Abstract
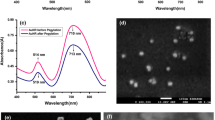
Gold nanorods (AuNRs) show surface plasmon absorption bands in the near-infrared region. This characteristic property has stimulated utilization of gold nanorods as novel nanoprobes for noninvasive bioimaging, such as photoacoustic tomography. Herein, we discuss the synthesis of a series of gold nanorods coated with pH-responsive polymers to investigate the effect of the surface structure and zeta potential of nanoparticles on cellular uptake via a surface charge-mediated endocytic pathway. The surface of the gold nanorods was modified with polyethylene glycol (PEG@AuNR) and tertiary amine derivatives, specifically, diethylaminoethyl ester (1@AuNRs), its amide analog (2@AuNRs), and dimethylaminoethyl ester (3@AuNRs). It was found that the pH-sensitivity of 1@AuNRs was relatively high and the surface was positively charged at lower pH. In contrast, the tertiary amino group of 1@AuNRs was deprotonated to form an electrostatically neutral surface at higher pH. The pH-responsive gold nanorods were incubated with A549 cells (human lung cancer cells) to quantify the amount of cellular uptake using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. The results indicate that 1@AuNRs can be taken up efficiently in the cells, and thereafter, slowly flow out of the cells. Interestingly, only small amounts of the amide analog (2@AuNRs) were taken into the cells, suggesting minor structural changes may affect the interaction between the cell surface and AuNRs. This study highlights a potential application of pH-sensitive nanorods as a probe for bioimaging the acidic environment of tumors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. R. Arvizo, O. R. Miranda, M. A. Thompson, C. M. Pabelick, R. Bhattacharya, J. D. Robertson, V. M. Rotello, Y. S. Prakash and P. Mukherjee, Nano Lett. 10, 2543 (2010).
T. S. Hauck, A. A. Ghazani and W. C. W. Chan, Small 4, 153 (2008).
A. M. Alkilany, P. K. Nagaria, C. R. Hexel, T. J. Shaw, C. J. Murphy and M. D. Wyatt, Small 5, 701 (2009).
A. I. Hashim, X. Zhang, J. W. Wojtkowiak, G. V. Martinez and R. J. Gillies, NMR Biomed. 24, 582 (2011).
Y. Niidome, K. Nishioka, H. Kawasaki and S. Yamada, Chem. Commun. 2003, 2376.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Drs M. Inoue and S. Hosokawa (Kyoto University) for their assistance with the TEM and zeta potential measurements. This work was supported by the Program for Fostering Regional Innovation “Kyoto Environmental Nanotechnology Cluster” administered by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan (MEXT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, T., Kusaka, E., Isobe, Y. et al. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Coated with pH-Responsive Polymers and Evaluation of the Cellular Uptake. MRS Online Proceedings Library 1416, 1–6 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2012.477
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2012.477