Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effect of enalapril on plasma homocysteine (Hcy) levels and the association of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T polymorphism with the changes of Hcy levels in response to enalapril among patients with essential hypertension.
Methods
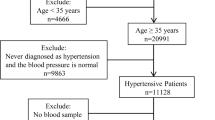
A total of 130 patients with mild-to-moderate essential hypertension were enrolled and enalapril was orally administered at a dose of 10 mg/d for eight weeks. Plasma Hcy levels were measured by denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC) at baseline and after eight weeks of treatment. Genotyping of MTHFR C677T polymorphism was performed by TaqMan probe technique.
Results
Compared with baseline, plasma Hcy levels did not change significantly after eight weeks (P=0.81). Stratified by baseline Hcy levels, a significant increase in plasma Hcy levels (P=0.02) among those with Hcy <10 μmol/L was observed, in contrast to no significant changes in plasma Hcy levels (P=0.54) among those with Hcy ≥10 μmol/L. No significant association was observed between MTHFR C677T polymorphism and changes in Hcy levels in response to enalapril.
Conclusions
Enalapril may cause an increase in plasma Hcy levels among the hypertensives with low baseline Hcy levels. There was no significant association between MTHFR C677T genotypes and changes in Hcy levels in response to enalapril among subjects with essential hypertension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson, A., Brattström, L., Israelsson, B., Isaksson, A., Hamfelt, A., Hultberg, B., 1992. Plasma homoeysteine before and after methionine loading with regard to age, gender and menopausal status. European Journal of Clinical Investigation, 22(2):79–87. [doi:10.1111/j.1365-2362.1992.tb01940.x]
Atar, I., Korkmaz, M.E., Demircan, S., Atar, I.A., Bozbaş, H., Aydinalp, A., Ozin, B., Yildirir, A., Müderrisoğlu, H., 2005. Beta blocker effects on plasma homocysteine levels in patients with hypertension. Atherosclerosis, 181(2):399–402. [doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2005.01.035]
Bots, M.L., Launer, L.J., Lindemans, J., Hoes, A.W., Hofman, A., Witteman, J.C., Koudstaal, P.J., Grobbee, D.E., 1999. Homocysteine and short-term risk of myocardial infarction and stroke in the elderly: the Rotterdam study. Archives of Internal Medicine, 159(1):38–44. [doi:10.1001/archinte.159.1.38]
Boushey, C.J., Beresford, S.A., Omenn, G.S., Motulsky, A.G., 1995. A quantitative assessment of plasma homocysteine as a risk factor for vascular disease. Probable benefits of increasing folic acid intakes. The Journal of the American Medical Association, 274(13):1049–1057. [doi:10.1001/jama.274.13.1049]
Brattstrom, L., Lindgren, A., Israelsson, B., Andersson, A., Hultberg, B., 1994. Homocysteine and cysteine: determinants of plasma levels in middle-aged and elderly subjects. Journal of Internal Medicine, 236(6):633–641. [doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.1994.tb00856.x]
Desouza, C., Keebler, M., McNamara, D.B., Fonseca, V., 2002. Drugs affecting homocysteine metabolism: impact on cardiovascular risk. Drugs, 62(4):605–616. [doi:10.2165/00003495-200262040-00005]
Dierkes, J., Westphal, S., 2005. Effect of drugs on homocysteine concentrations. Seminars in Vascular Medicine, 5(2):124–139. [doi:10.1055/s-2005-872398]
Frosst, P., Blom, H.J., Milos, R., Goyette, P., Sheppard, C.A., Matthews, R.G., Boers, G.J., den Heijer, M., Kluijtmans, L.A., van den Heuvel, L.P., et al., 1995. A candidate genetic risk factor for vascular disease: a common mutation in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. Nature Genetics, 10(1):111–113. [doi:10.1038/ng0595-111]
Graham, I.M., Daly, L.E., Refsum, H.M., Robinson, K., Brattström, L.E., Ueland, P.M., Palma-Reis, R.J., Boers, G.H., Sheahan, R.G., Israelsson, B., et al., 1997. Plasma homocysteine as a risk factor for vascular disease. The Eumpean Concerted Action Project. The Journal of the American Medical Association, 277(22):1775–1781. [doi:10.1001/jama.277.22.1775]
Gu, D.F., He, J., Wu, X.G., Duan, X.F., Yao, C.H., Wang, J.L., Reynolds, K., Chen, C.S., Klag, M.J., Whelton, P.K., 2006. Main causes and its modifiable risks of death among men and women in China. Chinese Journal of Prevention and Control of Chronic Non-communicable Diseases, 14(3):149–154 (in Chinese).
