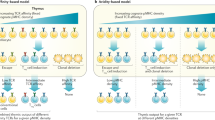
Abstract
Our studies on the immune response to foreign antigens are reviewed as they relate to the mechanisms of peripheral immune tolerance. The activation of suppressor T cells by distinct modes of antigen presentation is discussed. Through the use of mice expressing transgenic T-cell receptors specific for foreign antigens, we have concluded that the separable mechanisms of anergy and active suppression by CD25+T cells work in concert to produce peripheral tolerance. In T-cell receptor Vβ8.1 transgenic mice rendered tolerant of Mls-1a, the absence of the cell surface marker 6C10 defines the anergic population of CD4+T cells, while 6C10+ CD4+ T cells are actively suppressed by CD25+T cells. Through discussion of these observations, we have developed a historical perspective on recent advances in the understanding of mechanisms of peripheral tolerance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greene MI, Sugimoto M, Benacerraf B: Mechanisms of regulation of cell-mediated immune responses. I. Effect of the route of immunization with TNP-coupled syngeneic cells on the induction and suppression of contact sersitivity to picrylchloride. J Immunol 1978;120:1604–1611.
Greene MI, Sy MS, Kripke M, et al.: Impairment of antigen-presenting cell function by ultraviolet radiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1979;76:6591–6595.
Perry LL, Dorf ME, Bach BA, et al.: Mechanisms of regulation of cell-mediated immunity: anti-1-A alloantisera interfere with induction and expression of T-cell-mediated immunity to cell-bound antigen in vivo. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 1980;15:279–292.
Fujimoto S, Greene MI, Sehon AH: Regtaltion of the immune response to tumor antigens. I. Immunosuppressor cells in tumor-bearing hosts. J Immunol 1976; 116:791–799.
Fujimoto S, Greene MI, Sehon AH: Regulation of the immune response to tumor antigens. II. The nature of immuno suppressor cells in tumor-bearing hosts. J Immunol 1976;116:800–806.
Perry LL, Dorf ME, Beracerraf B, Greene MI: Regulation of immune response to tumor antigen: interference with syngeneic tumor immunity by anti-IA alloantisera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1979;76:920–924.
Bach BA, Sherman L, Benacerraf B, Greene MI: Mechanisms of regulation of cell-mediated immunity. II. Induction and suppression of delayed-type hypersensitivity to azoberzenearsonate-coupled syngeneic cells. J Immunol 1978;121:1460–1468.
Greene MI, Perry LL, Benacerraf B: Regulation of the immune response to tumor antigen. Am J Pathol 1979; 95:159–169.
Jenkins MK, Schwartz RH: Antigen presentation by chemically modified splenocytes induces antigenspecific T cell unresponsiveness in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Med 1987;165:302–319.
Schwartz RH: A cell culture model for T lymphocyte clonal anergy. Science 1990;248:1349–1356.
Harding FA, McArthur JG, Gross JA, Raulet DH, Allison JP: CD 28-mediated signalling co-stimulates murine T cells and prevents induction of anergy in T-cell clones. Nature 1992;356:607–609.
Quill H, Schwartz RH: Stimulation of normal inducer T cell clones with antigen presented by purified Ia molecules in plarar lipid membranes: specific induction of a long-lived state of proliferative nonresponsiveness. J Immunol 1987;138:3704–3712.
Takahashi T, Kuniyasu Y, Toda M, Sakaguchi N, Itoh M, Iwata M, et al.: Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by CD25+CD4+raturally anergic and suppressive T cells: induction of autoimmune disease by breaking their anergic/suppressive state. Int Immunol 1998;10:1969–1980.
Thornton AM, Shevach EM: CD4+CD25+immunoregulatory T cells suppress polyclonal T cell activation in vitro by inhibiting interleukin 2 production. J Exp Med 1998;188:87–96.
Itoh M, Takahashi T, Sakaguchi N, Kuniyasu Y, Shimizu J, Otsuka F, et al.: Thymus and autoimmunity: production of CD25+CD4+naturally anergic and suppressive T cells as a key function of the thymus in maintaining immunnologic self-tolerance. J Immunol 1999;162:5317–5326.
Bhandoola A, Cho EA, Yui K, Saragovi HU, Greene MI, Quill H: Reduced CD3-mediated protein tyrosine phosphory lation in anergic CD4+and CD8+T cells. J Immunol 1993;151:2355–2367.
Quill H: Anergy as a mechanism of peripheral T cell tolerance. J Immunol 1996;156:1325–1327.
Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, Itoh M, Today M: Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. J Immunol 1995; 155:1151–1164.
Takemori T, Tada T: Properties of antigen-specific suppressive T cell factor in the regulation of antibody response of the mouse. I. In vivo activity and immunochemical characterizations. J Exp Med 1975;142:1241.
Greene MI, Dorf ME, Pierres M, Benacerraf B: Reduction of syngeneic tumor growth by an anti-I-J-alloantiserum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1977;74:5118–5121.
Murphy D, Herzenberg L, Okumura K, McDevitt H: A new 1 subregion (I-J) marked by a locus (Ia-4) controlling surface dete nninants on suppressor T lymphocytes. J Exp Med 1976;144:699–712.
Murphy, D, et al.: A single major pathway of T-lymphocyte interactions in antigen-specific immune suppression. Scand J Immunol 1981;13:1–10.
