Abstract
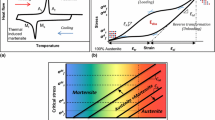
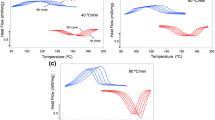
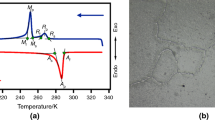
In this study, the effect of the cooling rate on the thermal and thermomechanical behavior of NiTiHf high-temperature shape memory alloy was studied by differential scanning calorimetry and via running isobaric thermal cycling experiments. The cooling rates were set to 5, 10, and 15 °C/min for each cycle in both experiments, while the heating rate was kept as 10 °C/min. It was found that the transformation temperatures and thermal hysteresis values do not depend on the change in the cooling rate. On the other hand, the austenite to martensite transformation enthalpy as measured from DSC analyses increases with the increase in the cooling rate due to the higher measurement sensitivity at higher scanning rates. Recoverable strain values which were determined from isobaric thermal cycling experiments do not differ since the transforming volume does not change with the change of the cooling rate. All these findings are explained based on the fundamental thermodynamical approach.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.J. Hartl and D.C. Lagoudas: Aerospace applications of shape memory alloys. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. G221, 535–552 (2007).
J.M. Jani, M. Leary, and A. Subic: Shape memory alloys in automotive applications. Appl. Mech. Mater.663, 248–253 (2014).
J.J. Epps and I. Chopra: In-flight tracking of helicopter rotor blades using shape memory alloy actuators. Smart Mater. Struct.10, 104–111 (2001).
F. El Feninat, G. Laroche, M. Fiset, and D. Mantovani: Shape memory materials for biomedical applications. Adv. Eng. Mater.4, 91–104 (2002).
K. Otsuka and X.B. Ren: Recent developments in the research of shape memory alloys. Intermetallics7, 511–528 (1999).
C.M. Wayman and T.W. Duerig: An Introduction to martensite and shape memory. In Engineering Aspects of Shape Memory Alloys, T.W. Duerig, K.N. Melton, D. Stockel, and C.M. Wayman, eds. (Butterworth, Boston, MA, 1990); p. 3.
K. Otsuka and X.B. Ren: Physical metallurgy of Ti-Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci.50, 511–678 (2005).
J. Ma, I. Karaman, and R.D. Noebe: High temperature shape memory alloys. Int. Mater. Rev.55, 257–315 (2010).
X.L. Meng, W. Cai, F. Chen, and L.C. Zhao: Effect of aging on martensitic transformation and microstructure in Ni-rich TiNiHf shape memory alloy. Scr. Mater.54, 1599–1604 (2006).
A. Evirgen, I. Karaman, R.D. Noebe, R. Santamarta, and J. Pons: Effect of precipitation on the microstructure and the shape memory response of the Ni50.3Ti29.7Zr20 high temperature shape memory alloy. Scr. Mater.69, 354–357 (2013).
A. Evirgen, I. Karaman, R. Santamarta, J. Pons, and R.D. Noebe: Microstructural characterization and shape memory characteristics of the Ni50.3Ti34.7Hf15 shape memory alloy. Acta Mater.83, 48–60 (2015).
A. Evirgen, I. Karaman, J. Pons, R. Santamarta, and R.D. Noebe: Role of nanoprecipitation on the microstructure and shape memory characteristics of a new Ni50.3Ti34.7Zr15 shape memory alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A655, 193–203 (2016).
A. Evirgen, F. Basner, I. Karaman, R.D. Noebe, J. Pons, and R. Santamarta: Effect of aging on the martensitic transformation characteristics of a Ni-rich NiTiHf high temperature shape memory alloy. Funct. Mater. Lett.5, 1250038 (2012).
A. Evirgen, I. Karaman, R. Santamarta, J. Pons, C. Hayrettin, and R.D. Noebe: Relationship between crystallographic compatibility and thermal hysteresis in Ni-rich NiTiHf and NiTiZr high temperature shape memory alloys. Acta Mater.121, 374–383 (2016).
R. Santamarta, R. Arroyave, J. Pons, A. Evirgen, I. Karaman, H.E. Karaca, and R.D. Noebe: TEM study of structural and microstructural characteristics of a precipitate phase in Ni-rich Ni-Ti-Hf and Ni-Ti-Zr shape memory alloys. Acta Mater.61, 6191–6206 (2013).
