Abstract
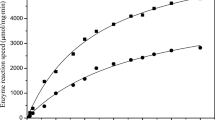
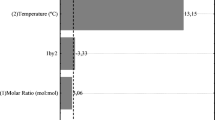
The last step of the production of four phthalimide-derived acids, designed to act as antiasthma drugs, was performed by enzymatic hydrolysis of the respective methyl or ethyl esters. The esters 4-ethyl-[2-(1,3-dioxo-1,3-dihydro-2-isoindoylyl)]-phenoxyacetic methyl ester (PHT-MET), 4-ethyl-[2-(1,3-dioxo-1,3-dihydro-2-isoindoylyl)]-phenoxyacetic ethyl ester, 4-(1,3-dioxo-1,3-dihydro-2-isoindoylyl)-phenoxyacetic ethyl ester, and 2-(1,3-dioxo-1, 3-dihydro-2-isoindoylyl)-phenoxyacetic ethyl ester were hydrolyzed by immobilized lipase. The enzymatic reaction could be used only to produce the desired 4-substituted compounds. The best result that was found to hydrolysis of PHT-MET, and, therefore, that ester was selected for optimization experiments in a three-phase system. Reactions were performed with solid biocatalyst (Lipozyme® RM IM), organic solvent phase (ethyl acetate), and aqueous phase (saturated Na2CO3 solution). To optimize the reaction conditions, an experimental design optimization procedure was used. The variables studied were the amount of enzyme, the temperature, and the volume of the aqueous solution. Time course experiments were then performed for different initial enzyme concentrations (0.5, 0.9, and 1.4 UH/mL of solvent). The optimized reaction conditions found were 20 mg of Lipozyme (0.9 UH/mLsolvent) and 5.0 mL of Na2CO3(sat) at 40°C for 6 h.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shelhamer, J. H., Marom, Z., Sun, F., Bach, M. K., and Kaliner, M. (1982), Chest 81, S36-S37.
Hay, D. W. P., Torphy, T. J., and Undem, B. J. (1995), Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 16, 304–309.
Hart, T., Lamont, A., and Williams, D. (1998), DDT 3, 516–521.
Lima, L. M. (2001), PhD thesis. IQ/UFRJ, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
Jaeger, K.-E., Dijkstra, B. W., and Reetz, M. T. (1999), Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 53, 315–351.
Shibatane, T., Omori, K., Akatsuka, H., Kawai, E., and Matsumae, H. (2000), J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzymat. 10, 141–149.
De Crescenzo, G., Ducret, A., Trani, M., and Lortie, R. (2000), J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzymat. 9, 49–56.
Sánchez, A., Valero, F., Lafuente, J., and Solá, C. (2000), Enzyme Microb. Technol. 27, 157–166.
D’Antona, N., Lombardi, P., Nicolosi, G., and Salvo, G. (2002), Process Biochem. 38(3), 373–377.
Steenkamp, L. and Brady, D. (2003), Enzyme Microb. Technol. 32(3–4), 472–477.
Lin, H. and Tsai, S. (2003), J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzymat. 24–25(1), 111–120.
Long, W. S., Bhatia, B., and Kamaruddin, A. (2003), J. Membr. Sci. 219(1–2), 69–88.
Freire, D. M. G., Gomes, P. M., Bon, E. P. S., and Sant’Anna, G. L. Jr. (1997), J. Braz. Soc. Microbiol. 28(1), 6–12.
Bevilaqua, J. B., Pinto, J. C., Lima, L. M., Barreiro, E. J., Alves, T. L. M., and Freire, D. M. G. (2004), Biochem. Eng. J. 21, 103–110.
Wehtje, E., and Adlercreutz, P. (1997), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 55(5), 798–805.
Wehtje, E., Costes, D., and Adlercreutz, P. (1997), J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzymat. 3, 221–230.
Roy, A. and Chawla, H. P. S. (2001), Enzyme Microb. Technol. 29, 490–493.
Paiva, A. L., Balcão, V. M., and Malcata, F. X. (2000), Enzyme Microb. Technol. 27, 187–204.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bevilaqua, J.V., Lima, L.M., Cunha, A.G. et al. Hydrolysis of new phthalimide-derived esters catalyzed by immobilized lipase. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 121, 117–128 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:121:1-3:0117
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:121:1-3:0117