Abstract
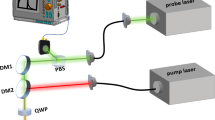
We are developing a new non-contact and non-destructive imaging technique which requires no sample preparation and provides similar content information as FTIR or Raman spectroscopy while being immune to fluorescence and offers a potentially faster scan rate and/or higher spatial resolution. It utilizes photo-thermal heating of the sample with a quantum cascade laser (or other suitable infrared laser) and measuring the resulting increase in thermal emissions by either an infrared (IR) detector or a laser probe consisting of a visible laser reflected from the sample. The latter case allows for further increases in the spatial resolution from ∼10 μm to ∼1 μm or better, with suitable experimental conditions. Since the thermal emission signal is proportional to the absorption coefficient, by tuning the wavelength of the IR laser we can directly measure the IR spectrum of the sample. By raster scanning over the surface of the sample we can obtain maps of the chemical composition of the sample surface. We demonstrate this technique by imaging the surface of a micro-fabricated flow-through chemical vapor preconcentrator consisting of a silicon frame and a suspended-perforated polyimide membrane with a pair of platinum heater traces, coated with a custom sorbent polymer for selective sorption of analyte. We measure the spatial resolution of our photo-thermal imaging system as well as discuss the conditions under which the spatial resolution can be further increased from the far-field diffraction limited resolution given by the combination of the imaging optic and IR excitation laser wavelength.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. C. Tam, in Photo-thermal Investigations of Solids and Fluids, edited by J. A. Sell, (Academic Press Inc., San Diego, CA, 1988).
R. Furstenberg, C. A. Kendziora, J. Stepnowski, S. V. Stepnowski, M. Rake, M. R. Papantonakis, V. Nguyen, G. K. Hubler and R. A. McGill, Appl. Phys. Lett., 93(22) (2008).
M. Martin, M. Crain, K. Walsh, R. A. McGill, E. Houser, J. Stepnowski, S. Stepnowski, H. D. Wu, S. Ross, Sensors And Actuators B - Chemical 126, 447–454 (2007).
B. A. Higgins, D. L. Simonson, E. J. Houser J. G. Kohl and R. A. McGill, J. Pol. Sci. Part A. 48, 3000–3009 (2010).
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by funding from ONR/NRL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furstenberg, R., Kendziora, C.A., Papantonakis, M.R. et al. Photo-Thermal Spectroscopic Imaging of MEMS Structures with Sub-Micron Spatial Resolution. MRS Online Proceedings Library 1415, 85–90 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2012.71
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2012.71