A. Evirgen, I. Karaman, R. Santamarta, J. Pons, and R.D. Noebe: Microstructural characterization and superelastic response of a Ni50.3Ti29.7Zr20 high temperature shape memory alloy. Scr. Mater.81, 12–15 (2014).
A.M. Perez-Sierra, J. Pons, R. Santamarta, I. Karaman, and R.D. Noebe: Stability of a Ni-rich Ni-Ti-Zr high temperature shape memory alloy upon low temperature aging and thermal cycling. Scr. Mater.124, 47–50 (2016).
L. Patriarca, Y. Wu, H. Sehitoglu, and Y.I. Chumlyakov: High temperature shape memory behavior of Ni50.3Ti25Hf24.7 single crystals. Scr. Mater.115, 133–136 (2016).
S.P. Aaron, G.S. Bigelow, J. Yang, D.P. Shukla, S.M. Saghaian, R. Rogers, A. Garg, H.E. Karaca, Y.I. Chumlyakov, K. Bhattacharya, and R.D. Noebe: Transformation strains and temperatures of a nickel-titanium-hafnium high temperature shape memory alloy. Acta Mater.76, 40–53 (2014).
L. Patriarca, H. Sehitoglu, E.Y. Panchenko, and Y.I. Chumlyakov: High-temperature functional behavior of single crystal Ni51.2Ti23.4Hf25.4 shape memory alloy. Acta Mater.106, 333–343 (2016).
B.C. Hornbuckle, T.T. Sasaki, G.S. Bigelow, R.D. Noebe, M.L. Weaver, and G.B. Thompson: Structure-property relationships in a precipitation strengthened Ni-29.7Ti-20Hf (at.%) shape memory alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A637, 63–69 (2015).
L. Patriarca and H. Sehitoglu: High-temperature superelasticity of Ni50.6Ti24.4Hf25.0 shape memory alloy. Scr. Mater.101, 12–15 (2015).
Y. Wu, L. Patriarca, H. Sehitoglu, and Y.I. Chumlyakov: Ultrahigh tensile transformation strains in new Ni50.5Ti36.2Hf13.3 shape memory alloy. Scr. Mater.118, 51–54 (2016).
W. Abuzaid and H. Sehitoglu: Functional fatigue of Ni50.3Ti25Hf24.7 – Heterogeneities and evolution of local transformation strains. Mater. Sci. Eng. A696, 482–492 (2017).
S.M. Saghaian, H.E. Karaca, H. Tobe, A.S. Turabi, S. Saedi, S.E. Saghaian, Y.I. Chumlyakov, and R.D. Noebe: High strength NiTiHf shape memory alloys with tailorable properties. Acta Mater.134, 211–220 (2017).
H.E. Karaca, S. Saghaian, G. Ded, H. Tobe, B. Basaran, H.J. Maier, R.D. Noebe, and Y.I. Chumlyakov: Effects of nano-precipitation on the shape memory and material properties of an Ni-rich NiTiHf high temperature shape memory alloy. Acta Mater.61, 7422–7431 (2013).
O. Karakoc, C. Hayrettin, M. Bass, S.J. Wang, D. Canadinc, H.J. Mabe, D.C. Lagoudas, and I. Karaman: Effects of upper cycle temperature on the actuation fatigue response of NiTiHf high temperature shape memory alloys. Acta Mater.138, 185–197 (2017).
O. Karakoc, C. Hayrettin, D. Canadinc, and I. Karaman: Role of applied stress level on the actuation fatigue behavior of NiTiHf high temperature shape memory alloys. Acta Mater.153, 156–168 (2018).
H.H. Saygili, H.O. Tugrul, and B. Kockar: Effect of aging heat treatment on the high cycle fatigue life of Ni50.3Ti29.7Hf20 high-temperature shape memory alloy. Shap. Mem. Superelasticity5, 32–41 (2019).
N. Babacan, M. Bilal, C. Hayrettin, J. Liu, O. Benafan, and I. Karaman: Effects of cold and warm rolling on the shape memory response of Ni50Ti30Hf20 high-temperature shape memory alloy. Acta Mater.157, 228–244 (2018).
