Abstract
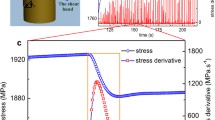
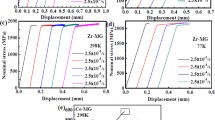
In this study, we demonstrated that the failure of bulk metallic glasses (BMGs) results from a sudden temperature rise within a shear band. Using a shear transformation zone model, we successfully calculated the temperature within a shear band and found it consistent with the observation from an in situ infrared thermographic system. The instantaneous temperature within a shear band at fracture agrees remarkably well with the glass transition temperature (Tg providing a new criterion to determine the strength of BMGs from their Tg. This agreement also discloses the fact that catastrophic failure of BMG is caused by the sudden drop in viscosity inside the shear band when the instantaneous temperature within a shear band approaches Tg.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. He, S.J. Poon, G.J. Shiflet: Synthesis and properties of metallic glasses that contain aluminum. Science 241, 1640 (1988).
R.W. Cahn: Materials science: Aluminum-based glassy alloys. Nature 341, 183 (1989).
A.L. Greer: Metallic glasses. Science 267, 1947 (1995).
C.T. Liu, L. Heatherly, D.S. Easton, C.A. Carmichael, J.H. Schneibel, C.H. Chen, J.L. Wright, M.H. Yoo, J.A. Horton, A. Inoue: Test environments and mechanical properties of Zr-base bulk amorphous alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 29(7), 1811 (1998).
W.L. Johnson: Bulk glass-forming metallic alloys: Science and technology. MRS Bull. 24(10), 42 (1999).
M.W. Chen, T. Zhang, A. Inoue, A. Sakai, T. Sakurai: Quasicrystals in a partially devitrified Zr65Al7.5Ni10Cu12.5Ag5 bulk metallic glass. Appl. Phys. Lett. 75(12), 1697 (1999).
J.J. Kim, Y. Choi, S. Suresh, A.S. Argon: Nanocrystallization during nanoindentation of a bulk amorphous metal alloy at room temperature. Science 295, 654 (2002).
H.J. Leamy, H.S. Chen, T.T. Wang: Plastic-flow and fracture of metallic glass. Metall. Trans. 3(3), 699 (1972).
F. Spaepen: A microscopic mechanism for steady state inhomogeneous flow in metallic glasses. Acta Metall. 25, 407 (1976).
A.S. Argon: Plastic deformation in metallic glasses. Acta Metall. 27, 47 (1979).
E. Pekarskaya, C.P. Kim, W.L. Johnson: In situ transmission electron microscopy studies of shear bands in a bulk metallic glass based composite. J. Mater. Res. 16(9), 2513 (2001).
P.E. Donovan, W.M. Stobbs: The structure of shear bands in metallic glasses. Acta Metall. 29(8), 1419 (1981).
T.C. Hufnagel, T. Jiao, Y. Li, L.Q. Xing, K.T. Ramesh: Deformation and failure of Zr57Ti5Cu20Ni8Al10 bulk metallic glass under quasi-static and dynamic compression. J. Mater. Res. 17(6), 1441 (2002).
W.J. Wright, R.B. Schwarz, W.D. Nix: Localized heating during serrated plastic flow in bulk metallic glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 319–321, 229 (2001).
J.J. Lewandowski, N.A. Stelmashenko, and A.L. Greer: Experimental observations of shear banding in bulk metallic glasses. The 2005 TMS Annual Meeting, San Francisco, CA, February 13–17, 2005.
A.S. Argon, L.T. Shi: Development of visco-plastic deformation in metallic glasses. Acta Metall. 31(4), 499 (1983).
M.L. Falk, J.S. Langer: Dynamics of viscoplastic deformation in amorphous solids. Phys. Rev. E 57(6), 7192 (1998).
M.L. Falk: Molecular-dynamics study of ductile and brittle fracture in model noncrystalline solids. Phys. Rev. B 60(10), 7062 (1999).
C.A. Schuh, A.C. Lund, T.G. Nieh: New regime of homogeneous flow in the deformation map of metallic glasses: Elevated temperature nanoindentation experiments and mechanistic modeling. Acta Mater. 52(20), 5879 (2004).
J. Lu, G. Ravichandran, W.L. Johnson: Deformation behavior of the Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 bulk metallic glass over a wide range of strain-rates and temperatures. Acta Mater. 51(12), 3429 (2003).
M.D. Demetriou, W.L. Johnson: Modeling the transient flow of undercooled glass-forming liquids. J. Appl. Phys. 95(5), 2857 (2004).
K.M. Flores, R.H. Dauskardt: Mean stress effects on flow localization and failure in a bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater. 49, 2527 (2001).
A.W. Simpson, P.H. Hodkinson: Bubble raft model for an amorphous alloy. Nature 237, 320 (1972).
A.S. Argon, H.Y. Kuo: Plastic-flow in a disordered bubble raft (an analog of a metallic glass). Mater. Sci. Eng. 39, 101 (1979).
