Abstract
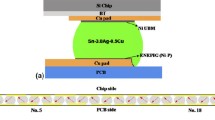
Effect of electromigration on mechanical shear behavior of flip chip solder joints consisting of 97Pb3Sn and 37Pb63Sn composite solder joints was studied. The under bump metallurgy (UBM) on the chip side was TiW/Cu/electroplated Cu, and the bond pad on the board side was electroless Ni/Au. It was found that the mode of shear failure has changed after electromigration and the mode depends on the direction of electron flow during electromigration. The shear induced fracture occurs in the bulkof 97Pb3Sn solder without current stressing, however, after 10 h current stressing at 2.55 × 104 A/cm2 at 140 °C, it occurs alternately at the cathode interfaces between solder and intermetallic compounds (IMCs). In the downward electron flow, from the chip to substrate, the failure site was at the Cu-Sn IMC/solder interface near the Si chip. However, in the upward electron flow, from the substrate to chip, failure occurred at the Ni-Sn IMC/solder interface near the substrate. The failure mode has a strong correlation to microstructural change in the solder joint. During the electromigration, while Pb atoms moved to the anode side in the same direction as with the electron flow, Sn atoms diffused to the cathode side, opposite the electron flow. In addition, electromigration dissolves and drives Cu or Ni atoms from UBM or bond pad at the cathode side into the solder. These reactions resulted in the large growth of Sn-based IMC at the cathode sides. Therefore, mechanical shear failure occurs predominantly at the cathode interface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.H. Lau, Y.H. Pao: Solder Joint Reliability of BGA, CSP, Flip Chip, and Fine Pitch SMT Assembles (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1997), p. 47.
K.N. Tu: Recent advances on electromigration in very-large-scale-integration of interconnects. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 5451 (2003).
T.Y. Lee, K.N. Tu, S.M. Kuo, D.R. Frear: Electromigration of eutectic SnPb solder interconnects for flip chip technology. J. Appl. Phys. 89, 3189 (2001).
T.Y. Lee, K.N. Tu, D.R. Frear: Electromigration of eutectic SnPb and SnAg3.8Cu0.7 flip chip solder bumps and under-bump metallization. J. Appl. Phys. 90, 4502 (2001).
W.J. Choi, E.C.C. Yeh, K.N. Tu: Mean-time-to-failure study of flip chip solder joints on Cu/Ni(V)/Al thin-film under-bump-metallization. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 5665 (2003).
J.W. Nah, K.W. Paik, J.O. Suh, K.N. Tu: Mechanism of electromigration-induced failure in the 97Pb–3Sn and 37Pb–63Sn composite solder joints. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 7560 (2003).
Y.C. Hsu, T.L. Shao, C.J. Yang, C. Chen: Electromigration study in SnAg3.8Cu0.7 solder joints on Ti/Cr–Cu/Cu under-bump metallization. J. Electron. Mater. 32, 1222 (2003).
T.L. Shao, K.C. Lin, C. Chen: Electromigration studies of flip chip Sn95/Sb5 solder bumps Cr/Cr–Cu/Cu under-bump metallization. J. Electron. Mater. 32, 1278 (2003).
T.L. Shao, S.H. Chiu, C. Chen, D.J. Yao, C.Y. Hsu: Thermal gradient in solder joints under electrical-current stressing. J. Electron. Mater. 33, 1350 (2004).
T.L. Shao, Y.H. Chen, S.H. Chiu, C. Chen: Electromigration failure mechanisms for SnAg3.5 solder bumps on Ti/Cr–Cu/Cu under-bump metallization pads. J. Appl. Phys. 96, 4518 (2004).
Y.H. Lin, C.M. Tsai, Y.C. Hu, Y.L. Lin, C.R. Kao: Electromigration-induced failure in flip-chip solder joints. J. Electron. Mater. 34, 27 (2005).
Y.H. Lin, Y.C. Hu, C.M. Tsai, C.R. Kao, K.N. Tu: In situ observation of the void formation-and-propagation mechanism in solder joints under current-stressing. Acta Mater. 53, 2029 (2005).
Y.H. Liu, K.L. Lin: Damages and microstructural variation of high-lead and eutectic SbPb composite flip chip solder bumps induced by electromigration. J. Mater. Res. 20, 2184 (2005).
J.W. Nah, J.O. Suh, K.N. Tu: Effect of current crowding and Joule heating on electromigration-induced failure in flip chip composite solder joints tested at room temperature. J. Appl. Phys. 98, 013715 (2005).
F. Ren, J.W. Nah, H. Gan, J.O. Suh, K.N. Tu, B. Xiong, L. Xu, J. Pang Effect of electromigration on mechanical behavior of solder joints, in Materials, Technology and Reliability of Advanced Interconnects—2005, edited by P.R. Besser, A.J. McKerrow, F. Iacopi, C.P. Wong, and J. Vlassak (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 863 Warrendale, PA, 2005), B10.2.
L.L. Mercado, V. Sarihan, Y. Guo, A. Mawer: Impact of solder pad size on solder joint reliability in flip chip PBGA packages. IEEE Trans. Adv. Packag. 23, 416 (2000).
J.H.L. Pang, D.Y.R. Chong, T.H. Low: Thermal cycling analysis of flip-chip solder joint reliability. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 24, 705 (2001).
Y. Kariya, T. Hosoi, S. Terashima, M. Tanaka, M. Otsuka: Effect of silver content on the shear fatigue properties of Sn–Ag–Cu flip-chip interconnects. J. Electron. Mater. 33, 321 (2004).
V.K. Nagesh, R. Peddada, S. Ramalingam, B. Sur, A. Tai Challenges of flip chip on organic substrate assembly technology, in Proc. 49th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (IEEE, Piscataway, NJ, 1999), p. 975.
R. Shukla, V. Murali, A. Bhansali Flip chip CPU package technology at Intel: A technology and manufacturing overview, in Proc. 49th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (IEEE, Piscataway, NJ, 1999), p. 945.
Y. Guo, S.M. Kuo, C. Zhang: Reliability evaluations of under bump metallurgy in two solder systems. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 24, 655 (2001).
E.C.C. Yeh, W.J. Choi, K.N. Tu, P. Elenius, H. Balkan: Current-crowding-induced electromigration failure in flip chip solder joints. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 580 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nah, JW., Ren, F., Paik, KW. et al. Effect of electromigration on mechanical shear behavior of flip chip solder joints. Journal of Materials Research 21, 698–702 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2006.0086
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2006.0086