Abstract
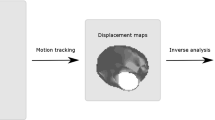
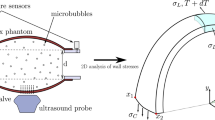
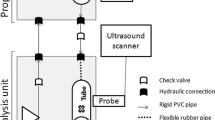
Two alternatives to standard tensile testing of arteries are discussed. The first involves inflation of arteries and simultaneous measurement of radial displacement with intra-vascular ultrasound (IVUS). The second involves the measurement of load versus displacement during micro-indentation of the intimal surface. The IVUS technique is used to study the nonlinear stiffening of porcine coronaries during inflation and, ultimately, it may provide a method to determine mechanical properties in vivo. Processing of the IVUS data relies on accurate determination of the luminal/intimal and medial/advential boundaries during inflation. The microindentation technique is used to study the effect of loading rate on tissue stiffness, recovery, and internal dissipation. Ultimately, this technique may provide a method to measure local mechanical properties in the vicinity of an atherosclerotic plaque, for example. Accurate determination of the initial contact point between the indenter and intima is required, however. The techniques appear to successfully capture significant, nonlinear, time-dependent properties of arterial tissue.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Fuster, B. Stein, J.A. Ambrose, L. Badimon, J.J. Badimon, and J.H. Chesebro, Circ. 82 (supp II), pp. II–47 (1990).
P. Constantinides, Am. J. Cardiol. 66, pp. 37G–40G (1990).
A.I. Veress, D.G. Vince, P.M. Anderson, J.F. Cornhill, E.E. Herderick, J.D. Klingensmith, B.D. Kuban, N.L. Greenberg, and J.D. Thomas, Z Kardiol. 89(Suppl. 2), pp. 92–100 (2000).
D.J. Patel, J.S. Janicki, and T.E. Carew, Circ. Res. 25, pp. 765–779 (1969).
H.W. Weisacker, H. Lambert, and K. Pacale, J. Biomech 16, pp. 703–715 (1981).
P.B. Dobrin, J. Biomech. 19(5), pp. 351–358 (1986).
R.H. Cox, Am. J. Physiol. 235(5), pp. H533–H541 (1978).
P.B. Dobrin, J. Biomech. 19(5), pp. 351–358 (1986).
M. Anliker, W.E. Moritz, and E. Ogden, J. Biomech. 1, pp. 235–246 (1968).
E.M.L. Attinger, Circ. Res. 22, pp. 829–840 (1968).
R.H. Cox, J. Biomech. 8, pp. 293–300 (1975).
P.B. Dobrin and J.M. Doyle, Circ. Res. 27, pp. 105–119 (1970).
A.G. Hudentz and E. Monos, Acta Phys. Sci. Hungaricai 75, pp. 111–122 (1981).
P.B. Dobrin and Mrkvicka, J. Hypertension 10(Suppl. 6), pp. S7–S10 (1992).
J. Ophir, E.I. Cespedes, H. Ponnekanti, Y. Yazki, and X. Li, Imaging 13(2), pp. 111–34 (1991).
C.L. deKorte, H.A. Woutman, A.F. vander Steen, G. Pasterkamp, and E.I. Cespedes, Ultrasonics 38(1–8), pp. 387–90 (2000).
J.D. Klingensmith, R. Shekhar, and D.G. Vince, IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 19(10), pp. 1–17 (2000).
B.S. Gow and C.D. Hadfield, Circ. Res. 45, pp. 588–594 (1979).
K.L. Johnson, Contact Mechanics, Cambridge University Press, New York 1987.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anderson, P.M., Glaser, E.N., Veress, A.I. et al. Using Indentation and Intra-Vascular Ultrasound to Measure Arterial Response. MRS Online Proceedings Library 662, 24 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-662-MM2.4
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-662-MM2.4