Abstract
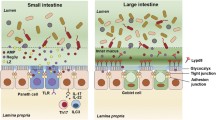
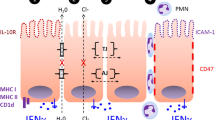
The intestinal epithelium serves as one of human's primary interfaces with the outside world. This interface is very heavily colonized with bacteria and yet permits absorption of life-sustaining nutrients while protecting the tissues below from microbial on slaught. Although the gut epithelium had been classically thought to achieve this function primarily by functioning as a passive, albeit highly selective, barrier, research over the last decade has demonstrated that in fact the epithelium plays a very active role in protecting the host from the bacteria that colonize it. As a consequence of its mediation of mucosal immunity, intestinal epithelial dysfunction appears to be central to diseases associated with aberrant gut mucosal immune responses such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). This article reviews: (1) how the gut epithelium participates in regulating innate immune inflammatory responses to enteric pathogens, (2) how these responses may regulate the adaptive immune system, (3) mechanisms that may resolve acute inflammation and (4) how epithelial dysfunction may participate in regulating both the active and chronic phases of IBD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takeuchi A: Electron microscope studies of experimental Salmonella infection. Am J Pathol 1967;50:109–119.
Gewirtz AT, Reed KA, Merlin D, Neish AS, Madara JL: Modeling Microbial-epithelial interactions in the intestine. Methods Microbiol 2002;31:377–396.
McCormick BA, Colgan SP, Archer CD, Miller SI, Madara JL: Salmonella typhimurium attachment to human intestinal epithelial monolayers: transcellular signalling to subepithelial neutrophils. J Cell Biol 1993;123:895–907.
Hooper LV, Bry L, Falk PG, Gordon JI: Host-microbial symbiosis in the mammalian intestine: exploring an internal ecosystem. Bioessays 1998;20:336–343.
Madara JL, Parkos CA, Nusrat A, Atisook K, Kaoutzani P: The movement of solutes across tight junctions. NY Acad Sci 1992;664:47–60.
Mallow EB, Harris A, Salzman N, Russell JP, DeBerardinis RJ, Ruchelli E, Bevins CL: Human enteric defensins. Gene structure and developmental expression. J Biol Chem 1996;271:4038–4045.
Dickinson BL, Badizadegan K, Wu Z, Ahouse JC, Zhu X, Simister NE, et al.: Bidirectional FcRn-dependent IgG transport in a polarized human intestinal epithelial cell line. J Clin Invest 1999;104:903–911.
Keates S, Keates AC, Mizoguchi E, Bhan A, Kelly CP: Entenocytes are the primary source of the chemokine ENA-78 in normal colon and ulcerative colitis. Am J Physiol 1997;273:G75-G82.
Jung HC, Eckmann L, Yang SK, Panja A, Fierer J, Morzycka-Wroblewska E, Kagnoff MF: A distinct array of proinflammatory cytokines is expressed in human colon epithelial cells in response to bacterial invasion. J Clin Invest 1995;95:55–65.
McCormick BA, Parkos CA, Colgan SP, Carnes DK, Madara JL: Apical secretion of a pathogen-elicited epithelial chemoattractant (PEEC) activity in response to surface colonization of intestinal epithelia by Salmonella typhimurium. J Immunol 1998;160:455–456.
Medzhitov R, Janeway CA Jr.: Decoding the patterns of self and nonself by the innate immune system. Science 2002;296:298–300.
Schwandner R, Dziarski R, Wesche H, Rothe M, Kirschning CJ: Peptidoglycan- and lipoteichoic acid-induced cell activation is mediated by toll-like receptor 2. J Biol Chem 1999;274:17406–17409.
Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Huffel CV, Du X, et al.: Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science 1998;282:2085–2088.
Hayashi F, Smith KD, Ozinsky A, Hawn TR, Yi EC, Goodlett DR, et al.: The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. Nature 2001;410:1099–1103.
Gewirtz AT, Navas TA, Lyons S, Godowski PJ, Madara JL: Cutting edge: bacterial flagellin activates basolaterally expressed tlr5 to induce epithelial proinflammatory gene expression. J Immunol 2001;167:1882–1885.
Bauer S, Kirschning CJ, Hacker H, Redecke, V, Hausmann S, Akira S, et al.: Human TLR9 confers responsiveness to bacterial DNA via species-specific CpG motif recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001;98:9237–9242.
Lee CA: Pathogenicity islands and the evolution of bacterial pathogens. Infect Agents Dis 1996;5:1–7.
Maurelli AT, Fernandez RE, Bloch CA, Rode CK, Fasano A: “Black holes” and bacterial pathogenicity: a large genomic deletion that enhances the virulence of Shigella spp. and entero invasive Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998;95:3943–3948.
Gewirtz AT, Simon PO Jr, Schmitt CK, Taylor LJ, Hagedorn CH, O'Brien AD, et al.: Salmonella typhimurium translocates flagellin across intestinal epithelia inducing a proinflammatory response. J Clin Invest 2001;107:99–109.
