Abstract
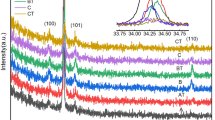
ZnO:Al and Zn1-xMgxO:Al films have been deposited by magnetron sputtering from ceramic targets at substrate temperatures from room temperature to 500 °C. We studied the relation between the electronic transport and the structural properties as a function of the deposition temperature. Films with the lowest resistivity (7·10−4 Ω cm for ZnO:Al and 3.6·10−3 Ω cm for Zn1-xMgxO:Al) can be prepared for deposition temperatures around 300 °C. This optimum is accompanied by the highest carrier concentration and the highest Hall mobility. Changes in crystalline quality and free carrier concentration are explained as a result of a bombardment of the films by high energetic negative oxygen ions during growth and by phase segregation for higher deposition temperatures. The dependence of the Hall mobility on the carrier concentration can be explained by grain barrier scattering for n <≈ 5·1020 cm−3 and by ionized impurity scattering for n >≈ 5·1020 cm−3. From the fit of the μ(n) dependence for both materials a trap density at grain boundaries of Nt ≈ 2.3·1013 cm−2 was determined.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Ginley, H. Hosono, and D. Paine, eds: Handbook of Transparent Conductors (Springer, New York, 2010).
K. Ellmer and R. Mientus: Carrier transport in polycrystalline transparent conductive oxides: A comparative study of zinc oxide and indium oxide. Thin Solid Films 516, 4620 (2008).
P. Jackson, D. Hariskos, E. Lotter, S. Paetel, R. Wuerz, R. Menner, W. Wischmann, and M. Powalla: New world record efficiency for Cu(In, Ga)Se(2) thin-film solar cells beyond 20%. Prog. Photovoltaics 19, 894 (2011).
S. Siebentritt and U. Rau: Cu-Chalcopyrites—Unique materials for thin-film solar cells, In Wide-Gap Chalcopyrites, S. Siebentritt and U. Rau, eds; Springer, Berlin, 2006; p. 1.
P. Baruch, A. Devos, P.T. Landsberg, and J.E. Parrott: On some thermodynamic aspects of photovoltaic solar-energy conversion. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 36, 201 (1995).
S. Siebentritt: Wide gap chalcopyrites: Material properties and solar cells. Thin Solid Films 403, 1 (2002).
U. Rau and M. Turcu: Role of surface band gap widening in Cu(In, Ga)(Se, S)2 thin-films for the photovoltaic performance of ZnO/CdS/Cu(In, Ga)(Se, S)2 heterojunction solar cells, in Compound Semiconductor Photovoltaics, edited by R. Noufi, W.N. Shafarman, D. Cahen, and L. Stolt (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 763, Warrendale, PA, 2003) B8.8, p. 335.
A. Yamada, K. Matsubara, K. Sakurai, S. Ishizuka, H. Tampo, P.J. Fons, K. Iwata, and S. Niki: Effect of band offset on the open circuit voltage of heterojunction CuIn1-xGaxSe2 solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 5607 (2004).
T. Minemoto, T. Negami, S. Nishiwaki, H. Takakura, and Y. Hamakawa: Preparation of Zn1-xMgxO films by radio frequency magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 372, 173 (2000).
W.I. Park, G.C. Yi, and H.M. Jang: Metalorganic vapor-phase epitaxial growth and photoluminescent properties of Zn1-xMgxO(0 ≤ x ≤ 0.49) thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 2022 (2001).
J. Rodriguez-Carvajal: FULLPROF: A Program for Rietveld Refinement and Pattern Matching Analysis, in Abstracts of the Satellite Meeting on Powder Diffraction of the XV Congress of the IUCr (Toulouse, France, 1990) p. 127.
P. Scherrer: Determination of size and structure of colloidal particles by x-ray diffraction. Gött. Nachr 2, 98 (1918).
T.D. Keijser, J. Langford, E. Mittemeijer, and A. Vogels: Use of the Voigt function in a single-line method for the analysis of x-ray diffraction line broadening. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 15, 308 (1982).
