Abstract
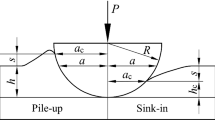
The present paper deals with the plastic deformation process into metallic materials occurring in the subindenter region during the loading cycle of spherical indentation test. Load–indentation-depth curve and plastic strains field evolution in the region beneath the indenter are examined using finite element analysis (FEA). The FE model was set up and validated by comparison with experimental spherical indentations carried out on two different materials (Al6082-T6, AISI H13) under four different friction conditions, corresponding to friction coefficients equal to 0.0, 0.1, 0.3, and 0.5. It is confirmed that friction effects on load–indentation-depth curves are negligible for the investigated penetration depths, whereas the plastic deformation process is affected by the contact conditions. The investigation shows that, although the L–h curve is not affected by the contact conditions up to medium values of the penetration depth, remarkable effects are produced in the overall plastic core under the indenter. A strong correlation between plastic strains field and friction coefficient is especially observed at low values of this parameter, whereas a saturation of the phenomena is found for medium-high values of the friction coefficient.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.T. Cheng and C.M. Cheng: Relationship between hardness, elastic modulus and the work of indentation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 614 (1998).
A.E. Giannakopoulos and S. Suresh: Determination of elastoplas-tic properties by instrumented sharp indentation. Scr. Mater. 40, 1191 (1999).
M. Dao, N. Chollacoop, K.J. Van Vliet, T.A. Venkatesh, and S. Suresh: Computational modelling of the forward and reverse problems in instrumented sharp indentation. Acta Mater. 49, 3899 (2001).
M. Mata and J. Alcalá: The role of friction on sharp indentation. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 52, 145 (2004).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation. Advances in understanding and refinements to methodology. J. Mater. Res. 19, 3 (2004).
B. Taljat, T. Zacharia, and F. Kosel: New analytical procedure to determine stress-strain curve from spherical indentation data. Int. J. Solids Struct. 33, 4411 (1998).
E.G. Herbert, G.M. Pharr, W.C. Oliver, B.N. Lucas, and J.L. Hay: On the measurement of stress-strain curves by spherical indentation. Thin Solid Films 398–399, 331 (2001).
A. Nayebi, R. El Abdi, O. Bartier, and G. Mauvoisin: New procedure to determine steel mechanical parameters from spherical indentation technique. Mech. Mater. 34, 243 (2002).
Y.P. Cao and J. Lu: A new method to extract the plastic properties of metals materials from an instrumented spherical indentation loading curve. Acta Mater. 52, 4023 (2004).
H. Lee, J.H. Lee, and G.M. Pharr: A numerical approach to spherical techniques for material property evaluation. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 53, 2037 (2005).
M. Zhao, N. Ogasawara, N. Chiba, and X. Chen: A new approach to measure the elastic-plastic properties of bulk materials using spherical indentation. Acta Mater. 54, 23 (2006).
M. Beghini, L. Bertini, and V. Fontanari: Evaluation of the stress-strain curve of metallic materials by spherical indentation. Int. J. Solids Struct. 43, 2441 (2006).
Y.P. Cao, X. Qian, and N. Huber: Spherical indentation into elastoplastic materials. Indentation-response based definitions of the representative strain. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 454–455, 1 (2007).
Y.T. Cheng and C.M. Cheng: Scaling approach to conical indentation in elastic-plastic solids with work hardening. J. Appl. Phys. 84, 1284 (1998).
Y.T. Cheng and C.M. Cheng: Scaling, dimensional analysis and indentation measurements. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 44, 91 (2004).
S.D. Mesarovic and N.A. Fleck: Spherical indentation of elastic-plastic solids. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 455, 2707 (1999).
H. Hertz: Miscellaneous Papers by H. Hertz, edited by D.E. Jones and J.A. Schott (Macmillan, London, 1896).
D. Tabor: The Hardness of Metals (Clarendon Press, Oxford, UK, 1951).
K.L. Johnson: The correlation of indentation experiments. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 18, 115 (1970).
K.L. Johnson: Contact Mechanics (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1985).
R. Hill, B. Storakes, and A.B. Zdunek: A theoretical study of the Brinnel hardness test. Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. A 436, 301 (1989).
B. Taljat and G.M. Pharr: Development of pile-up during spherical indentation of elastic-plastic solids. Int. J. Solids Struct. 41, 3891 (2004).
H. Habbad, B.G. Mellor, and S. Syngellakis: Post-yield characterization of metals with significant pile-up through spherical indentation. Acta Mater. 54, 1965 (2006).
M. Beghini, L. Bertini, L. Bosio, V. Fontanari, and R. Valleggi: Design of the “Diaptometro”, testing machine for the mechanical characterization of metallic materials by instrumented spherical indentation. Proceedings AIAS 2006, Ancona, Italy, 13–16 September 2006, on-line at (www.aiasonline.org).
K.J. Bathe: Finite Element Procedure (Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ, 1996).
A. Nayebi, O. Bartier, G. Mauvoisin, and R. El Abdi: New method to determine the mechanical properties of heat treated steels. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 43, 2679 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beghini, M., Bertini, L., Fontanari, V. et al. Numerical analysis of plastic deformation evolution into metallic materials during spherical indentation process. Journal of Materials Research 24, 1270–1278 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0142
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0142