T. Umale, D. Salas, B. Tomes, R. Arróyave, and I. Karaman: The effects of wide range of compositional changes on the martensitic transformation characteristics of NiTiHf shape memory alloys. Scr. Mater.161, 78–83 (2018).
Z.G. Wang, T.X. Zu, and Y. Huo: Effect of heating/cooling rate on the transformation temperatures in TiNiCu shape memory alloys. Thermochim. Acta436, 153–155 (2005).
K. Nurveren, A. Akdogan, and W.M. Huang: Evolution of transformation characteristics with heating/cooling rate in NiTi shape memory alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol.196, 129–134 (2008).
Q. Meng, H. Yang, Y. Liu, and T. Nam: Transformation intervals and elastic strain energies of B2-B19’ martensitic transformation of NiTi. Intermetallics18, 2431–2434 (2010).
P.C.C. Monteiro, Jr., L.L. Luciana, T.A. Netto, and M.A. Savi: Experimental investigation of the influence of the heating rate in an SMA actuator performance. Sens. Actuat. A199, 254–259 (2013).
M.G. Faulkner, J.J. Amaraj, and A. Bhattacharyya: Experimental determination of thermal and electrical properties of Ni-Ti shape memory wires. Smart Mater. Struct.9, 632–639 (2000).
B. Kockar, I. Karaman, J.I. Kim, Y.I. Chumlyakov, J. Sharp, and C.J.M. Yu: Thermomechanical cyclic response of an ultrafinegrained NiTi shape memory alloy. Acta Mater.56, 3630–3646 (2008).
H.E. Karaca, E. Acar, H. Tobe, and S.M. Saghaian: NiTiHf-based shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol.30, 1530–1544 (2014).
X.D. Han, C.Y. Chung, R. Wang, Z. Zhang, J.K.L. Lai, and D.Z. Yang: Martensitic transformation in Ti36.5Ni48.5Hf15 high temperature shape memory alloy. Mater. Trans. JIM38, 842–851 (1997).
K.C. Atli, I. Karaman, R.D. Noebe, A. Garg, Y.I. Chumlyakov, and I.V. Kireeva: Shape memory characteristics of TL19.5Ni25Pd25Sc0.5 high-temperature shape memory alloy after severe plastic deformation. Acta Mater.59, 4747–4760 (2011).
S. Qiu, V.B. Krishnan, S.A. Padula, R.D. Noebe, D.W. Brown, B. Clausen, and R. Vaidyanathan: Measurement of the lattice plane strain and phase fraction evolution during heating and cooling in shape memory NiTi. Appl. Phys. Lett.95, 141906 (2009).
P. Wollants, J.R. Roos, and L. Delaey: Thermally and stress-induced thermoelastic martensitic transformations in the reference frame of equilibrium thermodynamics. Prog. Mater. Sci.37, 227–288 (1993).
J.A. Bevis, R. Bottom, J. Duncan, I. Farhat, M. Forrest, D. Furniss, P. Gabbott, B. MacNaughtan, and S. Nazhat: A practical introduction to differential scanning calorimetry. In Principles and Applications of Thermal Analysis, P. Gabbott, ed. (Blackwell Publishing, Oxford, UK, 2008); p. 9.
ASTM F2004: Standard Test Method for Transformation Temperature of Nickel-Titanium Alloys by Thermal Analysis.
K.C. Atli, I. Karaman, R.D. Noebe, A. Garg, Y.I. Chumlyakov, and I.V. Kireeva: Improvement in the shape memory response of Ti50.5Ni24.5Pd25 high-temperature shape memory alloy with scandium microalloying. Metall. Mater. Trans. A41A, 2485–2497 (2010).
K.C. Atli, I. Karaman, and R.D. Noebe: Influence of tantalum additions on the microstructure and shape memory response of Ti50.5Ni24.5Pd25 high temperature shape memory alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A613, 250–258 (2014).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Turkish Aerospace Industries [Grant No. DKTM/2015/10].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akgul, O., Tugrul, H.O. & Kockar, B. Effect of the cooling rate on the thermal and thermomechanical behavior of NiTiHf high-temperature shape memory alloy. Journal of Materials Research 35, 1572–1581 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2020.139
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2020.139