, R.J., 1993. Nitrogen and planting date effects on low-protein spring barley.Agron. J.,85:1170–1174.
Yin, C., Zhang, G.P., Wang, J.M., Chen, J.X., 2002. Variation of beta-amylase activity in barley as affected by cultivar and environmental and its relation to protein content and grain weight.J. Cereal Sci.,36:307–312.
Zhang, G.P., Wang, J.M., Chen, J.X., Wu, F.B., Ding, S.R. 2005. The effect of cultivar and environment on beta-amylase activity is associated with the change of protein content in barley grains.J. Agron. Crop Sci., in Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30270779 and 30471022) and Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (SRFDP) (No. 20020335028), China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, Jc., Chen, Jx., Wang, Jm. et al. Protein and hordein fraction content in barley seeds as affected by sowing date and their relations to malting quality. J Zheijang Univ Sci B 6, 1069–1075 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.B1069
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.B1069