Abstract
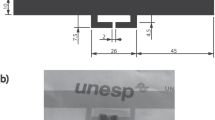
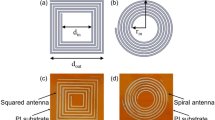
A rapid low-pressure plasma sintering process of inkjet-printed silver nanoparticles is reported, yielding a conductivity of 11.4% of bulk silver within 1 min of plasma exposure and a final conductivity up to 40% of bulk silver for longer sintering times. The maximum processing temperature did not exceed 70 °C, which enabled the use of cost-effective polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foils. Fully functional radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags were prepared with inkjet-printed antennas, which showed similar results as screen-printed devices. The inkjet-printed antennas require significantly less materials, hence thinner layers, than the screen-printed references.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Huang, F. Liao, S. Molesa, D. Redinger, and V. Subramanian: Plastic-compatible low resistance printable gold nanoparticle conductors for flexible electronics. J. Electrochem. Soc. 150(7), G412 (2003).
S.B. Fuller, E.J. Wilhelm, and J.M. Jacobson: Inkjet printed nanoparticle microelectromechanical systems. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 11(1), 54 (2002).
I. Reinhold, C.E. Hendriks, R. Eckardt, J.M. Kranenburg, J. Perelaer, R.R. Baumann, and U.S. Schubert: Argon plasma sintering of inkjet printed silver tracks on polymer substrates. J. Mater. Chem. 19(21), 3384 (2009).
R.R. Søndergaard, M. Hösel, and F.C. Krebs: Roll-to-roll fabrication of large area functional organic materials. J. Polym. Sci., Part B: Polym. Phys. 51(1), 16 (2013).
D.Y. Shin, Y. Lee, and C.H. Kim: Performance characterization of screen printed radio frequency identification antennas with silver nanopaste. Thin Solid Films 517(21), 6112 (2009).
T. Kowalik, S. Worch, A. Hartwig, and H. Joachimi: Conductive UV curable adhesives for printed RFID antenna structures. Macromol. Symp. 254(1), 300 (2007).
J. Perelaer, P.J. Smith, D. Mager, D. Soltman, S.K. Volkman, V. Subramanian, J.G. Korvink, and U.S. Schubert: Printed electronics: The challenges involved in printing devices, interconnects, and contacts based on inorganic materials. J. Mater. Chem. 20(39), 8446 (2010).
P.J. Smith, D.Y. Shin, J.E. Stringer, B. Derby, and N. Reis: Direct inkjet printing and low temperature conversion of conductive silver patterns. J. Mater. Sci. 41(13), 4153 (2006).
A. Kamyshny, J. Steinke, and S. Magdassi: Metal-based inkjet inks for printed electronics. Open Appl. Phys. J. 4, 19 (2011).
J. Perelaer, A.W.M. de Laat, C.E. Hendriks, and U.S. Schubert: Inkjet printed silver tracks: Low temperature curing and thermal stability investigation. J. Mater. Chem. 18(27), 3209 (2008).
S. Gamerith, A. Klug, H. Scheiber, U. Scherf, E. Moderegger, and E.J.W. List: Direct inkjet printing of Ag-Cu nanoparticle and Ag-precursor based electrodes for OFET applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 17(16), 3111 (2007).
R.S. Goeke and A.K. Datye: Model oxide supports for studies of catalyst sintering at elevated temperatures. Top. Catal. 46(1–2), 3 (2007).
J. Perelaer and U.S. Schubert: Novel approaches for low temperature sintering of inkjet-printed inorganic nanoparticles for roll-to-roll (R2R) applications. J. Mater. Res. 28 (2013). doi: 10.1557/jmr.2012.419.
S-J.L. Kang: Sintering: Densification, Grain Growth, and Microstructure, 1st ed. (Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Burlington, 2005), pp. 37–77.
H.H. Lee, K.S. Chou, and K.C. Huang: Inkjet printing of nanosized silver colloids. Nanotechnology 16(10), 2436 (2005).
J. Perelaer, R. Jani, M. Grouchko, A. Kamyshny, S. Magdassi, and U.S. Schubert: Plasma and microwave flash sintering of a tailored silver nanoparticle ink, yielding 60% bulk conductivity on cost-effective polymer foils. Adv. Mater. 24(29), 3993 (2012).
