Abstract
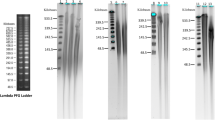
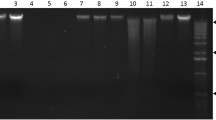
An automated nucleic acid extraction procedure with magnetic particles originally designed for isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) from animal tissues was tested for plant material. We isolated genomic DNA and total RNA from taxonomically diverse plant species representing conifers (Scots pine), broad-leaved trees (silver birch and hybrid aspen), dwarf shrubs (bilberry), and both monocotyledonous (regal lily) and dicotyledonous (Saint John’s wort, round-leaved sundew, and tobacco) herbaceous plants. Buffers developed for DNA extraction were successfully used in addition to manufacturer’s extraction kits. The quality of RNA was appropriate for many applications, but the quality of DNA was not always sufficient for polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification. However, we could strikingly improve the quality by eliminating the adherent compounds during the extraction or later in the PCR phase. Our results show that the use of the procedure could be extended to diverse plant species. This procedure is especially suitable for small sample sizes and for simultaneous processing of many samples enabling large-scale plant applications in population genetics, or in the screening of putative transgenic plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Do, N. and Adams, R. P. (1991) A simple technique for removing plant polysaccharide contaminants from DNA. Biotechniques 10, 162–166.
Demeke, T. and Adams, R. P. (1992) The effects of plant polysaccharides and buffer additives on PCR. Biotechniques 12, 332–334.
John, M. E. (1992) An efficient method for isolation of RNA and DNA from plants containing polyphenolics. Nucleic Acids Res. 20, 2381.
Levi, A., Galau, G. A., and Wetzstein, H. Y. (1992) A rapid procedure for the isolation of RNA from high-phenolic-containing tissue of pecan. HortSci. 27, 1316–1318.
Chang, S., Puryear, J., and Cairney, J. (1993) A simple and efficient method for isolating RNA from pine trees. Plant Mol. Biol. Reptr. 11, 113–116.
Rogers, S. O. and Benedich, A. J. (1994) Extraction of total cellular DNA from plants, algae and fungi. In Plant Molecular Biology Manual. Gelvin, S. B. and Schilerpoort, R. A., eds., Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp. D1, 1–8.
Kim, C. S., Lee, C. H., Shin, J. S., Chung, Y. S., and Hyung, N. I. (1997) A simple and rapid method for isolation of high quality genomic DNA from fruit trees and conifers using PVP. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 1085, 1086.
Kiefer, E., Heller, W., and Ernst, D. (2000) A simple and efficient protocol for isolation of functional RNA from plant tissues rich in secondary metabolites. Plant Mol. Biol. Reptr. 18, 33–39.
Rodriques-Pousada, R., Van Montagu, M., and Van der Straeten, D. (1990) A protocol for preparation of total RNA from fruit. Technique 2, 292–294.
Hultman, T., Stahl, S., Hornes, E., and Uhlen, M. (1989) Direct solid phase sequencing of genomic and plasmid DNA using magnetic beads as solid support. Nucleic Acids Res. 18, 5107–5112.
Gelsthorpe, A. R., Gelsthorpe, K., and Sokol, R. J. (1997) Extraction of DNA using monoclonal anti-DNA and magnetic beads. Biotechniques 22, 1080–1082.
Rudi, K., Kroken, M., Dahlberg, O. J., Deggerdal, A., Jakobsen, K. S., and Larsen F. (1997) Rapid, universal method to isolate PCR-ready DNA using magnetic beads. Biotechniques 22, 506–511.
Karrer, E. E., Lincoln, J. E., Hogenhout S., et al. (1995) In situ isolation of mRNA from individual plant cells: creation of cell-specific cDNA libraries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 3814–3818.
Heinrich, T., Washer, S., Marshall, J., Jones, M. G., and Potter, R. H. (1997). Subtractive hybridization of cDNA from small amounts of plant tissue. Mol. Biotechnol. 8, 7–12.
Obata, K., Segawa, O., Yakabe, M., et al. (2001) Development of a novel method for operating magnetic particles, Magtration Technology, and its use for automating nucleic acid purification. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 91, 500–503.
Dilwort, E. and Frey, J. (2000) A rapid method for high throughput DNA extraction from plant material for PCR amplification. Plant Mol. Biol. Reptr. 18, 61–64.
Edwards, K., Johnstone, C., and Thompson, C. (1991). A simple and rapid method for the preparation of plant genomic DNA for PCR analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 19, 1349.
Pich, U. and Schubert, I. (1993). Midiprep method for isolation of DNA from plants with a high content of polyphenolics. Nucleic Acids Res. 21, 3328.
