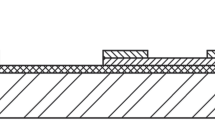
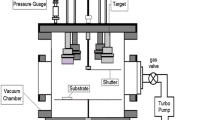
Abstract
Strain sensors based on thin films of indium tin oxide (ITO) have been developed for a variety of applications, where the measurement of both static and dynamic strain are required at elevated temperatures. ITO thin films were prepared by rf reactive sputtering in Ar:O2 mixtures from high density, electrically conductive targets having a nominal composition of 90% In2O3 and 10% SnO2. The resulting ITO films exhibited room temperature resistivities between 2×10−2 and 2×102 Ω cm, an optical bandgap of 3.5 ev and tested “n” type by hot probe. These same films exhibited large negative gage factors (G=Δρ/Δρε) when tested at room temperature and a relatively low temperature coefficient of resistance when tested at elevated temperature in air. Specifically, gage factors approaching −100 with little hysteresis were observed for strains up to 700 μin/in and TCR’s as low as 195 ppm/°C have been measured for the sputtered ITO films. In addition, these films were electrically stable and readily formed ohmic contacts with platinum at temperatures up to 1180°C. In this paper, we report on the electrical properties and piezoresistive properties of ITO based strain gages at temperatures up to 1180°C. Prospects of using ITO thin films as the active strain elements in high temperature strain gages and the characteristics of strain sensors based on ITO are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jih-Fen Lei, “A Resistance Strain Gage with Repeatable and Cancelable Apparent Strain for Use to 800° C”, NASA Report No. CR-185256, 1990.
P. Kayser, J.C. Goderoy and L. Leca, “High-Temperature Thin Film Strain Gauges”, Sensors and Actuators 37-38, 328–332 (1993).
M. M. Lemcoe, “High-Temperature Strain Gage Measurements to 2000°F: Can it be done?”, Sensors Expo International Conference Proceedings, p. 203C–1–7, 1989.
W.H. Atkinson, M.A. Cyr and R.D. Strange, “Development of Sensors for Ceramic Components in Advanced Propulsion Systems-Phase Two”, NASA Rept No. 195283,1994.
G.R. Witt, “The Electromechanical Properties of Thin Films and the Thin Film Strain Gauge”, Thin Solid Films 22, 133–156 (1974).
S.E. Dyer, P.S. Amons, A. Bruins Slot and O.J. Gregory, “Preparation and Piezoresistive Properties of Reactively Sputtered Indium Tin Oxide Thin Films”, Thin Solid Films, in press.
O.J. Gregory, A. Bruins Slot, P.S. Amons and E.E. Crisman, “High Temperature-Strain Gages Based on Reactively Sputtered A1Nx Thin Films”, Surface and Coatings Technology, in press.
G.L. Bir and G.E. Pikus. Symmetry and Strain Induced Effects in Semiconductors, Hoisted Press, New York, 1974, p. 369.
Charles S. Smith, “Piezoresistance Effect in Ge and Si”, Phys. Rev., series 2, 94, 42, (1954).
P.A. Beck, B.A. Auld, and Ki-Soo Kim, “Silicon Sensors as Process Monitoring Devices”, Res Nondestructive Evaluation 5, 71–93 (1993).
C. Kittel, Introduction to Solid State Physics, 5th Edit., John Wiley & Sons, NY, 1976.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank NASA-Lewis Research Center, Cleveland Ohio for support of this work under NASA Grant NAG3-1428.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gregory, O.J., Dyer, S.E., Amons, P.S. et al. Characteristics of a Reactively Sputtered Indium Tin Oxide Thin Film Strain Gage for Use at Elevated Temperatures. MRS Online Proceedings Library 403, 597–602 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-403-597
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-403-597