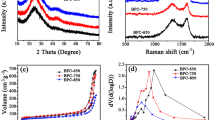
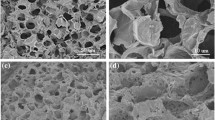
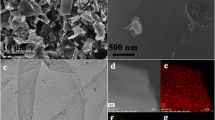
Abstract
Porous carbon derived from biomass materials with enrich, low cost, clean, and renewable merits, exhibits various physical and chemical properties. So, it is of great significance to rationally utilize biomass materials for producing porous carbon with low cost to reduce overusing fossil fuel and environmental pollution. In this report, porous carbon has been fabricated using fruits shells of the Paulownia tomentosa by a facile method of KOH-activation. The as-obtained porous carbon containing a larger number of micropores and slight mesopores possesses a high specific surface area (1914.4 m2/g) and well hierarchical porosity. As the anode for sodium ion batteries, the porous carbon sample displays superior cycling stability and rate capability, delivering a reversible specific capacity of 179 mA h/g at 50 mA/g after 100 cycles and a discharge specific capacity of 100 mA h/g at 1 A/g.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Liu, Y. Li, Y-S. Hu, H. Li, L. Chen, and X. Huang: A waste biomass derived hard carbon as a high-performance anode material for sodium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 4 (34), 13046 (2016).
Y. Nishi: Lithium ion secondary batteries; past 10 years and the future. J. Power Sources 100 (1), 101 (2001).
D. Qin and S. Chen: A sustainable synthesis of biomass carbon sheets as excellent performance sodium ion batteries anode. J. Solid State Electrochem. 21 (5), 1305 (2017).
L. Fan, X. Li, B. Yan, J. Feng, D. Xiong, D. Li, L. Gu, Y. Wen, S. Lawes, and X. Sun: Controlled SnO2 crystallinity effectively dominating sodium storage performance. Adv. Energy Mater. 6 (10), 1502057 (2016).
X. Li, X. Li, L. Fan, Z. Yu, B. Yan, D. Xiong, X. Song, S. Li, K.R. Adair, D. Li, and X. Sun: Rational design of Sn/SnO2/porous carbon nanocomposites as anode materials for sodium-ion batteries. Appl. Surf. Sci. 412 (Suppl. C), 170 (2017).
X. Song, X. Li, Z. Bai, B. Yan, D. Li, and X. Sun: Morphology-dependent performance of nanostructured Ni3S2/Ni anode electrodes for high performance sodium ion batteries. Nano Energy 26 (Suppl. C), 533 (2016).
V. Palomares, P. Serras, I. Villaluenga, K. Hueso, J. Gonzalez, and T. Rojo: Na-ion batteries, recent advances and present challenges to become low cost. Energy Storage Syst. 5 (3), 5884–5901 (2012).
S. Zhang, J. Zhang, S. Wu, W. Lv, F. Kang, and C. Yuan: Research advances of carbon-based anode materials for sodium-ion batteries. Acta Chim. Sin. 75 (2), 163 (2017).
R.R. Gaddam, D. Yang, R. Narayan, K. Raju, N.A. Kumar, and X.S. Zhao: Biomass derived carbon nanoparticle as anodes for high performance sodium and lithium ion batteries. Nano Energy 26 (Suppl. C), 346 (2016).
P. Kalyani and A. Anitha: Biomass carbon & its prospects in electrochemical energy systems. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 38 (10), 4034 (2013).
M. Rana, K. Subramani, M. Sathish, and U.K. Gautam: Soya derived heteroatom doped carbon as a promising platform for oxygen reduction, supercapacitor and CO2 capture. Carbon 114, 679 (2017).
S. De, A.M. Balu, J.C. van der Waal, and R. Luque: Biomass-derived porous carbon materials: Synthesis and catalytic applications. ChemCatChem 7 (11), 1608 (2015).
H. Wang, W. Yu, J. Shi, N. Mao, S. Chen, and W. Liu: Biomass derived hierarchical porous carbons as high-performance anodes for sodium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 188, 103 (2016).
H. Varma, Avinesh, R. Narasimman, and K. Prabhakaran: Preparation and characterization of hierarchical porous carbon by a hard-template. Mater. Sci. Forum 830–831, 585 (2015).
S. Zhao, C. Li, W. Wang, H. Zhang, M. Gao, X. Xiong, A. Wang, K. Yuan, Y. Huang, and F. Wang: A novel porous nanocomposite of sulfur/carbon obtained from fish scales for lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 1 (10), 3334 (2013).
W. Chen, H. Zhang, Y. Huang, and W. Wang: A fish scale based hierarchical lamellar porous carbon material obtained using a natural template for high performance electrochemical capacitors. J. Mater. Chem. 20 (23), 4773 (2010).
C. Guo, R. Hu, W. Liao, Z. Li, L. Sun, D. Shi, Y. Li, and C. Chen: Protein-enriched fish “biowaste” converted to three-dimensional porous carbon nano-network for advanced oxygen reduction electrocatalysis. Electrochim. Acta 236, 228 (2017).
