Abstract
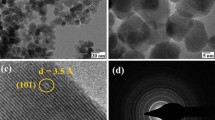
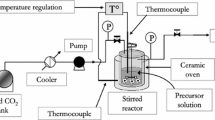
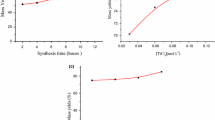
High purity anatase titanium dioxide (TiO2) and iron (Fe)-doped TiO2 nanocrystals were prepared by a continuous flow synthesis method using isopropanol-water mixtures as solvent in supercritical or near-critical conditions. The method allows complete control of size (5–20 nm) and crystallinity (10–100%) of the nanoparticles and provides quick synthesis with a residence time of ∼10 s that can be scaled up to commercial production. It is found that the average crystallite size can be easily controlled by adjusting the ratio between isopropanol and water in the solvent, whereas the crystallinity is mainly controlled by the reaction temperature. As-prepared Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles appear to be single phase, but Fe3+ ions most likely do not occupy the Ti4+ sites in the anatase TiO2 crystal structure.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Fujishima, T.N. Rao, and D.A. Tryk: Titanium dioxide photocatalysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol., C 1, 1 (2000).
A. Fujishima and K. Honda: Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 238, 37 (1972).
B. O’Regan and M. Grätzel: A low-cost, high-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 films. Nature 353, 737 (1991).
M. Crätzel: Photoelectrochemical cells. Nature 414, 338 (2001).
M. Grätzel: Conversion of sunlight to electric power by nanocrystalline dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol., A 164, 3 (2004).
M. Grätzel: Solar energy conversion by dye-sensitized photovoltaic cells. Inorg. Chem. 44, 6841 (2005).
D. Chen, F. Huang, Y.B. Cheng, and R.A. Caruso: Mesoporous anatase TiO2 beads with high surface areas and controllable pore sizes: A superior candidate for high-performance dye-sensitized solar cells. Adv. Mater. 21, 2206 (2009).
G. Li, L. Li, J. Boerio-Goates, and B.F. Woodfield: High purity anatase TiO2 nanocrystals: Near room-temperature synthesis, grain growth kinetics, and surface hydration chemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 8659 (2005).
A.V. Vorontsov, A.A. Altynnikov, E.N. Savinov, and E.N. Kurkin: Correlation of TiO2 photocatalytic activity and diffuse reflectance spectra. J. Photochem. Photobiol., A 144, 193 (2001).
J.M. Pettibone, D.M. Cwiertny, M. Scherer, and V.H. Grassian: Adsorption of organic acids on TiO2 nanoparticles: Effects of pH, nanoparticle size, and nanoparticle aggregation. Langmuir 24, 6659 (2008).
H.D. Jang, S.K. Kim, and S.J. Kim: Effect of particle size and phase composition of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the photocatalytic properties. J. Nanopart. Res. 3, 141 (2001).
T.P. Chou, Q. Zhang, B. Russo, G.E. Fryxell, and G. Cao: Titania particle size effect on the overall performance of dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 6296 (2007).
M.E. Simonsen, H. Jensen, Z.S. Li, and E.G. Søgaard: Surface properties and photocatalytic activity of nanocrystalline titania films. J. Photochem. Photobiol., A 200, 192 (2008).
C. Li, Y. Luo, D. Li, J.L. Mi, L. Sø, P. Hald, Q. Meng, and B.B. Iversen: Performance enhanced dye-sensitized solar cells based on anatase TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized using a rapid, green and scalable supercritical fluid process. Cryst. Eng. Comm. (2012, submitted).
Y. Fan, G. Chen, D. Li, Y. Luo, N. Lock, A.P. Jensen, A. Mamakhel, J. Mi, S.B. Iversen, Q. Meng, and B.B. Iversen: Highly selective deethylation of Rhodamine B on TiO2 prepared in supercritical fluids. Int. J. Photoenergy 2012, 173865 (2012).
T.C. Jagadale, S.P. Takale, R.S. Sonawane, H.M. Joshi, S.I. Patil, B.B. Kale, and S.B. Ogale: N-doped TiO2 nanoparticle based visible light photocatalyst by modified peroxide sol−gel method. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 14595 (2008).
M.A. Khan, M.S. Akhtar, and O.B. Yang: Synthesis, characterization and application of sol–gel derived mesoporous TiO2 nanoparticles for dye-sensitized solar cells. Sol. Energy 84, 2195 (2010).
F. Sauvage, D. Chen, P. Comte, F. Huang, L.P. Heiniger, Y.B. Cheng, R.A. Caruso, and M. Graetzel: Dye-sensitized solar cells employing a single film of mesoporous TiO2 beads achieve power conversion efficiencies over 10%. ACS Nano 4, 4420 (2010).
