Abstract
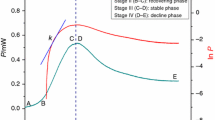
The effect of Li(I) on the metabolism of mitochondria isolated from Carassius auratus liver tissue was investigated by microcalorimetric method to provide evidence for mitochondria hypothesis of biporlar disorder (BPD) and to explore therapeutic mechanism of drug for treatment of BPD. Obvious stimulation induced by Li(I) on mitochondria metabolism was reflected by power-time (P-t) curves. The power-time curves of hepatic mitochondria metabolism without Li(I) could be divided into four parts: lag phase, active recovery phase, stationary phase, and decline phase. When Li(I) was added, the second heat peak occurred in a concentration-dependent sequence. Considering the first heat peak on the p-t curves, Li(I) in the range of therapeutic and lower concentration induced slight alterations in comparison with the characteristic heat peak observed in the control. However, Li(I) above the therapeutic concentration resulted in significant changes. Heat output increased with the concentration of Li(I), but the rate constant (k 2) and the maximum heat power (P max2) for the second heat peak reached maximum value in the range of therapeutic concentration. Mechanism of activation of mitoKatp was suggested and discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Ramprasad, Magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging studies of lithium, Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 47, 111–121 (2005).
G. N. Schrauzer, Occurrence, dietary intakes, nutritional essentiality, J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 21, 14–21 (2002).
M. Schou, in Lithium and the Cell: Pharmacology and Biochemistry, N. J. Birch, ed., Academic, London, pp. 1–6 (1991).
G. J. Moore, J. M. Bebchuk, I. B. Wilds, G. Chen, and H. K. Manji, Lithium-induced increase in human brain grey matter, Lancet 356, 1241–1242 (2000).
C. J. Hough and D. M. Chuang, The mitochondrial hypothesis of bipolardisorder, Bipolar Disord. 2, 145–147 (2000).
T. D. King, G. N. Bijur, and R. S. Jope, Caspase-3 activation induced by inhibition of mitochondrial complex I is facilitated by glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta and attenuated by lithium, Brain Res. 919, 106–114 (2001).
R. S. Jope and L. Song, K. Kolasa, Inositol trisphosphate, cyclic AMP, and cyclic GMP in rat brain regions after lithium and seizures, Biol. Psychiatry 31, 505–514 (1992).
J. Nordenberg, C. Panet, L. Wasserman, et al., The anti-proliferative effect of lithium chloride on melanoma cells and its reversion by myoinositol, Br. J. Cancer 55, 41–46 (1987).
S. Washizuka, A. Ikeda, and N. Kato, Possible relationship between mitochondrial DNA polymorphisms and lithium response in bipolar disorder, Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 6, 421–424 (2003).
K. Iwamoto, M. Bundo, and T. Kato, Altered expression of mitochondria-related genes in postmortem brains of patients with bipolar disorder or schizophrenia, as revealed by large-scale DNA microarray analysis, Hum. Mol. Genet. 14, 241–253 (2005).
J. Murashita, T. Kato, T. Shioiri, T. Inubushi, and N. Kato, Altered brain energy metabolism in lithium-resistant bipolar disorder detected by photic stimulated P-31-MR spectroscopy. Psychol. Med. 30, 107–115 (2000).
A. Yildiz, C. M. Moore, G. S. Sachs, et al., Lithium-induced alterations in nucleoside triphosphate levels in human brain: a proton-decoupled (31)P magnetic resonance spectroscopy study, Psychiatry Res. Neuroimag. 138, 51–59 (2005).
A. Moretti, A. Gorini, and R. F. Villa, Affective disorders, antidepressant drugs and brain Metabolism, Mol. Psychiatry 8, 773–785 (2003).
R. B. Kemp, The application of heat conduction microcalorimetry to study the metabolism and pharmaceutical modulation of cultured mammalian cells, Thermochim. Acta 380, 229–244 (2001).
J. Nedergaard, B. Canno, and O. Lindberg, Microcalorietry of isolated mammalian cells, Nature 267, 518–520 (1977).
X. Q. Wang, C. L. Xie, and S. S. Qu, Microcalorimetric study of mitochondrial metabolism, Thermochim. Acta 176, 69–74 (1991).
X. Li, Y. Liu, F. J. Deng, C. X. Wang, and S. S. Qu, Microcalorimetric studies of the toxic effect of sodium selenite on the mitochondria metabolism of Carassius auratus liver, Biol. Trace Element Res. 77, 261–270 (2000).
K. Detlef, S. Marion, and D. Jurgen, Oxidative phosphorylation in myocardial mitochondria in situ: a calorimetric study on permeabilized cardiac muscle preparations Mol. Cell. Biochem. 74, 101–113 (1997).
P. J. Zhou, H. T. Zhou, Y. Liu, S. S. Qu, and Y. G. Zhu, Calorimetric and DSC study of mitochondria isolated from cytoplasmic male sterileline of rice, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 76, 1003–1013 (2004).
L. Wadsö, A multi channel isothermal heat conduction calorimeter for cement hydration studies, International Congress of the Chemistry of Cement, Durban, South Africa (2003).
L. Wadso, F. Gomez, I. Sjoholm, and P. Rocculic, Effect of tissue wounding on the results from calorimetric measurements of vegetable respiration, Thermochim. Acta 422, 89–93 (2004).
P. J. Zhou, H. T. Zhou, Y. Liu, S. S. Qu, and Y. G. Zhu, Study on the energy release of rice mitochondria under different conditions by means of microcalorimetry, J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 48, 1–11 (2001).
S. J. Richard, Li(I) and GSK-3: one inhibitor, two inhibitory actions, multiple outcomes, Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 24, 441–443 (2003).
R. P. Helen, Reports the ups and downs of Li(I), Nature 425, 118–120 (2003).
S. J. H. Ashcroft and F. M. Ashcroft, Properties and functions of ATP-sensitive K-channels, Cell. Signal. 2, 197–214 (1990).
I. Inoue, ATP-sensitive K+ channel in the mitochondrial inner membrane, Nature 352, 244–247 (1991).
O. Jilkina, B. Kuzio, J. Gary, G. Clifford, D. L. Folmes, and H. J. Kong Sarcolemmal and mitochondrial effects of a KATP opener, P-1075, in “polarized” and “depolarized” Langendorff-perfused rat hearts, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1617, 39–50 (2003).
G. N. Bijur and R. S. Jope, Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta is highly activated in nuclei and mitochondria, Neuroreport 14, 2415–2419 (2003).
G. Agam and G. Shaltiel, Possible role of 3′(2′)-phosphoadenosine-5′-phosphate phosphatase in the etiology and therapy of bipolar disorder, Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 27, 723–727 (2003).
W. P. Tseng and S. Y. Lin-Shiau, Long-term lithium treatment prevents neurotoxic effects of beta-bungarotoxin in primary cultured neurons, J. Neurosci. Res. 69, 633–641 (2002).
K. C. Thompson, Pharmaceutical application of calorimetric measurements in the new millennium, Thermochim. Acta 355, 83–87 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, HR., Qin, CQ., Zhang, ZH. et al. Stimulation effect of lithium on the metabolic activity of liver tissue mitochondria measured by microcalorimetry. Biol Trace Elem Res 114, 163–173 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:114:1:163
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:114:1:163