Abstract
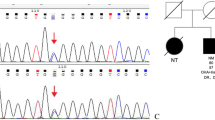
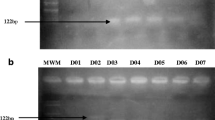
The aim of this study was to investigate the presence of mutations in the islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) gene in a Spanish population with type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). Using polymerase chain reaction single-stranded conformation polymorphism, we examined the coding region and the 5′-untranslated region (UTR) of the IAPP gene in 177 unrelated type 2 diabetic patients, 110 healthy control subjects, 38 women with GDM, and 38 gestational control subjects. Mutations were confirmed by DNA sequencing. A heterozygous C-to-A nucleotide substitution at +79 bp in intron 2 of the IAPP gene was detected. The frequencies of the +79-bp polymorphism (A allele) were 6.8% in type 2 diabetic patients, 7.7% in nondiabetic control subjects, 11.8% in women with GDM, and 9.2% in gestational control subjects. No AA genotypes were detected. Nondiabetic subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes bearing the CA genotype had lower low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels than subjects bearing wild genotype. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed an independent association (p<0.001; odds ratio: 0.33; 95% confidence interval: 0.17–0.63). We did not detect any sequence variant within exons 1 or 2. One diabetic patient was heterozygous for a silent mutation at codon 31 of exon 3 (Asn31 AAC→AAT). Our findings indicate that the presence of the +79-bp polymorphism of the IAPP gene in nondiabetic subjects and in patients with type 2 diabetes is associated with lower levels of LDL cholesterol. Furthermore, abnormalities of the coding regions or the 5′-UTR of the IAPP gene are not associated with type 2 diabetes or GDM in the Spanish population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clark, A., Edwards, C. A., Ostle, L. R., et al. (1989). Cell Tissue Res. 257, 179–185.
Kahn, S. E., D’Alessio, D. A., Schwartz, M. W., et al. (1990). Diabetes 39, 634–638.
Westermark, P., Wernstedt, C., Wilander, E., Hayden, D. W., O’Brien, T. D., and Johnson, K. H. (1987). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 3881–3885.
Cooper, G. J., Willis, A. C., Clark, A., Turner, R. C., Sim, R. B., and Reid, K. B. (1987). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 8628–8632.
Charge, S. B., Esiri, M. M., Bethune, C. A., Hansen, B. C., and Clark, A. (1996). J. Pathol. 179, 443–447.
Khan, S. E., Andrikopoulos, S., and Verchere, B. (1999). Diabetes 48, 241–253.
Young, I. D., Ailles, L., Narindrasorasak, S., Tan, R., and Kisilevsky, R. (1992). Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 116, 951–954.
Glenner, G. G. and Wong, C. W. (1984). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 120, 885–890.
Fernandez-Madrid, I., Levy, E., Marder, K., and Frangione, B. (1991). Ann. Neurol. 30, 730–733.
Martin, J. B. (1999). N. Engl. J. Med. 340, 1970–1980.
Nishi, M., Sanke, T., Seino, S., et al. (1989). Mol. Endocrinol. 3, 1775–1781.
Mosselman, S., Höppener, J. W. M., Lips, C. J. M., and Jansz, H. S. (1989). FEBS Lett. 247, 154–158.
Sakagashira, S., Sanke, T., Hanabusa, T., et al. (1996). Diabetes 45, 1279–1281.
Chuang, L.-M., Lee, K.-C., Huang, C. N., Wu, H. P., Tai, T.-Y., and Lin, B. J. (1998). Diabetologia 41, 1250–1251.
Nishi, M., Bell, G. I., and Steiner, D. F. (1990). Diabetologia 33, 628–630.
Cook, J. T. E., Patel, P. P., Clark, A., et al. (1991). Diabetologia 34, 103–108.
Birch, C. L., Fagan, L. J., Armstrong, M. J., Turnbull, D. M., and Walker, M. (1997). Diabetologia 40, 1113.
Kautsky-Willer, A., Thomaseth, B., Ludvik, B., et al. (1997). Diabetes 46, 607–614.
Wareham, N. J., Swinn, R., Fineman, M. S., et al. (1998). Diabetes Care 21, 668–669.
de Koning, E. J., Morris, E. R., Hofhuis, F. M., et al. (1994). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 8467–8471.
Lorenzo, A., Razzaboni, B., Weir, G. C., and Yankner, B. A. (1994). Nature 368, 756–760.
Janson, J., Soeller, W. C., Roche, P. C., et al. (1996). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 7283–7288.
Aoyama, T., Sawamura, T., Furutani, Y., Matsuoka, R., Yoshida, M. C., and Fujiwara, H. (1999). Biochem. J. 339, 177–184.
Brown, S. D., Twells, R., Hey, P. J., et al. (1999). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 248, 879–888.
Powell, D. S., Maksoud, H., Hattersley, A. T., et al. (1999). Diabetologia 42, A146 (abstract).
Vidal, J., Verchere, C. B., Andrikopoulos, S., Hull, R. L., Wang, F., and Kahn, S. E. (2000). Diabetes 49, 951-P (abstract).
World Health Organization (1985). Technical Report Series, 727. World Health Organization: Geneva.
Friedewald, W. T., Levy, R. I., and Fredrickson, D. S. (1972). Clin. Chem. 18, 499–502.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rojas, I., Gomis, R., Casals, E. et al. Polymorphism in intron 2 of islet amyloid polypeptide gene is associated with lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in nondiabetic subjects and in type 2 diabetic patients. Endocr 19, 185–189 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:19:2:185
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:19:2:185