T. Minami, T. Miyata, T. Yamamoto, and H. Toda: Origin of electrical property distribution on the surface of ZnO: Al films prepared by magnetron sputtering. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 18, 1584 (2000).
R. Dinnebier and S. Billinge: Principles of powder diffraction, in Powder Diffraction Theory and Practice, edited by R. Dinnebier and S. Billinge (The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, 2008), p. 19.
M. Chen, Z.L. Pei, X. Wang, C. Sun, and L.S. Wen: Dependence of structural, electrical, and optical properties of ZnO: Al films on substrate temperature. J. Mater. Res. 16, 2118 (2001).
B. Szyszka: Transparent and conductive aluminum-doped zinc oxide films prepared by mid-frequency reactive magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 351, 164 (1999).
R. Cebulla, R. Wendt, and K. Ellmer: Al-doped zinc oxide films deposited by simultaneous RF and dc excitation of a magnetron plasma: Relationships between plasma parameters and structural and electrical film properties. J. Appl. Phys. 83, 1087 (1998).
W. Pies and A. Weiss: b108, II.1.1 Simple oxides, in Landolt-Börnstein - Group III: Crystal and Solid State Physics, Numerical Data and Functional Relationships in Science and Technology, edited by K. Hellwege and A. Hellwege (Springer, Berlin, 1975) p. 40.
K. Ellmer: Electrical properties, in Transparent Conductive Zinc Oxide: Basics and Applications in Thin Film Solar Cells, edited by K. Ellmer, A. Klein, and B. Rech (Springer, Berlin, 2008) p. 35.
K. Ellmer and T. Welzel: Reactive magnetron sputtering of transparent conductive oxide thin films: Role of energetic particle (ion) bombardment. J. Mater. Res. 27(5), 765 (2012).
H. Windischmann: Intrinsic stress in sputter-deposited thin-films. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater Sci. 17, 547 (1992).
A. Janotti and C.G. Van de Walle: Fundamentals of zinc oxide as a semiconductor. Rep. Prog. Phys. 72, 126501 (2009).
K. Shirouzu, T. Ohkusa, M. Hotta, N. Enomoto, and J. Hojo: Distribution and solubility limit of Al in Al2O3-doped ZnO sintered body. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 115, 254 (2007).
S. Cornelius, M. Vinnichenko, N. Shevchenko, A. Rogozin, A. Kolitsch, and W. Moller: Achieving high free electron mobility in ZnO: Al thin films grown by reactive pulsed magnetron sputtering. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 042103 (2009).
I. Sieber, N. Wanderka, I. Urban, I. Dorfel, E. Schierhorn, F. Fenske, and W. Fuhs: Electron microscopic characterization of reactively sputtered ZnO films with different Al-doping levels. Thin Solid Films 330, 108 (1998).
J.P. Han, P.Q. Mantas, and A.M.R Senos: Densification and grain growth of Al-doped ZnO. J. Mater. Res. 16, 459 (2001).
T. Welzel, T. Dunger, B. Liebig, and F. Richter: Determination of energy modulations of negative oxygen ions during pulsed magnetron sputtering of magnesium oxide. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 20, 035020 (2011).
T. Welzel, R. Kleinhempel, T. Dunger, and F. Richter: Ion energy distributions in magnetron sputtering of zinc aluminium oxide. Plasma Process. Polym. 6, S331 (2009).
D. Depla, S. Heirwegh, S. Mahieu, J. Haemers, and R. De Gryse: Understanding the discharge voltage behavior during reactive sputtering of oxides. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 013301 (2007).
S. Mahieu and D. Depla: Correlation between electron and negative O- ion emission during reactive sputtering of oxides. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 121117 (2007).
A. Ohtomo, M. Kawasaki, T. Koida, K. Masubuchi, H. Koinuma, Y. Sakurai, Y. Yoshida, T. Yasuda, and Y. Segawa: MgxZn1-xO as a II-VI wide-gap semiconductor alloy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 2466 (1998).