H-S. Kim, S.R. Dhage, D-E. Shim, and H.T. Hahn: Intense pulsed light sintering of copper nanoink for printed electronics. Appl. Phys. A 97(4), 791 (2009).
M. Grouchko, A. Kamyshny, C.F. Mihailescu, D.F. Anghel, and S. Magdassi: Conductive inks with a "built-in" mechanism that enables sintering at room temperature. ACS Nano 5(4), 3354 (2011).
Y. Tang, W. He, G. Zhou, S. Wang, X. Yang, Z. Tao, and J. Zhou: A new approach causing the patterns fabricated by silver nanoparticles to be conductive without sintering. Nanotechnology 23, 355304 (2012).
M. Hosel and F.C. Krebs: Large-scale roll-to-roll photonic sintering of flexo printed silver nanoparticle electrodes. J. Mater. Chem. 22(31), 15683 (2012).
D. Angmo, T.T. Larsen-Olsen, M. Jørgensen, R.R. Søndergaard, and F.C. Krebs: Roll-to-roll inkjet printing and photonic sintering of electrodes for ITO free polymer solar cell modules and facile product integration. Adv. Energy Mater. (2012). doi: 10.1002/aenm.201200520.
S.H. Ko, H. Pan, C.P. Grigoropoulos, C.K. Luscombe, J.M.J. Frechet, and D. Poulikakos: Air stable high resolution organic transistors by selective laser sintering of inkjet printed metal nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(14) (2007).
N.R. Bieri, J. Chung, D. Poulikakos, and C.P. Grigoropoulos: Manufacturing of nanoscale thickness gold lines by laser curing of a discretely deposited nanoparticle suspension. Superlattices Microstruct. 35(3–6), 437 (2004).
M.L. Allen, M. Aronniemi, T. Mattila, A. Alastalo, K. Ojanpera, M. Suhonen, and H. Seppa: Electrical sintering of nanoparticle structures. Nanotechnology 19(17) (2008).
J. Leppaniemi, M. Aronniemi, T. Mattila, A. Alastalo, M. Allen, and H. Seppa: Printed WORM memory on a flexible substrate based on rapid electrical sintering of nanoparticles. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 58(1), 151 (2011).
R. Roy, D. Agarwal, J.P. Chen, and S. Gedevanishvili: Full sintering of powdered-metal bodies in a microwave field. Nature 399(6737), 668 (1999).
J. Perelaer, B-J. de Gans, and U.S. Schubert: Inkjet printing and microwave sintering of conductive silver tracks. Adv. Mater. 18(16), 2101 (2006).
S. Wunscher, S. Stumpf, A. Teichler, O. Pabst, J. Perelaer, E. Beckert, and U.S. Schubert: Localized atmospheric plasma sintering of inkjet printed silver nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 22(47), 24569 (2012).
J. Perelaer, R. Abbel, S. Wünscher, R. Jani, T. van Lammeren, and U.S. Schubert: Roll-to-roll compatible sintering of inkjet printed features by photonic and microwave exposure: From non-conductive ink to 40% bulk silver conductivity in less than 15 seconds. Adv. Mater. 24(19), 2620 (2012).
R.D. Deegan: Pattern formation in drying drops. Phys. Rev. E 61(1), 475 (2000).
S.L. Merilampi, T. Bjorninen, A. Vuorimaki, L. Ukkonen, P. Ruuskanen, and L. Sydanheimo: The effect of conductive ink layer thickness on the functioning of printed UHF RFID antennas. Proc. IEEE 98(9), 1610 (2010).
Acknowledgments
For financial support, the authors thank the Dutch Polymer Institute (DPI, technology area HTE) as well as the European Community’s Seventh Framework Program (FP7/2007–2013) under grant agreement no. 248816. Renzo Paulus, Laboratory of Organic and Macromolecular Chemistry, Friedrich-Schiller-University, Jena, is kindly acknowledged for his assistance with the TGA measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wolf, F.M., Perelaer, J., Stumpf, S. et al. Rapid low-pressure plasma sintering of inkjet-printed silver nanoparticles for RFID antennas. Journal of Materials Research 28, 1254–1261 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.73
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.73