Abstract
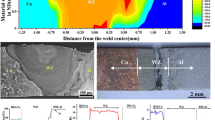
The U.S. Bureau of Mines has studied the capacitive discharge weld interface between Al and Fe using optical and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Capacitive discharge welding (CDW) is a rapid solidification process in which the amount of molten metal at the interface is small compared to the sample size. As a result, high cooling rates (106 K/s) can be achieved, providing a weldment made up of small grains. Large magnetic fields produced by the process tend to mix the molten metals at the interface to form a complex alloy, the nature of which depends upon the starting electrode materials. This effect is characterized by a marblecake pattern in optical micrographs. The amount of mixing is related to the melting temperature of the cathode with respect to the anode. Increased mixing occurs when the melting temperature of the cathode is higher than the melting temperature of the anode. TEM has revealed that when aluminum is the anode material, the iron grains of the cathode are surrounded by a layer of aluminum. When the iron is the anode, a thin layer of iron surrounds the aluminum grains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Jones, Mater. Sci. Eng., 5, 1 (1969).
T. E. Shoup, C. C. Pease and M. Tamiuasu, in Metals Handbook. Vol. 6. 9th ed. (ASM, Metals Park, OH 1983), p. 729.
J. H. Devletian, Weld. J., 66, 33 (1987).
S. Venkataraman, and J. H. Devletian, Weld. J. (suppl.), 67, 111s (1988).
S. Venkataraman, and J. H. Devletian, in Principles of Solidification and Materials Processing. Vol 2. edited by R. Trivedi, J. A. Sekhar, and J. Mazumdar (Trans Tech Publications, New York, 1988), p. 859.
C. J. Einerson, D. E. Clark and J. H. Devletian, in Proc. of the 1987 ASME/JSME Thermal Engineering Joint Conf.. Volume Three, edited by P. J. Marto and I. Tanasawa (ASME, New York, 1987), p. 217.
R. D. Wilson, J. A. Hawk, and J. H. Devletian, in Joining and Adhesion of Advanced Inorganic Materials, edited by A. H. Carim, D. S. Schwartz, R. S. Silberglitt, and R. E. Loehman (to be publ. Mater. Res. Soc. Proc., Pittsburgh, PA).
S. Kuo, Welding Metallurev (John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1987), p. 202.
S. Kuo, Welding Metallurev (John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1987),. p. 146.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Dr. Roger L. Nielsen, Oregon Sate University, for performing the microprobe analyses on the CDW samples. The authors are grateful for the help and discussions provided by Dr. John W. Simmons during the course of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dogan, C.P., Wilson, R.D. & Hawk, J.A. CD Weld Interfacial Structure for Al-Fe Based Couples. MRS Online Proceedings Library 314, 169–175 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-314-169
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-314-169