C.X. Wu, Y.M. Lu, D.Z. Shen, and X.W. Fan: Effect of Mg content on the structural and optical properties of Mg (x) Zn(1-x) O alloys. Chin. Sci. Bull. 55, 90 (2010).
D. Lide, ed: Ionic Radii in Crystals, in CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2008) p. 12.11.
A. Leineweber and E.J. Mittemeijer: Anisotropic strain-like line broadening due to composition variations. Adv. X-Ray Anal. 46, 43 (2003).
K. Ellmer: Resistivity of polycrystalline zinc oxide films: Current status and physical limit. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 34, 3097 (2001).
G. Masetti, M. Severi, and S. Solmi: Modeling of carrier mobility against carrier concentration in arsenic-doped, phosphorus-doped, and boron-doped silicon. IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 30, 764 (1983).
J.Y.W Seto: Electrical properties of polycrystalline silicon films. J. Appl. Phys. 46, 5247 (1975).
E.H. Sondheimer: The mean free path of electrons in metals. Adv. Phys. 1, 1 (1952).
J.F. Chang and M.H. Hon: The effect of deposition temperature on the properties of Al-doped zinc oxide thin films. Thin Solid Films 386, 79 (2001).
M. Chen, Z.L. Pei, X. Wang, Y.H. Yu, X.H. Liu, C. Sun, and L.S. Wen: Intrinsic limit of electrical properties of transparent conductive oxide films. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 33, 2538 (2000).
R. Lipperheide, T. Weis, and U. Wille: Generalized Drude model: Unification of ballistic and diffusive electron transport. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 13, 3347 (2001).
L. Nordheim: Electron theory of metals. II. Annalen der Physik 401, 641 (1931).
C.H. Seager: Grain-boundaries in polycrystalline silicon. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 15, 271 (1985).
J. Steinhauser, S. Fay, N. Oliveira, E. Vallat-Sauvain, D. Zimin, U. Kroll, and C. Ballif: Electrical transport in boron-doped polycrystalline zinc oxide thin films. Phys. Status Solidi A 205, 1983 (2008).
C.B. Alcock, V.P. Itkin, and M.K. Horrigan: Vapor-pressure equations for the metallic elements—298-2500-K. Can. Metall. Q. 23, 309 (1984).
P. Liley, R. Reid, and E. Buck: Physical and chemical data, in CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, edited by R. Weast and M. Astle (CRC Press, Inc., Florida, 1981/1982) p, 3.147.
T. Suga, S. Kameyama, S. Yoshioka, T. Yamamoto, I. Tanaka, and T. Mizoguchi: Characterization of nanotextured AIN thin films by x-ray absorption near-edge structures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 163113 (2005).
F. Kröger: The Chemistry of Imperfect Crystals (North-Holland Publishing Company, New York, 1974).
S.B. Zhang, S.H. Wei, and A. Zunger: Intrinsic n-type versus p-type doping asymmetry and the defect physics of ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 63, 075205 (2001).
Y.M. Sun and H.Z. Wang: The electronic properties of native interstitials in ZnO. Physica B 325, 157 (2003).
P. Erhart, K. Albe, and A. Klein: First-principles study of intrinsic point defects in ZnO: Role of band structure, volume relaxation, and finite-size effects. Phys. Rev. B 73, 205203 (2006).
N. Roberts, R.P. Wang, A.W. Sleight, and W.W. Warren: Al-27 Ga. impurity nuclear magnetic resonance ZnO: Al ZnO: Ga. Phys. Rev. B 57, 5734 (1998).
Acknowledgment
We thank the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (Richard A. Wilhelm) for the assistance during the RBS measurements and Dag Riebisch for performing most of the electrical measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bikowski, A., Ellmer, K. Influence of the deposition temperature on electronic transport and structural properties of radio frequency magnetron-sputtered Zn1-xMgxO:Al and ZnO:Al films. Journal of Materials Research 27, 2249–2256 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.113
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.113