H. Ru, K. Xiang, W. Zhou, Y. Zhu, X.S. Zhao, and H. Chen: Bean-dreg-derived carbon materials used as superior anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 222, 551 (2016).
X. Yu, Y. Wang, L. Li, H. Li, and Y. Shang: Soft and wrinkled carbon membranes derived from petals for flexible supercapacitors. Sci. Rep. 7, 45378 (2017).
Y. Cai, Y. Luo, H. Dong, X. Zhao, Y. Xiao, Y. Liang, H. Hu, Y. Liu, and M. Zheng: Hierarchically porous carbon nanosheets derived from Moringa oleifera stems as electrode material for high-performance electric double-layer capacitors. J. Power Sources 353, 260 (2017).
Y. Gong, D. Li, C. Luo, Q. Fu, and C. Pan: Highly porous graphitic biomass carbon as advanced electrode materials for supercapacitors. Green Chem. 19 (17), 4132 (2017).
W. Huang, H. Zhang, Y. Huang, W. Wang, and S. Wei: Hierarchical porous carbon obtained from animal bone and evaluation in electric double-layer capacitors. Carbon 49 (3), 838 (2011).
Y-H. Ke, E-T. Yang, X. Liu, C-L. Liu, and W-S. Dong: Preparation of porous carbons from non-metallic fractions of waste printed circuit boards by chemical and physical activation. Carbon 60 (Suppl. C), 563 (2013).
S. Imtiaz, J. Zhang, Z.A. Zafar, S. Ji, T. Huang, J.A. Anderson, Z. Zhang, and Y. Huang: Biomass-derived nanostructured porous carbons for lithium–sulfur batteries. Sci. China Mater. 59 (5), 389 (2016).
J. Wang and S. Kaskel: KOH activation of carbon-based materials for energy storage. J. Mater. Chem. 22 (45), 23710 (2012).
D. Lozano-Castelló, J.M. Calo, D. Cazorla-Amorós, and A. Linares-Solano: Carbon activation with KOH as explored by temperature programmed techniques, and the effects of hydrogen. Carbon 45 (13), 2529 (2007).
T. Otowa, R. Tanibata, and M. Itoh: Production and adsorption characteristics of MAXSORB: High-surface-area active carbon. Gas Sep. Purif. 7 (4), 241 (1993).
M. Thommes, K. Kaneko, A.V. Neimark, J.P. Olivier, F. Rodriguez-Reinoso, J. Rouquerol, and K.S.W. Sing: Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 87 (9–10), 929 (2015).
K. Kierzek, E. Frackowiak, G. Lota, G. Gryglewicz, and J. Machnikowski: Erratum to “Electrochemical capacitors based on highly porous carbons prepared by KOH activation”. Electrochim. Acta 49 (7), 1169 (2004).
H. Ye, Y-X. Yin, S. Xin, and Y-G. Guo: Tuning the porous structure of carbon hosts for loading sulfur toward long lifespan cathode materials for Li–S batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 1 (22), 6602 (2013).
J. Ou, L. Yang, Z. Zhang, and X. Xi: Nitrogen-doped porous carbon derived from horn as an advanced anode material for sodium ion batteries. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 237, 23 (2017).
D. Xiong, X. Li, Z. Bai, H. Shan, L. Fan, C. Wu, D. Li, and S. Lu: Superior cathode performance of nitrogen-doped graphene frameworks for lithium ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9 (12), 10643 (2017).
X. Shi, Z. Zhang, Y. Fu, and Y. Gan: Self-template synthesis of nitrogen-doped porous carbon derived from zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 as an anode for sodium ion batteries. Mater. Lett. 161, 332 (2015).
S. Deheryan, D.J. Cott, P.W. Mertens, M. Heyns, and P.M. Vereecken: Direct correlation between the measured electrochemical capacitance, wettability and surface functional groups of carbon nanosheets. Electrochim. Acta 132, 574 (2014).
J. Ou, L. Yang, and X. Xi: Hierarchical porous nitrogen doped carbon derived from horn comb as anode for sodium-ion storage with high performance. Electron. Mater. Lett. 13 (1), 66 (2016).
P. Simon and Y. Gogotsi: Materials for electrochemical capacitor. Nat. Mater. 7 (11), 845–854 (2008).
H. Liu, M. Jia, N. Sun, B. Cao, R. Chen, Q. Zhu, F. Wu, N. Qiao, and B. Xu: Nitrogen-rich mesoporous carbon as anode material for high-performance sodium-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7 (49), 27124 (2015).
Z.J. Qiao, M.M. Chen, C.Y. Wang, and Y.C. Yuan: Humic acids-based hierarchical porous carbons as high-rate performance electrodes for symmetric supercapacitors. Bioresour. Technol. 163, 386 (2014).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51572194 and 51672189), The Key Project of the Tianjin Science & Technology Support Program (17YFZCGX00550), and Academic Innovation Funding of Tianjin Normal University (52XC1404).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Li, X., Li, X. et al. Paulownia tomentosa derived porous carbon with enhanced sodium storage. Journal of Materials Research 33, 1236–1246 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.452
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.452