Germain R, Theze J, Waltenbaugh C, Dorf M, Benacerraf BH: Antigen-specific T cell-mediated suppression. II. In vitro induction by I-J-coded L-glutamic acid50-L-tyrosine50 (GT)-specific T cell suppressor factor (GT-T8F) of suppressor T cells (T82) bearing distinct 1-J de terminants. J Immunol 1978;121:602–607.
Minami M, Aoki I, Honji N, Waltenbaugh C, Dorf M: The role of I-J and Igh determinants on Fl-derived suppressor factor in controlling restriction specificity. J Exp Med 1983;158:1428–1443.
Minami M, Honji N, Dorf M: Mechanism responsible for the induction of I-J restriction on TS3 suppressor cells. J Exp Med 1982;156:1502–1515.
Kupper T, Green D: Immunoregulation after thermal injury: sequential appearance of I-J+, Ly-1 T suppressor inducer cells and Ly-2 T suppressor effector cells following thermal trauma in mice. J Immunol 1984;133:3047–3053.
Asano Y, Nakayama T, Kubo M, Yagi J, Tada T: Epitopes associated with MHC restriction site of T cells. III. I-J epitope on MHC-restricted T helper cells. J Exp Med 1987;166:1613–1626.
Galvan M, Murali-Krishna K, Ming LL, Baum L, Ahmed R: Alterations in Cell Surface Carbohydrates on T Cells from Virally Infected Mice Can Distinguish Effector/Memory CD8+T Cells from Naive Cells. J Immunol 1998;161:641–648.
Saouaf SJ, Zerva L, Greene MI: Peripheral Tolerance to the Azobenzene arsonate Hapten in V alpha 3.1 T cell Receptor Transgenic Mice. Transgenics 1994;1:171–183.
Yui K, Komori S, Katsumata M, Siegel RM, Greene MI: Self-reactive T cells canescape clonal deletion in T-cell receptor V beta 8.1 transgenicmice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990;87:7135–7139.
Maier CC, Bhandoola A, Borden W, Yui K, Hayakawa K, Greene MI: Unique molecular surface features of in vivo tolerized T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95:4499–4503.
Maeda H, Fujimoto S, Greene MI: Suppressor T cells regulate the nonanergic cell population thatremains after peripheral tolerance is induced to the Mls-1 antigen in T cell receptor Vbeta 8.1 transgenic mice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2000;97:13257–13262.
Tan KN, Datlof BM, Gilmore JA, Kronman AC, Lee JH, Maxam AM, et al.: The T cell receptor V alpha 3 gene segment is associated with reactivity to p-azobenzene-arsonate. Cell 1988;54:247–261.
Greene MI, Nelles MJ, Sy MS, Nisonoff A: Regulation of immunity to the azobenzenearso nale haplen. Adv Immunol 1982;32:253–300.
Saouaf SJ, et al.: Azobenzenearsonate Hapten Specific T Cell Receptor Alpha Chain Transgenic Mice. Transgenics 1994;1:185–201.
Pullen AM, Wade T, Marrack P, Kappler JW: Identification of the region of T cell receptor beta chain that interacts with the self-superantigen Mls-1a. Cell 1990; 61:1365–1374.
Cazenave P-A, et al.: V beta 17 gene polymorphism in wild-derived mouse strains: Two amino acid substitutions in the V beta 17 region greatly alter T cell receptor specificity. Cell 1990;63:717–728.
Dellabona P, Peccoud J, Kappler J, Marrack P, Benoist C, Mathis D: Superantigens interact with MHC class II molecules outside of the antigen groove. Cell 1990;62:1115–1121.
MacDonald HR, Schneider R, Lees RK, Howe RC, Acha-Orbea H, Festenstein H, et al.: T-cell receptor V beta use predicts reactivity and tolerance to Mlsa-encoded antigens. Nature 1988;332:40–45.
Webb SR, O'Rourke AM, Sprent J: Factors influencing the fale of T cells responding to Mls antigens. Semin Immunol 1992;4:329–336.
Gui M, et al.: Peripheral CD4+T cell maturation recognized by increrased expression of Thy-1/CD90 bearing the 6C10 carbohydrate epitope. J Immunol 1999: 163:4796–4804.
Hayakawa K, Hardy RR: Murine CD4+T-cell subsets. Immunol Rev 1991;123:145–168.
Shimizu J, et al.: Stimulation of CD25(+)CD4(+) regulatory T cells through GITR breaks immunological selftolerance. Nat Immunol 2002;3:135–142.
McHugh RS, et al.: CD4(+)CD25(+) immunoregulatory T cells: gene expression analysis reveals a functional role for the glucocorticoid-induced TNFreceptor. Immunity 2002;16:311–323.
Fu T, Shen Y, Fugimoto S: Tumor-specific CD4+suppressor T-cell clone capable of inhibiting rejection of syngeneic sarcoma in A/J mice. Int J Cancer 2000;87:680–687.
Shimizu J, Yamazaki S, Sakaguchi S: Induction of tumor immunity by removing CD25+CD4+T Cells: Acommon basis between tumor immunity and autoimmunity. J Immunol 1999;163:5211–5218.
Onizuka S, et al.: Tumor rejection by in vivo administration of anti-CD25 (interleukin-2 receptor α) monoclonal antibody. Cancer Res 1999;59:3128–3133.
Rose N: The role of infection in the pathogenesis of autoimmunedisease. Semin Immunol 1998;10:5–13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saouaf, S.J., Brennan, P.J., Shen, Y. et al. Mechanisms of peripheral immune tolerance. Immunol Res 28, 193–199 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/IR:28:3:193
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/IR:28:3:193