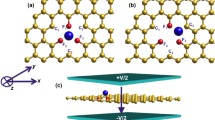
Abstract
There is pressing need in computation of a universal phase change memory consolidating the speed of RAM with the permanency of hard disk storage. A potentiated scanning tunneling microscope tip traversing the soliton separating a metallic, ABA-stacked phase and a semiconducting ABC-stacked phase in trilayer graphene has been shown to permanently transform ABA-stacked regions to ABC-stacked regions. In this study, we used density functional theory (DFT) calculations to assess the energetics of this phase-change and explore the possibility of organic functionalization using s-triazine to facilitate a reverse phase-change from rhombohedral back to Bernal in graphene trilayers. A significant deviation in the energy per simulated atom arises when s-triazine is adsorbed, favoring the transformation of the ABC phase to the ABA phase once more. A phase change memory device utilizing rapid, energy-efficient, reversible, field-induced phase-change in graphene trilayers could potentially revolutionize digital memory industry.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meena, J., Sze, S., Chand, U. & Tseng, T.-Y. Overview of emerging nonvolatile memory technologies. Nanoscale Res Lett 9, 526 (2014).
Hong, S, Auciello, O & Wouters, D. Emerging Non-Volatile Memories. (2014). at http://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/978-1-4899-7537-9.pdf [accessed on 02-11-15]
Yu, H & Wang, Y. Design Exploration of Emerging Nano-scale Non-volatile Memory. (2014). at http://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/978-1-4939-0551-5.pdf (accessed on 05-11-15)
Hu, J.-M., Li, Z., Chen, L.-Q. & Nan, C.-W. High-density magnetoresistive random access memory operating at ultralow voltage at room temperature. Nature Communications 2, 553 (2011).
Raoux, S, Xiong, F, Wuttig, M & Pop, E. Phase change materials and phase change memory. MRS Bulletin (2014). doi:10.1557/mrs.2014.139
Ferrari, AC, Meyer, JC, Scardaci, V & Casiraghi, C. Raman spectrum of graphene and graphene layers. Physical review … (2006). http://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.187401 [accessed on 14-06-15]
Lui, C., Li, Z., Mak, K., Cappelluti, E. & Heinz, T. F. Observation of an electrically tunable band gap in trilayer graphene. Nature Physics 7, 944–947 (2011).
Jhang, S. et al. Stacking-order dependent transport properties of trilayer graphene. arXiv (2011). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.84.161408
Avetisyan, AA, Partoens, B & Peeters, FM. Stacking order dependent electric field tuning of the band gap in graphene multilayers. Physical Review B 81, 115432 (2010).
Xu, P. et al. A pathway between Bernal and rhombohedral stacked graphene layers with scanning tunneling microscopy. Appl Phys Lett 100, 201601 (2012).
Yankowitz, M. et al. Electric field control of soliton motion and stacking in trilayer graphene. Nature Materials 13, 786–789 (2014).
Graf, D. et al. Spatially resolved Raman spectroscopy of single- and few-layer graphene. Nano Lett. 7, 238–42 (2007).
Lipkind, D. & Chickos, J. An examination of the vaporization enthalpies and vapor pressures of pyrazine, pyrimidine, pyridazine, and 1,3,5-triazine. Structural Chemistry 20, 49–58 (2009).
Zhang, W. et al. Molecular adsorption induces the transformation of rhombohedral- to Bernal-stacking order in trilayer graphene. Nat Commun 4, (2013).
Giannozzi, P. et al. QUANTUM ESPRESSO: a modular and open-source software project for quantum simulations of materials. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 21, 395502 (2009).
Kokalj, A. XCrySDen - a new program for displaying crystalline structures and electron densities. Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling 17, 176–179 (1999).
Vanderbilt, D. Optimally smooth norm-conserving pseudopotentials. Physical Review B 32, 8412 (1985).
Gygi, F. Electronic Structure Laboratory. (2014).
Monkhorst, HJ & Pack, JD. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Physical Review B (1976). at http://journals.aps.org/prb/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevB.13.5188 [accessed on 27-08-15]
Thonhauser, T, Cooper, VR, Li, S, Puzder, A & Hyldgaard, P. Van der Waals density functional: Self-consistent potential and the nature of the van der Waals bond. Physical Review B (2007). at http://journals.aps.org/prb/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevB.76.125112 [accessed on 27-08-15]
Rydberg, H, Schröder, E, Langreth, DC & Lundqvist, BI. Van der Waals density functional for general geometries. … review letters (2004). at http://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.246401 [accessed on 27-08-15]
Román-Pérez, G & Soler, JM. Efficient implementation of a van der Waals density functional: application to double-wall carbon nanotubes. Physical review letters (2009). at http://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.096102[accessed on 27-08-15]
Chang, C.-H., Fan, X., Li, L.-J. & Kuo, J.-L. Band Gap Tuning of Graphene by Adsorption of Aromatic Molecules. J Phys Chem C 116, 13788–13794 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atwa, M.M., AlAskalany, A., Elgammal, K. et al. Trilayer Graphene as a Candidate Material for Phase-Change Memory Applications. MRS Advances 1, 1487–1494 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2016.237
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2016.237