Abstract
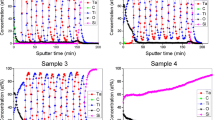
Previous studies have shown that the presence of hydrogen in multilayer samples containing Ti reduces ion beam mixing rates. The present study sought to determine why the magnitude of this effect depends on which metal is mixed into Ti and why it is correlated to the rate at which hydrogen leaves the sample during mixing. Hydrogen loss rates of multilayers were compared with those of bilayer samples designed to minimize the effect of mixing. For bilayers, hydrogen loss rates were smaller and did not depend on which metal was mixed into Ti in the same way that multilayer loss rates do. This suggests that hydrogen leaves the multilayer samples because it is bound less strongly in the mixed regions than in the Ti. The primary cause of hydrogen loss is mixing rather than ion beam induced desorption.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Børgesen, R. E. Wistrom, H. H. Johnson, and D. A. Lillenfeld: J. Mater. Res. 4, 821 (1989).
R. E. Wistrom, P. Børgesen, H. H. Johnson, and D. A. Lillenfeld: in Processing and Characterization of Materials Using Ion Beams, edited by L. E. Rehn, J. E. Greene, and F. A. Smid ( Mater. Res. Soc. Proc. 128, Pittsburgh, Pa 1989) pp. 219–224.
P. Børgesen, R. E. Wistrom, T. L. Alford, H. H. Johnson, and D. A. Lillenfeld:, Nucl. Instrum. and Meth. B43, 165 (1989).
P. Børgesen, D. A. Lillenfeld, R. E. Wistrom: to be published.
J. -P. Hirvonen, M. A. Elve, J. W. Mayer, and H. H. Johnson, Mater. Sci. and Eng. 90, 13 0987).
W. L. Johnson, Y. T. Cheng, M. Van Rossum, and M.-A. Nicolet, Nucl. Instrum. and Meth. B7/B8, 657 (1985).
J. J. Reilly, Z. Phys. Chem. NF 117, 155 (1979).
B. L. Doyle and P. S. Peercy: Appl. Phys. Lett. 34, 811 (1979).
R. Behrisch (ed.), Sputtering by Particle Bombardment I. Topics in Applied Physics, vol. 47, (Springer Verlag,1981).
O. Becker, W. Knippelberg, and K. Wien, Physica Scripta T6, 117 (1982).
M. Schluckebier, Th. Pfeiffer, K. Muskalla, W. Schmulling, and D. Kamke, Appl. Phys. A 42, 19 (1987).
M. Schluckebier, Th. Pfeiffer, K. Muskalla, W. Schmulling, and D. Kamke, Appl. Phys. A 42, 179 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wistrom, R.E., Borgesen, P. Why does Hydrogen Loss Rate Correlate with How Strongly Hydrogen Inhibits Ion Beam Mixing?. MRS Online Proceedings Library 157, 209–214 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-157-209
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-157-209