Wang, G. L., Wing, R. A., and Paterson, A. H. (1993) PCR amplification from single seeds, facilitating DNA marker-assisted breeding. Nucleic Acids Res. 21, 2527.
Kreike, J. (1990) Genetic analysis of forest tree populations: isolation of DNA from spruce and fir apices. Plant Mol. Biol. 14, 877–879.
McCarthy, P. L., Hansen, J. L., Zemetra, R. S., and Berger, P. H. (2002) Rapid identification of transformed wheat using a half-seed PCR assay. Biotechniques 32, 560–564.
Jaakola, L., Pirttilä, A. M., Halonen, M., and Hohtola, A. (2001) Isolation of high quality RNA from bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) fruit. Mol. Biotechnol. 19, 201–203.
Pirttilä, A. M., Hirsikorpi, M., Kämäräinen, T., Jaakola, L., and Hohtola, A. (2001) DNA isolation methods for medical and aromatic plants. Plant Mol. Biol. Reptr. 19, 273a-f.
Klopfenstein, N. B., Chun, Y. W., Kim, M. S., and Ahuja, M. R. (1997) Micropropagation, Genetic Engineering, and Molecular Biology of Populus. Rocky Mountain Forest and Range Experiment Station, Fort Collins, CO.
Bradshaw, H. D., Jr., Ceulemans R., Davis, J., and Stettler, R. (2000) Emerging model systems in plant biology: poplar (Populus) as a model forest tree. J. Plant Growth Regul. 19, 306–313.
Aljanabi, S. M. and Martinez, I. (1997) Universal and rapid salt-extraction of high quality genomic DNA for PCR-based techniques. Nucleic Acids Res. 25,4692,4693.
Aronen, T. S., Nikkanen, T. O., and Häggman, H. M. (2003) The production of transgenic Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) via the application of transformed pollen in controlled crossing. Transgenic Res. 12, 375–378.
Helariutta, Y., Elomaa, P., Kotilainen, M., Griesbach, R. J., Schröder, J., and Teeri, T. H. (1995) Chalcone synthase-like genes active during corolla development are differentially expressed and encode enzymes with different catalytic properties in Gerbera hybrida (Asteraceae). Plant Mol. Biol. 28, 47–60.
Jaakola, L., Määttä, K., Pirttilä, A. M., Törrönen, R., Kärenlampi, S., and Hohtola, A. (2002) Expression of genes involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis in relation to anthocyanin, proanthocyanidin, and flavonol levels during bilberry fruit development. Plant Physiol. 130, 729–739.
Aronen, T. and Häggman, H. (1995) Differences in Agrobacterium infections in silver birch and Scots pine. Eur. J. For. Path. 25, 197–213.
Piispanen, R., Aronen, T., Chen, X., Saranpää, P., and Häggman, H. (2003). Silver birch (Betula pendula) plants with aux and rol genes show consistent changes in morphology, xylem structure and chemistry. Tree Phys. 23, 721–733.
Bekesiova, I., Nap, J. P., and Mlynarova, L. (1999) Isolation of high quality DNA and RNA from leaves of the carnivorous plant Drosera rotundifolia. Plant Mol. Biol. Reptr. 17, 269–277.
Niemi, K. (2002) Ectomycorrhizal fungi and exogenous growth regulators in vegetative propagation of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.). PhD thesis, Kuopio University Publications C. Natural and Environmental Sciences, Finland.
Stulnig, T. M. and Amberger, A. (1994) Exposing contaminating phenol in nucleic acid preparations. Biotechniques 16, 403, 404.
Glasel, J. A. (1995) Validity of nucleic acid purities monitored by 260 nm/280 nm absorbance ratios. Biotechniques 18, 62, 63.
Pikaart, M. J. and Villeponteau, B. (1993) Suppression of PCR amplification by high levels of RNA. Biotechniques 14, 24, 25.
Stewart, C. N. and Via, L. E. (1993) A rapid CTAB DNA isolation technique useful for RAPD finger-printing and other PCR applications. Biotechniques 14, 748–750.
Koonjul, P. K., Brand, W. F., Farrant, J. M., and Lindsey, G. G. (1999) Inclusion of polyvinylpyrrolidone in the polymerase chain reaction reverses the inhibitory effects of polyphenolic contamination of RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 27, 915, 916.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vuosku, J., Jaakola, L., Jokipii, S. et al. Does extraction of DNA and RNA by magnetic fishing work for diverse plant species?. Mol Biotechnol 27, 209–215 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/MB:27:3:209
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/MB:27:3:209