Guilliams, T.G., 2004. Homocysteine-a risk factor for vascular diseases: guidelines for the clinical practice. The Journal of the American Nutraceutical Association, 7(1):11–24.
Homomcysteine Studies Collaboration, 2002. Homocysteine and risk of ischemic heart disease and stroke: a metaanalysis. The Journal of the American Medical Association, 288(16):2015–2022.
Hu, D.Y., Xu, X.P., 2008. Prevention of stroke relies on valid control “H” type hypertension. Chinese Journal of Internal Medicine, 47(12):976–977 (in Chinese).
Huang, H.W., Guo, M.H., Huang, J.X., Lin, R.J., Zhang, Y., Chen, Y.L., 2006. The analysis of plasma homocysteine among 1020 residents in community. Chinese Journal of Epidemiology, 27(8):721–724 (in Chinese).
Jacques, P.F., Bostom, A.G., Williams, R.R., Ellison, R.C., Eckfeldt, J.H., Rosenberg, I.H., Selhub, J., Rozen, R., 1996. Relation between folate status, a common mutation in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase, and plasma homocysteine concentrations. Circulation, 93(1):7–9.
Jacques, P.F., Bostom, A.G., Wilson, P.W., Rich, S., Rosenberg, I.H., Selhub, J., 2001. Determinants of plasma total homocysteine concentration in the Framingham Offspring cohort. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 73(3):613–621.
Jiang, S., Hsu, Y.H., Xu, X., Xing, H., Chen, C., Niu, T., Zhang, Y., Peng, S., Xu, X., 2004. The C677T polymorphism of the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene is associated with the level of decrease on diastolic blood pressure in essential hypertension patients treated by angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. Thrombosis Research, 113(6):361–369. [doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2004.04.005]
Kjeldsen, S.E., Julius, S., Hedner, T., Hansson, L., 2001. Stroke is more common than myocardial infarction in hypertension: analysis based on 11 major randomized intervention trials. Blood Pressure, 10(4):190–192. [doi:10.1080/08037050152669684]
Li, J.P., Huo, Y., Liu, P., Qin, X.H., Guan, D.M., Ge, J.B., Hu, J., Wang, Y.N., Zhang, F.M., Mao, G.Y., et al., 2007. Efficacy and safety of enalapril-folate acid tablets in lowering blood pressure and plasma homocysteine. Journal of Peking University: Health Sciences, 39(6):614–618 (in Chinese).
Madero, M., Sarnak, M.J., Stevens, L.A., 2006. Serum cystatin C as a marker of glomerular filtration rate. Current Opinion in Nephrology and Hypertension, 15(6):610–616. [doi:10.1097/01.mnh.0000247505.71915.05]
McNulty, H., Pentieva, K., Hoey, L., Ward, M., 2008. Homocysteine, B-vitamins and CVD. The Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 67(2):232–237. [doi:10.1017/S0029665108007076]
Nygård, O., Vollset, S.E., Refsum, H., Stensvold, I., Tverdal, A., Nordrehaug, J.E., Ueland, M., Kvåle, G., 1995. Total plasmahomocystein and cardiovaseular risk Profile. The Hordaland Homoeystein study. The Journal of the American Medical Association, 274(19):1526–1533. [doi:10.1001/jama.274.19.1526]
Poduri, A., Kaur, J., Thakur, J.S., Kumari, S., Jain, S., Khullar, M., 2008. Effect of ACE inhibitors and beta-blockers on homocysteine levels in essential hypertension. Journal of Human Hypertension, 22(4):289–294. [doi:10.1038/sj.jhh.1002325]
Rong, R., Zhang, A.M., Fan, C.H., Zhang, Z., 2009. The analysis of the relationship between serum homocysteine (HCY) and chemistries in patients of coronary heart disease. Chinese Journal of Laboratory, 13(1):77–80 (in Chinese).