Eaves-Pyles T, Murthy K, Liaudet L, Virag L, Ross G, Soriano FG, et al.: Flagellin, a novel mediator of Salmonella-induced epithelial activation and systemic inflammation: I kappa B alpha degradation, induction of nitric oxide synthase, induction of pro-inflammatory mediators, and cardiovascular dysfunction. J Immunol 2001;166:1248–1260.
Sierro F, Dubois B, Coste A, Kaiserlian D, Kraehenbuhl JP, Sirard JC: Flagellin stimulation of intestinal epithelial cells triggers CCL20-mediated migration of dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001;98: 13722–13727.
Eaves-Pyles TD, Wong HR, Odoms K, Pyles RB: Salmonella flagellin-dependent proinflammatory responses are localized to the conserved amino and carboxyl regions of the protein. J Immunol 2001;167:7009–7016.
Gewirtz AT: Intestinal epithelial toll-like receptors: to protect. And serve?. Curr Pham Des 2003;9:1–5.
Kopp E, Ghosh S: Inhibition of NF-kappa B by sodium salicylate and aspirin. Science 1994;265:956–959.
DiDonato JA, Hayakawa M, Rothwarf DM, Zandi E, Karin M: A cytokine-responsive IkappaB kinase that activates the transcription factor NF-kappaB. Nature 1997;388: 548–554.
Zhou D, Chen LM, Hernandez L, Shears SB, Galan JE: A Salmonella inositol polyphosphatase acts in conjunction with other bacterial effectors to promote host cell actin cytoskeleton rearrangements and bacterial internalization. Mol Microbiol 2001;39:248–259.
Hobbie S, Chen L, Davis R, Galan J: Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in the nuclear responses and cytokine production induced by Salmonella typhimurium incultured intestinal epithelial cells. J Immunol 1997;159:5550–5559.
Galan JE: Interactions of Salmonella with host cells: encounters of the closest kind. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998;95:14006–14008.
Kenny B, DeVinrey R, Stein M, Reinscheid DJ, Frey EA, Finlay BB: Enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) transfers its receptor for intimate adherence into mammalian cells. Cell 1997;91:511–520.
Girardin SE, Tournebize R, Mavris M, Page AL, Li X, Stark GR, et al.: CARD4/Nodl mediates NF-kappaB and JNK activation by invasive Shigella flexneri. EMBO Rep 2001;2:736–742.
Mounier J, Vasselon T, Hellio R, Lesourd M, Sansonetti PJ: Shigella flexneri enters human colonic Caco-2 epithelial cells through the basolateral pole. Infect Immun 1992;60:237–248.
Inohara N, Ogura Y, Fontalba A, Gutierrez O, Pon SF, Crespo J, et al.: Host recognition of bacterial muramyl dipeptide mediated through NOD2. Implications for Crohn's disease. J Biol Chem 2003;278:5509–5512.
Yu Y, Zeng H, Lyons S, Carlson A, Merlin D, Neish AS, Gewirtz AT: TLR5-mediated activation of p38 MAPK regulates IL-8 expression via a post-transcriptional mechanism. Am J Physiol 2003;285:G282-G290.
Nash S, Parkos CA, Nusrat A, Delp C, Madara JL: In vitro model of intestinal crypt abcess: A novel neutrophil-derived secretagogue activity. J Clin Invest 1991;87: 1474–1477.
Madara JL, Patapoff TW, Gillece-Castro B, Colgan SP, Parkos CA, Delp C, Mrsny RJ: 5-Adenosine monophosphate is the neutrophil-derived paracrine factor that elicits chloride secretion from T84 intestinal epithelial cells. J Clin Invest 1993;91:2320–2325.
Strohmeier GR, Lencer WI, Patapoff TW, Thompson LF, Carlson SL, Moe SJ, et al.: Surface expression, polarization, and functional significance of CD73 in human intestinal epithelia. J Clin Invest 1997;99; 2588–2601.
Strolmeier GR, Reppert SM, Lencer WI, Madara JL: The A2b adenosine receptor mediates cAMP responses to adenosine receptor agonists in human intestinal epithelia. J Biol Chem 1995;270:2387–2394.
Sitaraman SV, Si-Tahar M, Merlin D, Strohmeier GR, Madara JL: Polarity of A2b adenosine receptor expression determines characteristics of receptor desensitization. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2000;278: C1230–1236.
Lemon PF, Taylor CT, Stahl GL, Colgan SP: Neutrophil-derived 5′-adenosine monophosphate promotes endothelial barrier function via CD73-mediated conversion to adenosine and endothelial A2B receptor activation. J Exp Med 1998;188:1433–1443.
Narravula S, Lennon PF, Mueller BU, Colgan SP: Regulation of endothelial CD73 by adenosine: paracrine pathway for enhanced endothelial barrier function. J Immunol 2000;165:5262–5268.
Link AA, Kino T, Worth JA, McGuire JL, Crane ML, Chrousos GP, et al.: Ligand-activation of the adenosine A2a receptors inhibits IL-12 production by human monocytes. J Immunol 2000;164:436–442.
