Abstract
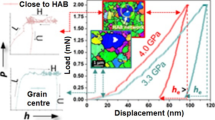
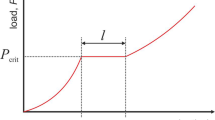
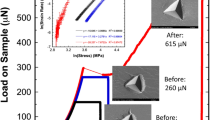
Plasticity initiation behavior that appears as a pop-in phenomenon on a loading process during indentation-induced deformation was investigated to reveal the effects of lattice defects such as grain boundary and solute element for various metallic materials including Fe alloys through instrumented nanoindentation techniques. The critical load Pc of pop-in on a loading process is lower in the vicinity of the grain boundary than in the grain interior, but the relative hardness of the boundary is equal to or greater than that in grain interior. In-solution Si produces a larger increase in the Pc for both the grain boundary and the grain interior in the Fe–Si alloy than in the interstitial-free steel. The maximum shear stress corresponding to the Pc underneath the indenter is directly proportional to the shear modulus in single crystals with various crystallographic structures. Microstructural effects on the Pc are considered based on some dislocation models.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Ohmura, T. Hara, and K. Tsuzaki: Relationship between nanohardness and microstructures in high-purity Fe-C as-quenched and quench-tempered martensite. J. Mater. Res. 18, 1465 (2003).
T. Ohmura, A. Minor, E. Stach, and J.W. Morris Jr.: Dislocation—grain boundary interactions in martensitic steel observed through in-situ nanoindentation in a TEM. J. Mater. Res. 19, 3626 (2004).
W.W. Gerberich, J.C. Nelson, E.T. Lilleodden, P. Anderson, and J.T. Wyrobek: Indentation induced dislocation nucleation: The initial yield point. Acta Mater. 44, 3585 (1996).
S.G. Corcoran, R.J. Colton, E.T. Lilleodden, and W.W. Gerberich: Anomalous plastic deformation at surfaces: Nanoindentation of gold single crystals. Phys. Rev. B 55, R16057 (1997).
D.F. Bahr, D.K. Kramer, and W.W. Gerberich: Non-linear deformation mechanisms during nanoindentation. Acta Mater. 46, 3605 (1998).
W.W. Gerberich, D.K. Kramer, N.I. Tymiak, A.A. Volinsky, D.F. Bahr, and M.D. Kriese: Nanoindentation-induced defect-interface interactions: Phenomena, methods and limitations. Acta Mater. 47, 4115 (1999).
S. Suresh, T-G. Nieh, and B.W. Choi: Nano-indentation of copper thin films on silicon substrates. Scr. Mater. 41, 951 (1999).
A. Gouldstone, H-J. Koh, K-Y. Zeng, A.E. Giannakopoulos, and S. Suresh: Discrete and continuous deformation during nanoindentation of thin films. Acta Mater. 48, 2277 (2000).
D. Lorenz, A. Zeckzer, U. Hilpert, P. Grau, H. Johansen, and H.S. Leipner: Pop-in effect as homogeneous nucleation of dislocations during nanoindentation. Phys. Rev. B 67, 172101 (2003).
A.M. Minor, E.T. Lilleodden, E.A. Stach, and J.W. Morris Jr.: Direct observations of incipient plasticity during nanoindentation of Al. J. Mater. Res. 19, 176 (2004).
Y. Shibutani and A. Koyama: Surface roughness effects on the displacement bursts observed in nanoindentation. J. Mater. Res. 19, 183 (2004).
T. Tsuru, Y. Shibutani, and Y. Kaji: Nanoscale contact plasticity of crystalline metal: Experiment and analytical investigation via atomistic and discrete dislocation models. Acta Mater. 58, 3096 (2010).
W.A. Soer, K.E. Aifantis, and J.T.M. De Hosson: Incipient plasticity during nanoindentation at grain boundaries in body-centered cubic metals. Acta Mater. 53, 4665 (2005).
T. Ohmura, K. Tsuzaki, and F. Yin: Nanoindentation-induced deformation behavior in the vicinity of single grain boundary of interstitial-free steel. Mater. Trans. 46, 2026 (2005).
A.M. Minor, S.A.S. Asif, Z. Shan, E.A. Stach, E. Cyrankowski, T.J. Wyrobek, and O.L. Warren: A new view of the onset of plasticity during the nanoindentation of aluminium. Nat. Mater. 5, 697 (2006).
T. Ohmura and K. Tsuzaki: Plasticity initiation and subsequent deformation behavior in the vicinity of single grain boundary investigated through nanoindentation technique. J. Mater. Sci. 42, 1728 (2007).
K. Sekido, T. Ohmura, T. Hara, and K. Tsuzaki: Effect of Dislocation Density on the Initiation of Plastic Deformation on Fe–C Steels. Mater. Trans. 53, 907 (2012).
M.G. Wang and A.H.W. Ngan: Indentation strain burst phenomenon induced by grain boundaries in niobium. J. Mater. Res. 19, 2478 (2004).
T.B. Britton, D. Randman, and A.J. Wilkinson: Nanoindentation study of slip transfer phenomenon at grain boundaries. J. Mater. Res. 24, 607 (2009).
Y. Yoshitomi, S. Suzuki, T. Ueda, S. Tsurekawa, H. Nakashima, and H. Yoshinaga: Grain boundary segregation in <110> symmetrical tilt bicrystals of an Fe-3%Si alloy. Scr. Metall. 32, 1067 (1995).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: Improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
K.L. Johnson: Contact Mechanics (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1985) pp. 84–106.
S. Shim, H. Bei, E.P. George, and G.M. Pharr: A different type of indentation size effect. Scr. Mater. 59, 1095 (2008).
T. Eliash, M. Kazakevich, V.N. Semenov, and E. Rabkin: Nanohardness of molybdenum in the vicinity of grain boundaries and triple junctions. Acta Mater. 56, 5640 (2008).
J.H. Westbrook: Segregation at grain boundaries. Int. Mater. Rev. 9, 415 (1964).
G.E. Dieter: Mechanical Metallurgy (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1986) p. 179.
K. Sekido, T. Ohmura, L. Zhang, T. Hara, and K. Tsuzaki: The effect of interstitial carbon on the initiation of plastic deformation of steels. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 530, 396 (2011).
S.N. Dub, I.K. Zasimchuk, and L.F. Matvienko: Effect of solid solution strengthening by iridium on the nucleation of dislocations in a molybdenum single crystal during nanoindentation. Phys. Solid State 53, 1404 (2011).
S.N. Dub, Y.Y. Lim, and M.M. Chaudhri: Nanohardness of high purity Cu (111) single crystal: The effect of indenter load and prior plastic sample strain. J. Appl. Phys. 107, 043510 (2010).
B. Sestak and S. Libovicky: Transition to crystallographic slip on Fe-3% Si single crystals at 78K. Acta Metall. 11, 1190 (1963).
R.C. Boettner and A.J. McEvily Jr.: Fatigue slip band formation in silicon-iron. Acta Metall. 13, 937 (1965).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Prof. Nakashima in Kyusyu University for providing the Fe–Si alloy sample. This work is partially supported by the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture, Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) No. 23560852 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohmura, T., Zhang, L., Sekido, K. et al. Effects of lattice defects on indentation-induced plasticity initiation behavior in metals. Journal of Materials Research 27, 1742–1749 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.161
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.161