Abstract
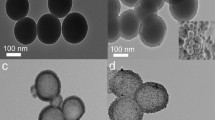
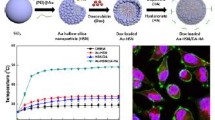
The hexagonal mesoporous silica MCM-41 nanospheres with Au nanorods (AuNRs) as core have been synthesized via a modified Stöber method by a process of hydration and condensation of tetraethoxysilane in a water–ethanol mixture. The AuNR@MCM-41 nanocomposites combine the photothermal characteristic with the mesopore of MCM-41 in one body. We utilized these core–shell materials for ibuprofen encapsulation and release in the simulated body fluid (pH 7.4) for the first time. The results certificated AuNR@MCM-41 nanocomposites as novel dual-functional materials could realize the light-driven release of drug due to the photothermal effect of the AuNRs. Such novel nanomaterials offer a new way for cancer treatment which combine hyperthermia with the chemotherapeutic drugs by synergistic effect.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.G. Trewyn, S. Giri, I.I. Slowing, and V.S.Y Lin: Mesoporous silica nanoparticle based controlled release, drug delivery, and biosensor systems. Chem. Commun. 31, 3236 (2007).
A.M. Smith, H. Duan, A.M. Mohs, and S. Nie: Bioconjugated quantum dots for in vivo molecular and cellular imaging. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 60, 1226 (2008).
J.R. McCarthy and R. Weissleder: Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles for targeted imaging and therapy. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 60, 1241 (2008).
K. Park, S. Lee, E. Kang, K. Kim, K. Choi, and I.C. Kwon: New generation of multifunctional nanoparticles for cancer imaging and therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 1553 (2009).
T. Maschmeyer, F. Rey, G. Sankar, and J.M. Thomas: Heterogeneous catalysts obtained by grafting metallocene complexes onto mesoporous silica. Nature 378, 159 (1995).
A. Corma: From microporous to mesoporous molecular sieve materials and their use in catalysis. Chem. Rev. 97, 2373 (1997).
A. Corma, M.S. Galletero, H. Garcia, E. Palomares, and F. Rey: Pyrene covalently anchored on a large external surface area zeolite as a selective heterogeneous sensor for iodide. Chem. Commun.. 2, 1100 (2002).
T. Nguyen, J. Wu, V. Doan, B.J. Schwartz, and S.H. Tolbert: Control of energy transfer in oriented conjugated polymer-mesoporous silica composites. Science 288, 652 (2000).
R. Hernandez, H. Tseng, J.W. Wong, J.F. Stoddart, and J.I. Zink: An operational supramolecular nanovalve. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 3370 (2004).
S. Angelos, Y. Yang, K. Patel, J.F. Stoddart, and J.I. Zink: pH-Responsive supramolecular nanovalves based on cucurbit[6]uril pseudorotaxanes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 2222 (2008).
K.C.F Leung, T.D. Nguyen, J.F. Stoddart, and J.I. Zink: Supramolecular nanovalves controlled by proton abstraction and competitive binding. Chem. Mater. 18, 5919 (2006).
D.P. Ferris, Y. Zhao, N.M. Khashab, H.A. Khatib, J.F. Stoddart, and J.I. Zink: Light-operated mechanized nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 1686 (2009).
C. Lai, B.G. Trewyn, D.M. Jeftinija, K. Jeftinija, S. Xu, S. Jeftinija, and V.S.Y Lin: A mesoporous silica nanosphere-based carrier system with chemically removable CdS nanoparticle caps for stimuli-responsive controlled release of neurotransmitters and drug molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 4451 (2003).
N.K. Mal, M. Fujiwara, and Y. Tanaka: Photocontrolled reversible release of guest molecules from coumarin-modified mesoporous silica. Nature 421, 350 (2003).
R. Weissleder: A clearer vision for in vivo imaging. Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 316 (2001).
S. Link and M.A. El-Sayed: Shape and size dependence of radiative, non-radiative and photothermal properties of gold nanocrystals. Int. Rev. Phys. Chem. 19, 409 (2000).
X. Huang, I.H. El-Sayed, W. Qian, and M.A. El-Sayed: Cancer cell imaging and photothermal therapy in the near-infrared region by using gold nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 2115 (2006).
C. Kim, P. Ghosh, and V.M. Rotello: Multimodal drug delivery using gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale 1, 61 (2009).
C.K. Kim, P. Ghosh, C. Pagliuca, Z. Zhu, S. Menichetti, and V.M. Rotello: Entrapment of hydrophobic drugs in nanoparticle monolayers with efficient release into cancer cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 1360 (2009).
W. Stober, A. Fink, and E. Bohn: Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 26, 62 (1968).
I. Gorelikov and N. Matsuura: Single-step coating of mesoporous silica on cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide-capped nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 8, 369 (2008).
C.J. Murphy, T.K. Sau, A.M. Gole, C.J. Orendorff, J. Gao, L. Gou, S.E. Hunyadi, and T. Li: Anisotropic metal nanoparticles: Synthesis, assembly, and optical applications. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 13857 (2005).
C.J. Murphy, A.M. Gole, S.E. Hunyadi, and C.J. Orendorff: One-dimensional colloidal gold and silver nanostructures. Inorg. Chem. 45, 7544 (2006).
K. Yano and Y. Fukushima: Particle size control of mono-dispersed super-microporous silica spheres. J. Mater. Chem. 13, 2577 (2003).
H. Cong, R. Toftegaard, J. Arnbjerg, and P.R. Ogilby: Silica-coated gold nanorods with a gold overcoat: Controlling optical properties by controlling the dimensions of a gold−silica−gold layered nanoparticle. Langmuir 26, 4188 (2010).
S. Link and M.A. El-Sayed: Spectral properties and relaxation dynamics of surface plasmon electronic oscillations in gold and silver nanodots and nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. B 103, 8410 (1999).
J. Andersson, J. Rosenholm, S. Areva, and M. Linden: Influences of material characteristics on ibuprofen drug loading and release profiles from ordered micro- and mesoporous silica matrices. Chem. Mater. 16, 4160 (2004).
M. Vallet-Regi, A. Ramila, R.P. Del Real, and J. Perez-Pariente: A new property of MCM-41: Drug delivery system. Chem. Mater. 13, 308 (2001).
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars of China (Grant No. 60925018) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 20971051 and 51002062).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, L., Dong, B., Jiang, Z. et al. Synthesis of novel core–shell structural AuNR@MCM-41 for infrared light-driven release of drug. Journal of Materials Research 26, 2414–2419 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2011.292
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2011.292