Abstract
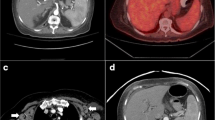
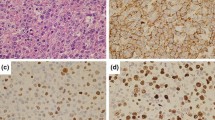
Splenic lymphoma with villous lymphocytes (SLVL) is a rare, slowly progressing, lymphoproliferative disease of B-cell origin. Treatment aimed at cure or remission is limited, and spontaneous remission has not been described. We report on a patient who after 4 years with untreated SLVL developed symptoms of mononucleosis and was found to have reactivation of latent Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection. During recovery from the EBV infection, complete remission from SLVL developed and lasted for 3 years, suggesting that the EBV infection induced an immune response that caused the SLVL remission.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oscier D, Fegan C, Hillmen P, et al. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2004;125:294–317.
Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Rai KR, et al. Guidelines for clinical protocols for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: recommendations of the National Cancer Institute-sponsored working group. Am J Hematol. 1988;29:152–163.
Bowen AL, Matutes E, Catovsky D. Splenic lymphoma with villous lymphocytes. Haematologica. 1999;84:90–92.
Linde A, Kallin B, Dillner J, et al. Evaluation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays with two synthetic peptides of Epstein-Barr virus for diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis. J Infect Dis. 1990; 161:903–909.
Bernard M, Drenou B, Pangault C et al. Spontaneous phenotypic and molecular blood remission in a case of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 1999;107:213–214.
Thomas R, Ribeiro I, Shepherd P, et al. Spontaneous clinical regression in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2002; 116:341–345.
Shirono K, Ikebe M, Inada T, Tsuda H. Transient regression in lymphocyte count in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia after viral infection. Acta Haematol. 1995;93:46–49.
Frick S, Frick P. Spontaneous remission in chronic lymphatic leukemia [in German]. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1993;123: 328–334.
Hansen RM, Libnoch JA. Remission of chronic lymphocytic leukemia after smallpox vaccination. Arch Intern Med. 1978;138: 1137–1138.
Keefer MJ, Weber MJ, Bottomley SS, Solanki DL, Hosty TA. Peripheral blood remission of hairy cell leukemia after transfusion hepatitis. Am J Hematol. 1987;25:277–284.
Abramson N, Castro S. Remission of hairy cell leukemia without treatment. Haematologia (Budap). 1997;28:259–264.
Macallan DC, Wallace DL, Irvine AJ, et al. Rapid turnover of T cells in acute infectious mononucleosis. Eur J Immunol. 2003;33: 2655–2665.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hansson, M., Linde, A. & Olsson, I. Reactivation of Latent Epstein Barr Virus Infection Induces Remission of Splenic Lymphoma with Villous Lymphocytes. Int J Hematol 81, 413–416 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.E0434
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.E0434