Sitaraman SV, Merlin D, Wang L, Wong M, Gewirtz AT, Si-Tahar M, Madara JL: Neutrophil-epithelial crosstalk at the intestinal lumenal surface mediated by reciprocal secretion of adenosine and IL-6. J Clin Invest 2001;107; 861–869.
Revan S, Montesinos MC, Naime D, Landau S, Cronstein BN: Adenosine A2 receptor occupancy regulates stimulated neutrophil function via activation of a serine/threonine protein phosphatase. J Biol Chem 1996;271:17114–17118.
Cronstein BN: A novel approach to the development of anti-inflammatory agents: adenosine release at inflamed sites. J Invest Med 1995;43:50–57.
Nash S, Stafford J, Madara JL: Effects of polymorphonuclear leukocyte transmigration on barrier function of cultured intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Clin Invest 1987;80:1104–1113.
Sansonetti PJ: Rupture, invasion and inflammatory destruction of the intestinal barrier by Shigella making sense of prokaryote-eukaryote cross-talks. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2001;25:3–14.
McCormick BA, Nusrat A, Parkos CA, D'Andrea L, Hofman PM, Carnes D, et al.: Unmasking of intestinal epithelial lateral membrane betal integrin consequent to transepithelial neutrophil migration in vitro facilitates invmediated invasion by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun 1997;65:1414–1421.
Schreiber S, Nikolaus S, Hampe J: Activation of nuclear factor kappa B inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 1998;42:477–484.
Jobin C, Sartor RB: NF-kappaB signaling proteins as therapeutic targets for inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2000;6:206–213.
Rask-Madsen J, Hammersgaard EA, Knudsen E: Rectal electrolyte transport and mucosal permeability in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. J Lab Clin Med 1973;81:342–353.
Strober W, James SP: The immunologic basis of inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Immunol 1986;6:415–432.
Hollander D: Intestinal permeability, leaky gut, and intestinal disorders. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 1999;1:410–416.
Cooper HS, Murthy SN, Shah RS, Sedergran DJ: Clinicopathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium experimental murine colitis. Lab Invest 1993;69:238–249.
Maggio-Price L, Shows D, Waggie K, Burich A, Zeng W, Escobar S, Morrissey P, Viney JL: Helicobacter bilis infection accelerates and H. hepaticus infection delays the development of colitis in multiple drug resistance-deficient (mdrla−/−) mice. Am J Pathol 2002;160: 739–751.
Neish AS, Gewirtz AT, Zeng H, Young AN, Hobert ME, Karmali V, et al.: Prokaryotic regulation of epithelial responses by inhibition of IkappaB-alpha ubiquitination [see comments] Science 2000;289:1560–1563.
Wang P, Wu P, Siegel MI, Egan RW, Billah MM: Interleukin (IL)-10 inhibits nuclear factor kappa B (NF kappa B) activation in human monocytes IL-10 and IL-4 suppress cytokine synthesis by different mechanisms. J Biol Chem 1995;270:9558–9563.
Kuhn R, Lohler J, Rennick D, Rajewsky K, Muller W: Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic enterocolitis [see comments], Cell. 1993;75:263–274.
Gewirtz AT, McCormick B, Neish AS, Petasis NA, Gronert K, Serhan CN, Madara JL: Pathogen-induced chemokine secretion from model intestinal epithelium is inhibited by lipoxin A4 analogs. J Clin Invest 1998;101: 1860–1869.
Gronert KG, Gewirtz AT, Madara JL, Serhan CN: Identification of a human enterocyte lipoxin A4 receptor that is regulated by IL-13, and INF-γ that inhibits TNF-α-induced IL-8 release. J Exp Med 1998;187:1285–1294.
Gewirtz AT, Collier-Hyams LS, Young AN, Kucharzik T, Guilford WJ, Parkinson JF, et al.: Lipoxin a(4) analogs attenuate induction of intestinal epithelial proinflammatory gene expression and reduce the severity of dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. J Immunol 2002; 168:5260–5267.
Gewirtz AT, Fokin VV, Petasis NA, Serhan CN, Madara JL: LXA4, aspirin-triggered 15-epi-LXA4, and their analogs selectively down regulate PMN azurophilic degranulation. Am J Physiol 1999;276:C988-C994.
Serhan CN Lipoxins and novel aspirin-triggered 15-epilipoxins (ATL): A jungle of cell-cell interactions or a therapeutic apportumity. Prostaglandins 1997;53: 107–137.
Godson C, Mitchell S, Harvey K, Petasis NA, Hogg N, Brady HR: Cutting edge: lipoxins rapidly stimulate nonphlogistic phagocytosis of apoptotic neutrophils by monocyte-derived macrophages J Immunol 2000; 164:1663–1667.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Y., Sitaraman, S. & Gewirtz, A.T. Intestinal epithelial cell regulation of mucosal inflammation. Immunol Res 29, 55–67 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/IR:29:1-3:055
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/IR:29:1-3:055