G.K. Mor, O.K. Varghese, M. Paulose, K. Shankar, and C.A. Grimes: A review on highly ordered, vertically oriented TiO2 nanotube arrays: Fabrication, material properties, and solar energy applications. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 90, 2011 (2006).
S. Chin, E. Park, M. Kim, G.N. Bae, and J. Jurng: Synthesis and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by chemical vapor condensation method with different precursor concentration and residence time. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 362, 470 (2011).
R.K. Wahi, Y. Liu, J.C. Falkner, and V.L. Colvin: Solvothermal synthesis and characterization of anatase TiO2 nanocrystals with ultrahigh surface area. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 302, 530 (2006).
I. Kartini, D. Menzies, D. Blake, J.C.D. da Costa, P. Meredith, J.D. Riches, and G.Q. Lu: Hydrothermal seeded synthesis of mesoporous titania for application in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). J. Mater. Chem. 14, 2917 (2004).
T. Adschiri, K. Kanazawa, and K. Arai: Rapid and continuous hydrothermal crystallization of metal oxide particles in supercritical water. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 75, 1019 (1992).
P. Hald, J. Becker, M. Bremholm, J.S. Pedersen, J. Chevallier, S.B. Iversen, and B.B. Iversen: Supercritical propanol–water synthesis and comprehensive size characterization of highly crystalline anatase TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Solid State Chem. 179, 2674 (2006).
N. Lock, P. Hald, M. Christensen, H. Birkedal, and B.B. Iversen: Continuous flow supercritical water synthesis and crystallographic characterization of anisotropic boehmite nanoparticles. J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 858 (2010).
J. Becker, P. Hald, M. Bremholm, J.S. Pedersen, J. Chevallier, S.B. Iversen, and B.B. Iversen: Critical size of crystalline ZrO2 nanoparticles synthesized in near- and supercritical water and supercritical isopropyl alcohol. ACS Nano 2, 1058 (2008).
S. Kawasaki, Y. Xiuyi, K. Sue, Y. Hakuta, A. Suzuki, and K. Arai: Continuous supercritical hydrothermal synthesis of controlled size and highly crystalline anatase TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Supercrit. Fluids 50, 276 (2009).
L.L. Toft, D.F. Aarup, M. Bremholm, P. Hald, and B.B. Iversen: Comparison of T-piece and concentric mixing systems for continuous flow synthesis of anatase nanoparticles in supercritical isopropanol/water. J. Solid State Chem. 182, 491 (2009).
J. Choi, H. Park, and M.R. Hoffmann: Effects of single metal-ion doping on the visible-light photoreactivity of TiO2. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 783 (2010).
C.Y. Wang, D.W. Bahnemann, and J.K. Dohrmann: A novel preparation of iron-doped TiO2 nanoparticles with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Chem. Commun. 1539 (2000).
E.D. Jeong, P.H. Borse, J.S. Jang, J.S. Lee, O-S. Jung, H. Chang, J.S. Jin, M.S. Won, and H.G. Kim: Hydrothermal synthesis of Cr and Fe codoped TiO2 nanoparticle photocatalyst. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 9, 250 (2008).
C.L. Luu, Q.T. Nguyen, and S.T. Ho: Synthesis and characterization of Fe-doped TiO2 photocatalyst by the sol-gel method. Adv. Nat. Sci.: Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 1, 015008 (2010).
K. Naeem and F. Ouyang: Preparation of Fe3+-doped TiO2 nanoparticles and its photocatalytic activity under UV light. Physica B 405, 221 (2010).
J.L. Mi, T.N. Jensen, P. Hald, J. Overgaard, M. Christensen, and B.B. Iversen: Glucose-assisted continuous flow synthesis of Bi2Te3 nanoparticles in supercritical/near-critical water. J. Supercrit. Fluids 67, 84 (2012).
S. Valencia, J.M. Marín, and G. Restrepo: Study of the band gap of synthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles using the sol-gel method and a hydrothermal treatment. The open Materials Science Journal 4, 9 (2010).
R. López and R. Gómez: Band-gap energy estimation from diffuse reflectance measurements on sol–gel and commercial TiO2: A comparative study. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 61, 1 (2012).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Danish National Research Foundation (Center for Materials Crystallography), the Danish Strategic Research Council (Center for Energy Materials), and the Danish Research Council for Nature and Universe (Danscatt).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mi, JL., Johnsen, S., Clausen, C. et al. Highly controlled crystallite size and crystallinity of pure and iron-doped anatase-TiO2 nanocrystals by continuous flow supercritical synthesis. Journal of Materials Research 28, 333–339 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.234
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.234