Abstract
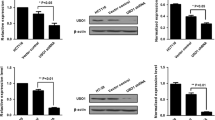
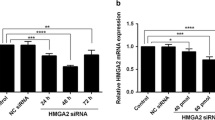
Eukaryotic initiation factor subunit c (eIF3c) has been identified as an oncogene that is over-expressed in tumor cells and, therefore, is a potential therapeutic target for gene-based cancer treatment. This study was focused on investigating the effect of small interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated eIF3c gene knockdown on colon cancer cell survival. The eIF3c gene was observed to be highly expressed in colon cancer cell models. The expression levels of the gene in eIF3c siRNA infected and control siRNA infected cells were compared via real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and western blotting analysis. Cell proliferation levels were analyzed employing 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) and colony formation assays. Furthermore, the effects of eIF3c gene knockdown on the cell cycle and apoptosis were analyzed using flow cytometry. The results showed that suppression of eIF3c expression significantly (P<0.001) reduced cell proliferation and colony formation of RKO colon cancer cells. The cell cycle was arrested by decreasing the number of cells entering S phase. Further, apoptosis was induced as a result of eIF3c knockdown. Collectively, eIF3c deletion effectively reduced the survival of colon cancer cells and could be used as a therapeutic tool for colon cancer therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bass, B.L., 2000. Double-stranded RNA as a template for gene silencing. Cell, 101(3):235–238. [doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(02)71133-1]
Caplen, N.J., Parrish, S., Imani, F., Fire, A., Morgan, R.A., 2001. Specific inhibition of gene expression by small double-stranded RNAs in invertebrate and vertebrate systems. PNAS, 98(17):9742–9747. [doi:10.1073/pnas.171251798]
Devi, G.R., 2006. SiRNA-based approaches in cancer therapy. Cancer Gene Ther., 13(9):819–829. [doi:10.1038/sj.cgt.7700931]
Elbashir, S.M., Harborth, J., Lendeckel, W., Yalcin, A., Weber, K., Tuschl, T., 2001. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature, 411(6836):494–498. [doi:10.1038/35078107]
Karaayvaz, M., Pal, T., Song, B., Zhang, C., Georgakopoulos, P., Mehmood, S., Burke, S., Shroyer, K., Ju, J., 2011. Prognostic significance of miR-215 in colon cancer. Clin. Colorect. Cancer, 10(4):340–347. [doi:10.1016/j.clcc.2011.06.002]
Loftus, B.J., Kim, U.J., Sneddon, V.P., Kalush, F., Brandon, R., Fuhrmann, J., Mason, T., Crosby, M.L., Barnstead, M., Cronin, L., 1999. Genome duplications and other features in 12 mb of DNA sequence from human chromosome 16p and 16q. Genomics, 60(3):295–308. [doi:10.1006/geno.1999.5927]
Longley, D.B., Allen, W.L., Johnston, P.G., 2006. Drug resistance, predictive markers and pharmacogenomics in colorectal cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer, 1766(2):184–196. [doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2006.08.001]
Mclornan, D.P., Barrett, H.L., Cummins, R., 2010. Prognostic significance of trail signaling molecules in stage II and III colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res., 16(13):3442–3451. [doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0052]
Scoles, D.R., 2008. eIF3c (eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3, subunit c). Atlas Genet. Cytogenet. Oncol. Haematol., 12:428–429.
Scoles, D.R., Yong, W.H., Qin, Y., Wawrowsky, K., Pulst, S.M., 2006. Schwannomin inhibits tumorigenesis through direct interaction with the eukaryotic initiation factor subunit c (eIF3c). Human Mol. Genet., 15(7):1059–1070. [doi:10.1093/hmg/ddl021]
Sonenberg, N., Hinnebusch, A.G., 2009. Regulation of translation initiation in eukaryotes: mechanisms and biological targets. Cell, 136(4):731–745. [doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.042]
Soneoka, Y., Cannon, P.M., Ramsdale, E.E., Griffiths, J.C., Romano, G., Kingsman, S.M., Kingsman, A.J., 1995. A transient three-plasmid expression system for the production of high titer retroviral vectors. Nucl. Acids Res., 23(4):628–633. [doi:10.1093/nar/23.4.628]
van de Veer, L.J., Dai, H., van de Vijver, M.J., 2002. Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature, 415(6871):530–536. [doi:10.1038/415530a]
Verma, U.N., Surabhi, R.M., Schmaltieg, A., Becerra, C., Gaynor, R.B., 2003. Small interfering RNAs directed against β-catenin inhibit the in vitro and in vivo growth of colon cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res., 9(4):1291–1300.
Zhang, L., Pan, X., Hershey, J.W., 2007. Individual overexpression of five subunits of human translation initiation factor eIF3 promotes malignant transformation of immortal fibroblast cells. J. Biol. Chem., 282(8):5790–5800. [doi:10.1074/jbc.M606284200]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The two authors contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, N., Wang, Y., Gu, Xd. et al. Effect of siRNA-mediated knockdown of eIF3c gene on survival of colon cancer cells. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 14, 451–459 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1200230
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1200230