Abstract
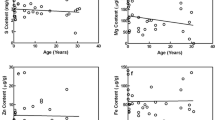
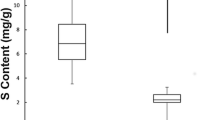
To elucidate compositional changes of the tendons and ligaments with aging, the authors investigated age-related changes of element contents in the insertion tendons of the biceps brachii muscle, central tendons of the diaphragma, Achilles’ tendons, posterior longitudinal ligaments (PLLs) of the cervical spine, ligamenta capitum femorum, and anterior cruciate ligaments. After ordinary dissections by medical students, the three tendons and three ligaments were resected and element contents were determined by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry. It was found that the elements, such as Ca, P, S, Mg, Na, Zn, and Fe, did not change significantly in the three tendons and two ligaments with aging, except for the PLLs where Ca and Mg increased significantly with aging and Fe decreased significantly with aging.
With regard to the relationships among elements, the common finding that there were significant correlations between Ca and P contents and between Ca and Mg contents was obtained in the three ligaments. Likewise, the common finding that there was a significant correlation between Ca and Mg contents was obtained in the three tendons. Regarding the relationship between Ca and P contents, the three tendons were different from the three ligaments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, T. Minami, et al., Age-related changes of mineral contents in human thoracic aorta and in the cerebral artery, Biol. Trace Element Res. 54, 23–31 (1996).
S. Tohno and Y. Tohno, Age-related differences in calcium accumulation in human arteries, Cell. Mol. Biol. 44, 1253–1263 (1998).
Y. Tohno, M. Utsumi, S. Tohno, et al., Age-dependent changes of mineral contents in man’s and woman’s calcanei, Biol. Trace Element Res. 60, 81–90 (1997).
S. Tohno, Y. Tohno, T. Minami, et al., Difference of mineral contents in human intervertebral disks and its age-related change, Biol. Trace Element Res. 52, 117–124 (1996).
Y. Tohno, Y. Takano, S. Tohno, et al., Age-dependent decreases of phosphorus and magnesium in human Achilles’ tendons, Biol. Trace Element Res. 74, 1–9 (2000).
M. Yamada, Y. Tohno, Y. Takaura, et al., Age-related changes of element contents in human tendon of the iliopsoas muscle and the relationships among elements, Biol. Trace Element Res. 91, 57–66 (2003).
Y. Tohno, Y. Moriwake, Y. Takano, et al., Age-related changes of elements in human anterior cruciate ligaments and ligamenta capitum femorum, Biol. Trace Element Res. 68, 181–192 (1999).
C. Azuma, Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, et al., Differences in accumulation of calcium in human plantar and palmar aponeuroses, Biol. Trace Element Res. 87, 57–68 (2002).
Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, H. Matsumoto, et al., A trial of introducing soft X-ray apparatus into dissection practice for students, J. Nara Med. Assoc. 36, 365–370 (1985) (in Japanese).
H. Minagi and A. T. Gronner, Calcification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: a cause of cervical myelopathy, Am. J. Roentgenol. Radium Ther. Nucl. Med. 105, 365–369 (1969).
Y. Hiramatsu and T. Nobechi, Calcification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine among Japanese, Radiology 100, 307–312 (1971).
H. Firooznia, V. M. Benjamin, R. S. Pinto, et al., Calcification and ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament of spine. Its role in secondary narrowing of spinal canal and cord compression, NY State J. Med. 82, 1193–1198 (1982).
K. Izawa, Comparative roentgenographical study on the incidence of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and other degenerative changes of the cervical spine among Japanese, Koreans, Americans and Germans, Nippon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zasshi 54, 461–474 (1980).
R. Strocchi, V. De Pasquale, A. Facchini, et al., Age-related changes in human anterior cruciate ligament collagen fibrils, Ital. J. Anat. Embryol. 101, 213–220 (1996).
D. Amiel, S. D. Kuiper, C. D. Wallace, et al., Age-related properties of medial collateral ligament and anterior cruciate ligament. A morphologic and collagen maturation study in the rabbit, J. Gerontol. 46, B159-B165 (1991).
R. Strocchi, V. De Pasquale, S. Guizzardi, et al., Human Achilles tendon: morphological and morphometric variations as a function of age, Foot Ankle 12, 100–104 (1991).
E. Ippolito, P. G. Natali, F. Postacchini, et al., Morphological, immunochemical, and biochemical study of rabbit Achilles tendon at various ages, J. Bone Joint Surg. 62A, 583–596 (1980).
Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, Y. Moriwake, et al., Accumulation of calcium and phosphorus accompanied by increase of magnesium and decrease of sulfur in human arteries, Biol. Trace Element Res. 82, 9–19 (2001).
Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, Y. Moriwake, et al., Simultaneous accumulation of calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium in various human arteries, Biol. Trace Element Res. 82, 21–28 (2001).
S. Tohno, Y. Tohno, Y. Moriwake, et al., Quantitative changes of calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium in common iliac arteries with aging, Biol. Trace Element Res. 84, 57–66 (2001).
S. Tohno, Y. Tohno, T. Minami, et al., Elements of calcified sites in human thoracic aorta, Biol. Trace Element Res. 86, 23–30 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamada, M., Tohno, Y., Tohno, S. et al. Age-related changes of elements and relationships among elements in human tendons and ligaments. Biol Trace Elem Res 98, 129–142 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:98:2:129
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:98:2:129