Abstract
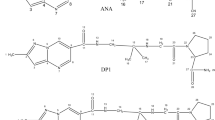
A stability-indicating reversed-phase liquid chromatographic (RPLC) method has been established for analysis of ramipril (RAM) and moexipril hydrochloride (MOEX.HCl) in the presence of the degradation products generated in studies of forced decomposition. The drug substances were subjected to stress by hydrolysis (0.1 m NaOH and 0.1 m HCl), oxidation (30% H2O2), photolysis (254 nm), and thermal treatment (80 °C). The drugs were degraded under basic and acidic conditions and by thermal treatment but were stable under other stress conditions investigated. Successful separation of the drugs from the degradation products was achieved on a cyanopropyl column with 40:60 (v/v) aqueous 0.01 m ammonium acetate buffer (pH 6)–methanol as mobile phase at a flow rate of 1 mL min−1. Detection was by UV absorption at 210 nm. Response was a linear function of concentration over the range 5–50 μg mL−1 (r > 0.9995), with limits of detection and quantitation (LOD and LOQ) of 0.04 and 0.09 μg mL−1, respectively, for RAM and 0.014 and 0.32 μg mL−1, respectively, for moexipril. The method was validated for specificity, selectivity, solution stability, accuracy, and precision. Statistical analysis proved the method enabled reproducible and selective quantification of RAM and MOEX as the bulk drug and in pharmaceutical preparations. Because the method effectively separates the drugs from their degradation products, it can be used as stability-indicating.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
National Heart and Blood Institute National High Blood Pressure Education Program (2003) Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure (JNC VII) express. Bethesda. From the NIH web site
Abrams AC (2004) Clinical drug therapy 7th edn. Canadian Pharmaceutical Association, Canada, pp 797–818
Sweetman SC (2005) Martindale the complete drug reference 34th edn. Pharmaceutical Press, London, pp 961–994
Hammes W, Hammes B, Buechsler U, Paar F, Boekens H (1995) J Chromatogr B 670:81–89
Erturk S, Cetin SM, Atmaca S (2003) J Pharm Biomed Anal 33:505–510
United States pharmacopeia (2005) 28-NF 23. United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Rockville
Eckert HG, Munscher G, Oekonomopulos R, Strecker H, Urbach H, Wissmann H (1985) Arzneim Forsch 35:1251–1256
Hajdu P, Schmidt D, Bomm M, Hack L, Keller A (1984) Arzneim Forsch 34:1431–1437
Ito M, Kuriki T, Goto J, Nambara T (1990) J Liq Chromatogr 13:991–1000
Aboul-Enein HY, Bakr SA (1992) Drug Dev Ind Pharm 18:1013–1022
Hogan BL, Williams M, Idiculla A, Veysoglu T, Parente E (2000) J Pharm Biomed Anal 23:637–651
Bakshi M, Singh B, Singh A, Singh S (2001) J Pharm Biomed Anal 26:1011–1025
Stability testing of new drug substances and products (Q1AR2), ICH harmonised tripartite guideline
Hanysova L, Vaclavkova M, Dohnal J (2005) J Pharm Biomed Anal 37:1179–1183
Strickley RG, Visor GC, Li-Hwa L, Gu L (1989) Pharm Res 6:971–976
Snyder RS, Kirkland JJ, Glajch JL (1997) Practical HPLC method development 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 698–700
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elshanawane, A.A., Mostafa, S.M. & Elgawish, M.S. Application of a Validated, Stability-Indicating LC Method to Stress Degradation Studies of Ramipril and Moexipril.HCl. Chroma 67, 567–573 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-008-0544-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-008-0544-3