Sacco, R.L., Adams, R., Albers, G., Alberts, M.J., Benavente, O., Furie, K., Goldstein, L.B., Gorelick, P., Halperin, J., Harbaugh, R., et al., 2006. Guidelines for prevention of stroke in patients with ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Council on Stroke: co-sponsored by the Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention. Stroke, 37(2):577–617. [doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000199147.30016.74]
Saposnik, G., Ray, J.G., Sheridan, P., McQueen, M., Lonn, E., Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation 2 Investigators, 2009. Homocysteine-lowering therapy and stroke risk, severity, and disability: additional findings from the HOPE 2 trial. Stroke, 40(4):1365–1372. [doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.529503]
Šebeková, K., Gazdíková, K., Syrová, D., Blazícek, P., Schinzel, R., Heidland, A., Spustová, V., Dzúrik, R., 2003. Effects of ramipril in nondiabetic nephropathy: improved parameters of oxidatives stress and potential modulation of advanced glycation end products. Journal of Human Hypertension, 17(4):265–270. [doi:10.1038/sj.jhh.1001541]
Spence, J.D., Howard, V.J., Chambless, L.E., Malinow, M.R., Pettigrew, L.C., Stampfer, M., Toole, J.F., 2001. Vitamin intervention for stroke prevention (VISP) trial: rationale and design. Neuroepidemiology, 20(1):16–25. [doi:10.1159/000054753]
Sun, Y., Chien, K.L., Hsu, H.C., Su, T.C., Chen, M.F., Lee, Y.T., 2009. Use of serum homocysteine to predict stroke, coronary heart disease and death in Ethnic Chinese: a 12-year prospective cohort study. Circulation Journal, 73(8):1423–1430. [doi:10.1253/circj.CJ-08-1077]
Sunder-Plassmann, G., Födinger, M., 2003. Genetic determinants of the homocysteine level. Kidney International, 63(s84):141–144. [doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.63.s84.52.x]
Trabetti, E., 2008. Homocysteine, MTHFR gene polymorphisms, and cardio-cerebrovascular risk. Journal of Applied Genetics, 49(3):267–282.
Ueland, P.M., Refsum, H., Stabler, S.P., Malinow, M.R., Andersson, A., Allen, R.H., 1993. Total homocysteine in plasma or serum: methods and clinical applications. Clinical Chemistry, 39(9):1764–1779.
Ueland, P.M., Hustad, S., Schneede, J., Refsum, H., Vollset, S.E., 2001. Biological and clinical implications of the MTHFR C677T polymorphism. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 22(4):195–201. [doi:10.1016/S0165-6147(00)01675-8]
Verhoef, P., Kok, F.J., Kluijtmans, L.A., Blom, H.J., Refsum, H., Ueland, P.M., Kruyssen, D.A., 1997. The 677C→T mutation in the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene: associations with plasma total homocysteine levels and risk of coronary atherosclerotic disease. Atherosclerosis, 132(1):105–113. [doi:10.1016/S0021-9150(97)00084-1]
Wald, D.S., Law, M., Morris, J.K., 2002. Homocysteine and CVD: evidence on causality from a meta-analysis. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.), 325(7374):1202. [doi:10.1136/bmj.325.7374.1202]
Wang, X., Qin, X., Demirtas, H., Li, J., Mao, G., Huo, Y., Sun, N., Liu, L., Xu, X., 2007. Efficacy of folic acid supplementation in stroke prevention: a meta-analysis. Lancet, 369(9576):1876–1882. [doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60854-X]
Wang, Y.J., Liu, L.S., Rao, K.Q., Xu, X.P., 2008. Thoughts for prevention of stroke in China: control both hypertension and hyperhomocysteinemia. National Medical Journal of China, 88(47):3316–3318 (in Chinese).
Westphal, S., Rading, A., Luley, C., Dierkes, J., 2003. Antihypertensive treatment and homocysteine concentrations. Metabolism, 52(3):261–263. [doi:10.1053/meta.2003.50060]
Xu, Y.L., Zhang, S.C., Li, J.P., Wang, M.D., Xing, H.X., Zang, T.H., Huo, Y., Xu, X.P., 2006. The modification of MTHFR gene polymorphism effect of the correlation between serum folic acid and plasma homocysteine. Acta Universitatis Medicinalis Anhui, 41(6):639–642 (in Chinese).
Yang, Q., Botto, L.D., Erickson, J.D., Berry, R.J., Sambell, C., Johansen, H., Friedman, J.M., 2006. Improvement in stroke mortality in Canada and the United States, 1990 to 2002. Circulation, 113(10):1335–1343. [doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.570846]
Zhan, Y.Q., Jin, Y., Li, Y.Z., 2001. A general introduction of clinical application of angiotension converting enzyme inhibitors. China Licensed Pharmacist, 7(1):3–6 (in Chinese).
Zhao, D., Liu, J., Wang, W., Zeng, Z., Cheng, J., Liu, J., Sun, J., Wu, Z., 2008. Epidemiological transition of stroke in China: twenty-one-year observational study from the Sino-MONICA-Beijing Project. Stroke, 39(6):1668–1674. [doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.502807]
Zhu, L.H., Xu, G.B., Yang, H.Y., 2001. Homocysteine and atherosclerosis. Chinese Journal of Laboratory Medicine, 24(2):121–123 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Ff., Huo, Y., Wang, X. et al. Effect of enalapril on plasma homocysteine levels in patients with essential hypertension. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 11, 583–591 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1001003
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1001003
Key words
- Essential hypertension
- Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T polymorphism
- Enalapril
- Homocysteine