K. Maeda, S. Takeuchi: Simple computer modeling of metallic amorphous structure. J. Phys. F 8(12), L283 (1978).
A.T. Zehnder, A.J. Rosakis: On the temperature distribution at the vicinity of dynamically propagating cracks in 4340 steel. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 39(3), 382 (1991).
J.A. Kallivayalil, A.T. Zehnder: Measurement of temperature field induced by dynamic crack growth in ß-C titanium. Int. J. Frac. 66, 99 (1994).
R. Weichert, K. Schonert: Heat generation at the tip of a moving crack. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 26, 151 (1978).
S.C. Glade, R. Busch, D.S. Lee, W.L. Johnson, R.K. Wunderlich, H.J. Fecht: Thermodynamics of Cu47Ti34Zr11Ni8, Zr52.5Cu17.9Ni14.6Al10Ti5 and Zr57Cu15.4Ni12.6Al10Nb5 bulk metallic glass forming alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 87(10), 7272 (2000).
J.P. Hirth, J. Lothe: Theory of Dislocations (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1967).
E.N. Mastrojannis, T. Mura, L.M. Keer: Stress-field of a planar elliptical dislocation loop. Philos. Mag. 35(4), 1137 (1977).
C.J. Gilbert, J.W. Ager, V. Schroeder, R.O. Ritchie, J.P. Lloyd, J.R. Graham: Light emission during fracture of a Zr-Ti-Ni-Cu-Be bulk metallic glass. Appl. Phys. Lett. 74(25), 3809 (1999).
Z.P. Lu, C.T. Liu: A new glass-forming ability criterion for bulk metallic glasses. Acta Mater. 50(13), 3501 (2002).
H. Kato, A. Inoue, H.S. Chen: Heating and structural disordering effects of the nonlinear viscous flow in a Zr55Al10Ni5Cu30 bulk metallic glass. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83(26), 5401 (2003).
X.H. Lin, W.L. Johnson, W.K. Rhim: Effect of oxygen impurity on crystallization of an undercooled bulk glass forming Zr-Ti-Cu-Ni-Al alloy. Mater. Trans. JIM 38(5), 473 (1997).
Z.P. Lu, C.T. Liu, J.R. Thompson, W.D. Porter: Structural amorphous steels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92(24), 245503 (2004).
R. Busch, W. Liu, W.L. Johnson: Thermodynamics and kinetics of the Mg65Cu25Y10 bulk metallic glass forming liquid. J. Appl. Phys. 83(8), 4134 (1998).
Z.P. Lu, Y. Li, T. Liu: Glass-forming tendency of bulk La-Al-Ni-Cu-(Co) metallic glass-forming liquids. J. Appl. Phys. 93(2), 1 (2003).
I.R. Lu, G. Wilde, G.P. Gorler, R. Willnecker: Thermodynamic properties of Pd-based glass-forming alloys. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 250–252, 577 (1999).
G. Wilde, I.R. Lu, R. Willnecker: Fragility, thermodynamic properties, and thermal stability of Pd-rich glass forming liquids. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 375–377, 417 (2004).
R. Busch, Y.J. Kim, W.L. Johnson, A.J. Rulison, W.K. Rhim, D. Isheim: Hemispherical total emissivity and specific heat capacity of deeply undercooled Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10.0Be22.5 melts. Appl. Phys. Lett. 66(23), 3111 (1995).
D. Okai, T. Fukami, T. Yamasaki, T. Zhang, A. Inoue: Temperature dependence of heat capacity and electrical resistivity of Zr-based bulk glassy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 375–377, 364 (2004).
Z.P. Lu and C.T. Liu: (unpublished data).
C.A. Schuh, T.G. Nieh: A survey of instrumented indentation studies on metallic glasses. J. Mater. Res. 19(1), 46 (2004).
Y. Li: (unpublished data).
W. Johnson L.: Bulk metallic glasses: An emerging engineering material. JOM 40(2002).
T. Mukai, T.G. Nieh, Y. Kawamura, A. Inoue, K. Higashi: Effect of strain rate on compressive behavior of a Pd40Ni40P20 bulk metallic glass. Intermetallics 10, 1071 (2002).
M. Calin, J. Eckert, L. Schultz: Improved mechanical behavior of Cu-Ti-based bulk metallic glass by in situ formation of nanoscale precipitates. Scripta Mater. 48, 653 (2003).
H. Kato, A. Inoue: Synthesis and mechanical properties of bulk amorphous Zr-Al-Ni-Cu alloys containing ZrC particles. Mater. Trans. JIM 38, 793 (1997).
J.G. Wang, B.W. Choi, T.G. Nieh, C.T. Liu: Crystallization and nanoindentation behavior of a bulk Zr-Al-Ti-Cu-Ni amorphous alloy. J. Mater. Res. 15, 798 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, B., Liu, C.T., Nieh, T.G. et al. Localized heating and fracture criterion for bulk metallic glasses. Journal of Materials Research 21, 915–922 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2006.0124
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2006.0124